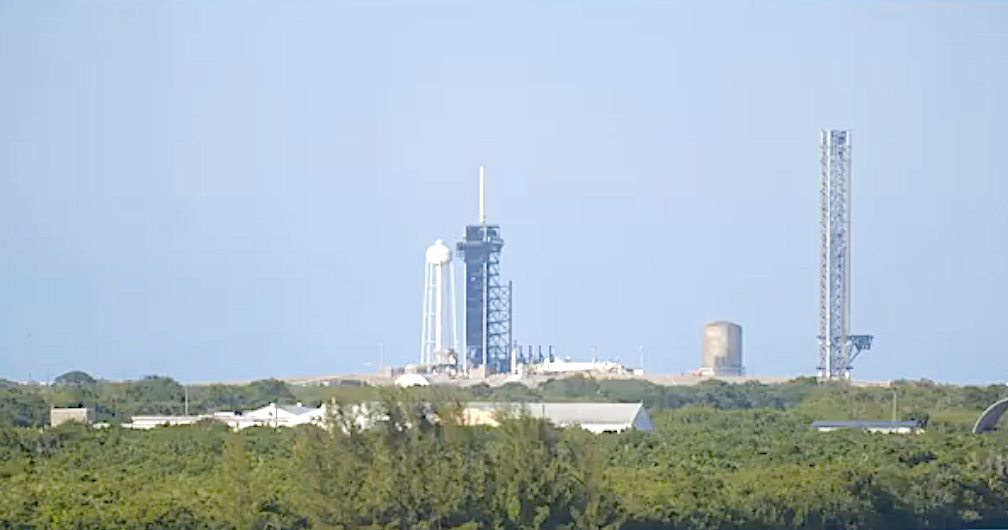
Europe’s newest rocket soon launches, taking with it many space missions each with a unique objective, destination and team at home, cheering them on. Whether launching new satellites to look back and study Earth, peer out to deep space or test important new technologies in orbit, the European Space Agency’s Ariane 6’s first flight will showcase the versatility and flexibility of this impressive, heavy-lift launcher.
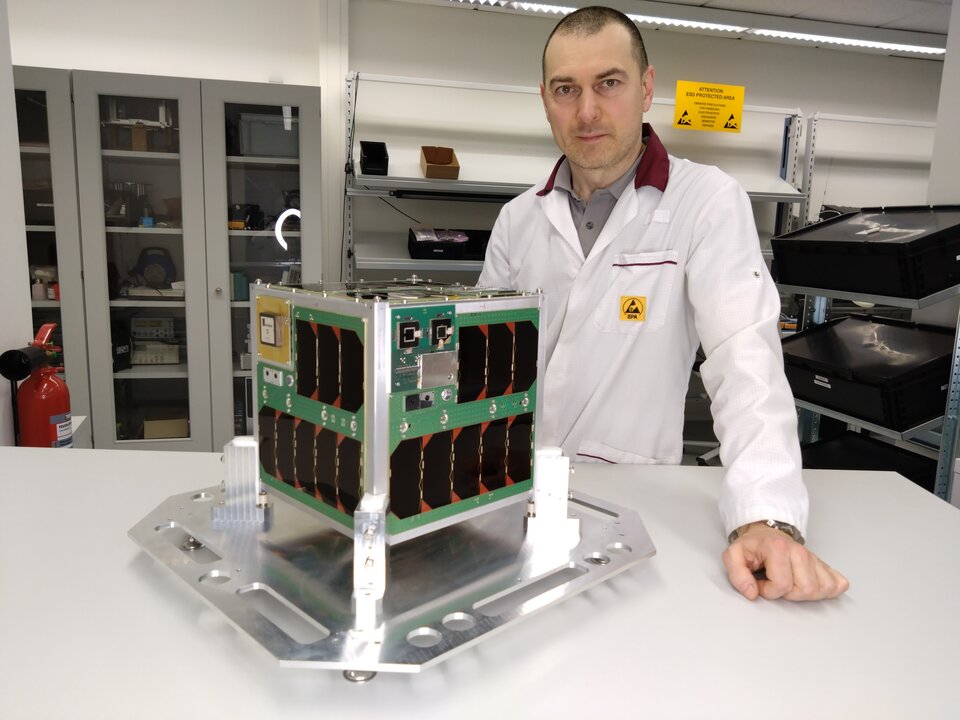
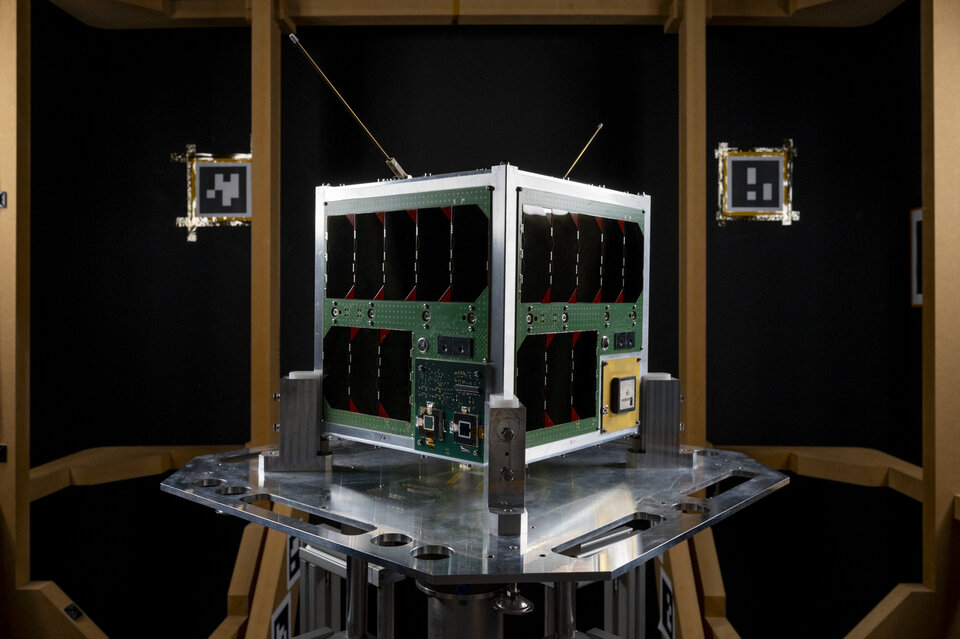
OOV-Cube (On Orbit Verification Cube) is a 25-by-25 cm nanosatellite that brings together unusual bedfellows: technology testing for wildlife tracking, the Internet of Things and more. Developed by the Technical University of Berlin and Berlin-based company RapidCubes, it will be launched into a low, circular orbit, just 580 km above Earth’s surface.
The mission is a single satellite, but it has several goals, experiments and demonstrations on board that could pave the way for new applications in the field of smallsat constellations.
“This mission has the potential to help with issues that are very important to people on Earth,” said Walter Frese, CEO of RapidCubes. “OOV-Cube will provide the scientific basis for reliable, energy-efficient communications on wildlife protection that are independent of infrastructure on the ground. In terms of conservation, it will also contribute to the technical research into how to prevent space debris. OOV-Cube will be the sixth satellite in a series I have been working on, and the most demanding so far in terms of its payloads. The moment the first data come down successfully brings up a lot of positive emotions. And for this mission, there’s the added pride that we are doing something important for the environment.”
By performing the first experimental demonstration of a ‘mioty’ high-performance Internet of Things communication protocol, OOV-Cube will test a technology that can be linked to miniaturized transmitters carried by animals, connecting them to scientists in real time. This would be particularly useful in remote areas without terrestrial infrastructure.
“Integrating our cloud detection network onto the machine learning hardware of OOV-Cube is a completely new experience,” said Alexander Balke, project manager of AITHER at TU Berlin. “I would have never dreamed that our work would now be launched into space in front of the whole world.“
The mission will also test image processing in orbit using Artificial Intelligence (AI) – an important and time-saving ability that would mean data on wildlife monitoring can be processed by the satellite in orbit, rather than later on the ground.
