
Less than a week after the September launch of GHGSat-C1 (‘Iris’), built by Space Flight Laboratory (SFL), GHGSat Inc. recorded the smallsat’s first successful measurement of a methane emission from a known oil and gas facility in Turkmenistan. A week later, the satellite operator tasked Iris to measure a much smaller, controlled methane release from a test site in Alberta, Canada. The satellite-based measurement was successful and confirmed with an airborne sensor.
Iris maps plumes of methane in the atmosphere down to 25m on the ground, detecting and measuring emissions from point sources 100 times smaller than any comparable system with a resolution 100 times higher, comparable to the emissions from a large landfill.
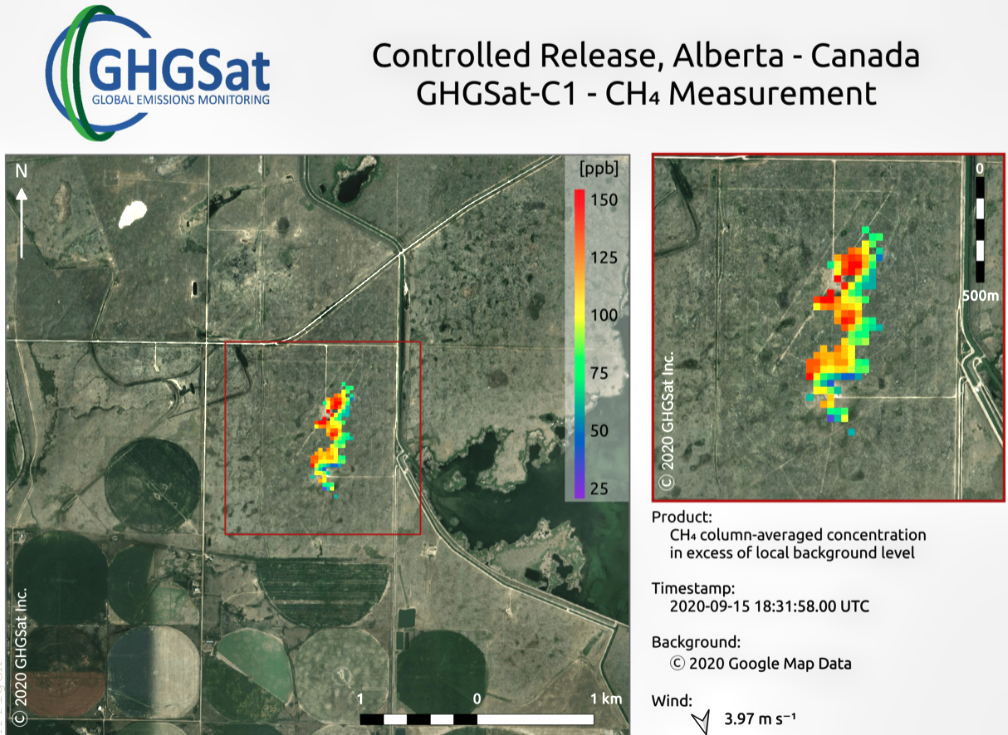
GHGSat Inc. created the sample image by colorizing the methane concentration measurements that exceeded normal background levels captured over the Alberta test site. The colorized measurements are overlaid on an aerial photograph to provide context.
Precise attitude control and sensor pointing are critical to the success of an atmospheric monitoring microsatellite like GHGSat-C1. The 20x30x40-centimeter satellite must keep its greenhouse gas measuring spectrometer pointed at an area of interest on the ground as the satellite continues on its path.
GHGSat-C1 (‘Iris’) was launched on September 2, 2020, aboard an Arianespace Vega rocket from the Guiana Space Center in French Guiana. Also on that launch was NEMO-HD, an Earth observation microsatellite built by SFL for Slovenia.
GHGSat Inc. awarded SFL the development contract for GHGSat-C1 after building the pathfinding GHGSat-D (“Claire”) smallsat in 2016. Using high-precision target tracking capabilities developed by SFL, Claire successfully demonstrated that sources of methane and other gas emissions could be detected and measured from space. SFL is currently developing another microsatellite, GHGSat-C2, for the company.
Executive Comments
“The successful measurement of methane concentrations in the air above the oil and gas facility indicates the advanced microsatellite attitude control and precise point technologies developed by SFL and built into GHGSat-C1 are functioning as designed,” said SFL Director Dr. Robert E. Zee. “We have a very mature and high-performance attitude control system that can handle various maneuvers and pointing modes with relative ease” said Zee. “In particular, we fine-tuned the attitude control required for GHGSat-C1 by leveraging the results from the GHGSat-D demonstration mission in 2016.”
Established at the University of Toronto Institute for Aerospace Studies (UTIAS) in 1998, SFL has developed CubeSats, nanosatellites, and microsatellites that have achieved more than 128 cumulative years of operation in orbit. These microspace missions have included SFL’s trusted attitude control and, in some cases, formation-flying capabilities. Other core SFL-developed components include modular (scalable) power systems, onboard radios, flight computers, and control software.
