SpaceFund has announced their new, SpaceFund Labs idea incubator. The goal of this new division of SpaceFund is to capture and turn exciting ideas into funded businesses by creating a unique incubation plan for each idea that is accepted into the program.
The economic frontier of space requires vision, but also serious and sober business planning. In its central role as a venture capital firm in a field that is literally taking off, SpaceFund is often presented with ideas that aren’t quite ready for prime time but hold great promise as potential enterprises. SpaceFund Labs is designed to take these very early-stage concepts and build successful businesses around them, including team formation, financial planning, corporate setup, legal consultation, and more.
In coming weeks the incubator will be bringing on top performers in a variety of industries as new advisors. This distinguished team of cross-disciplinary experts will help with vetting, ideation and company formation. SpaceFund’s venture capital investment division will then assess each company for viability and when appropriate, lead the new company’s first investment round.
“SpaceFund Labs is about discovering and nurturing the most brilliant ideas in AI, biotech, fintech, materials science, quantum mechanics and more to enhance humanity’s future in space,” said Meagan Crawford, co-founder and managing partner of SpaceFund. “SpaceFund Labs will take the best ideas that apply to space and turn them into profitable businesses. Sometimes we see holes in the marketplace that no one else is trying to capture. It’s our job, even our responsibility to our investors, to go out and capture that value by creating stellar teams and solid businesses that can get it done.”
“We provide both the real-world knowledge of the most experienced minds in the space industry and the critical experience-based coaching of VCs and financial experts,” said Rick Tumlinson, SpaceFund’s founder. “The SpaceFund brand stands behind the best.”
For more information or to submit ideas for consideration, please visit this direct link…


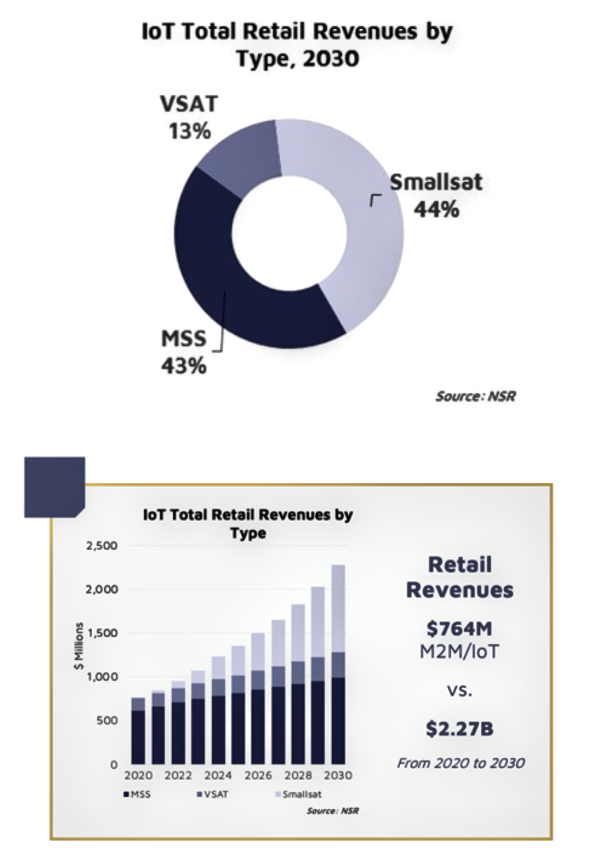
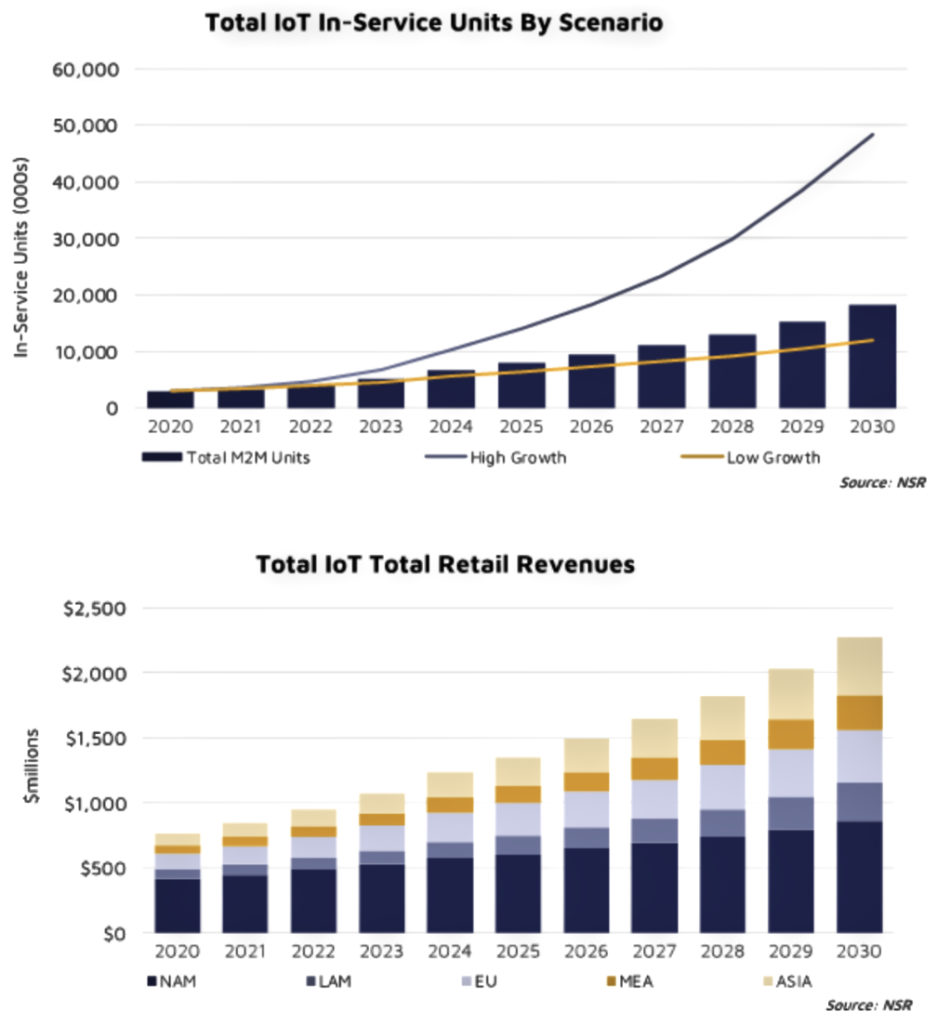





 ) programs. Rogue is looking to begin seeding its Orbot services constellation into LEO beginning in 2022.
) programs. Rogue is looking to begin seeding its Orbot services constellation into LEO beginning in 2022.