The satellite will also test and verify new cost-effective and efficient perovskite solar cells, verify a wide-angle camera with autofocus – a necessary prerequisite for docking maneuvers necessary for future service missions to refuel, repair or re-orbit satellites. Also important for future on-orbit service missions, OOV-Cube will verify an ‘L-band’ radio system for communications between satellites in low-Earth and geostationary orbits.
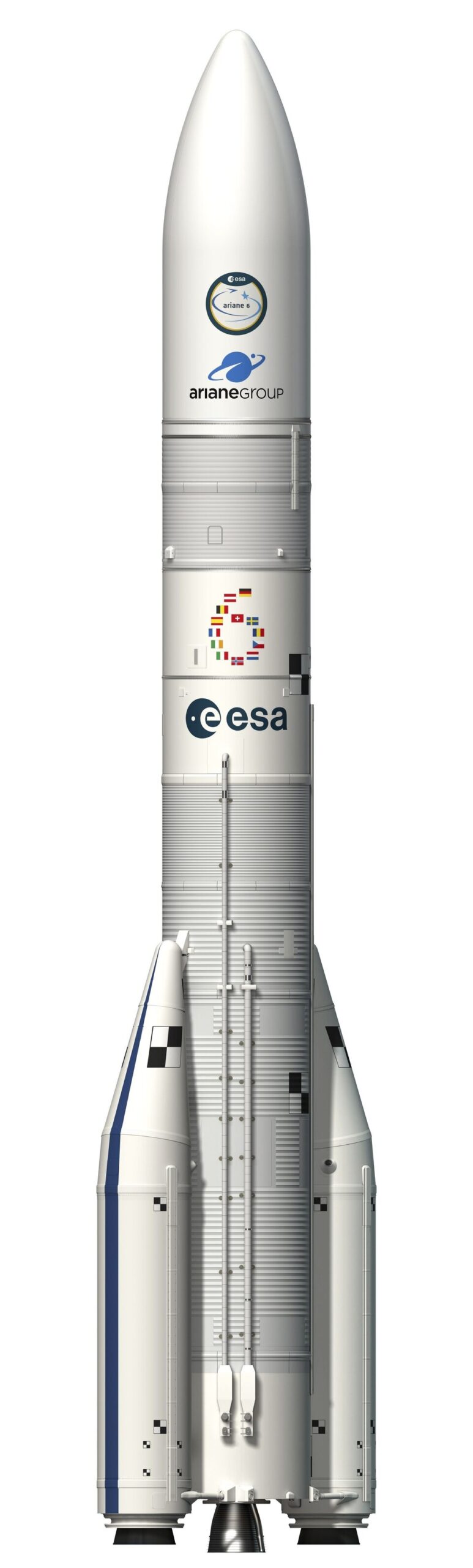
Ariane 6 is planned to launch in June-July 2024. It follows the hugely successful Ariane 5, Europe’s principal rocket for more than a quarter century, flying 117 times between 1996 and 2023 from Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana.
Ariane 6 has been designed for all possible futures. At its core is maximum versatility. It can put any satellite or payload into any orbital path. This is made possible with the new restartable Vinci engine that will power up the Ariane 6 upper stage again and again, stopping and starting to insert missions into any orbit they need to be. It will save enough fuel for a final burn to deorbit and reenter safely back through Earth’s atmosphere, or reorbit into a nearby ‘graveyard orbit’.
“We’re genuinely excited about this upcoming opportunity to fly on Europe’s new rocket, Ariane 6,” said Enrico Stoll, Chair of Space Technology at the Technical University of Berlin. “TU Berlin has a proven track record with 28 developed and operated satellites over the last decades, and the OOV-Cube mission holds special significance for us. It represents one of the first instances where we’ll be operating an experiment on a satellite developed by one of our spin-offs, RapidCubes, which adds a really interesting dimension to our experience in the field.”