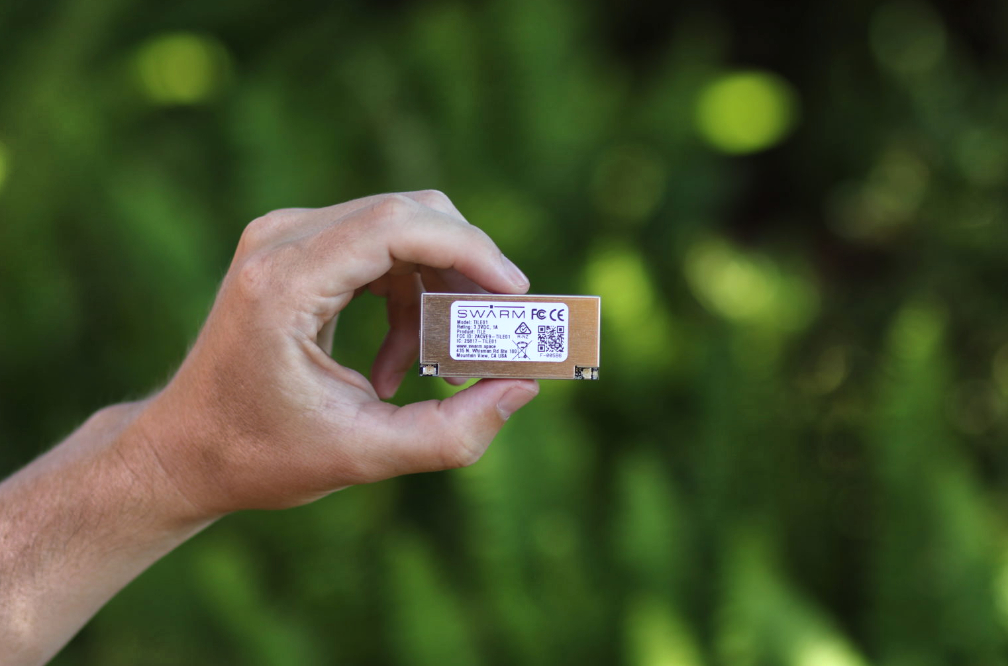
After three years of technical innovation, building, and testing, the hardware product and data service is now available from Swarm Technologies.
Swarm was founded in 2017 to solve a global problem: that device connectivity remains inaccessible in much of the world and is prohibitively expensive for many industries — Swarm’s affordable network can now connect IoT devices at what the company calls “an unprecedented scale.”
Now, every person and IoT device can have affordable access to two-way data services from any point on Earth at all times. The firm’s global network enables customers to build their businesses and scale them globally overnight by harnessing the power of smallsat connectivity.
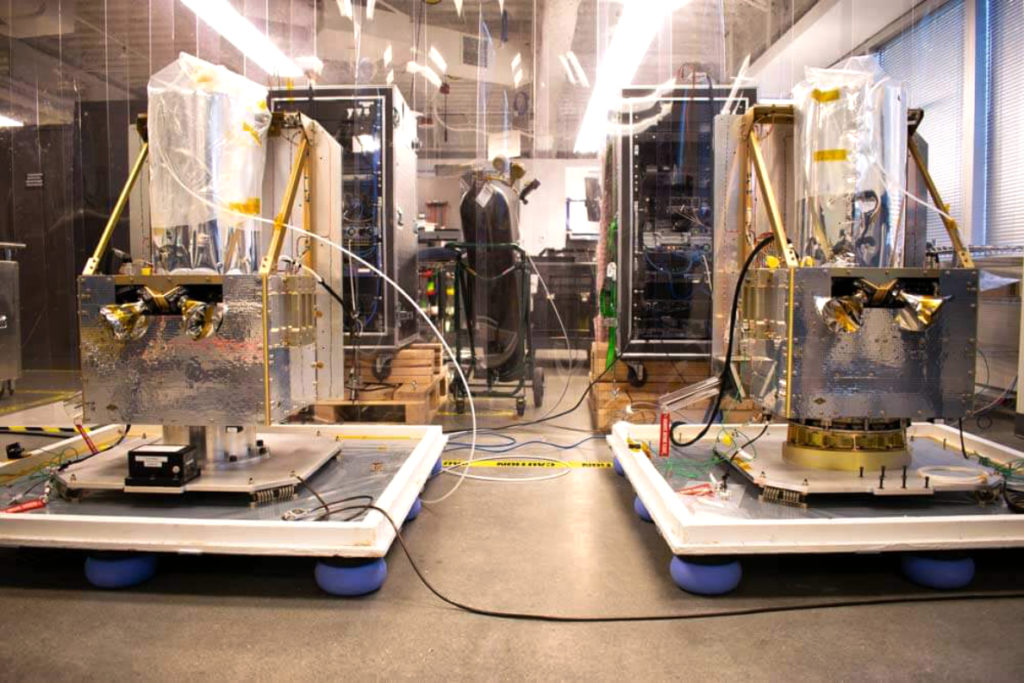
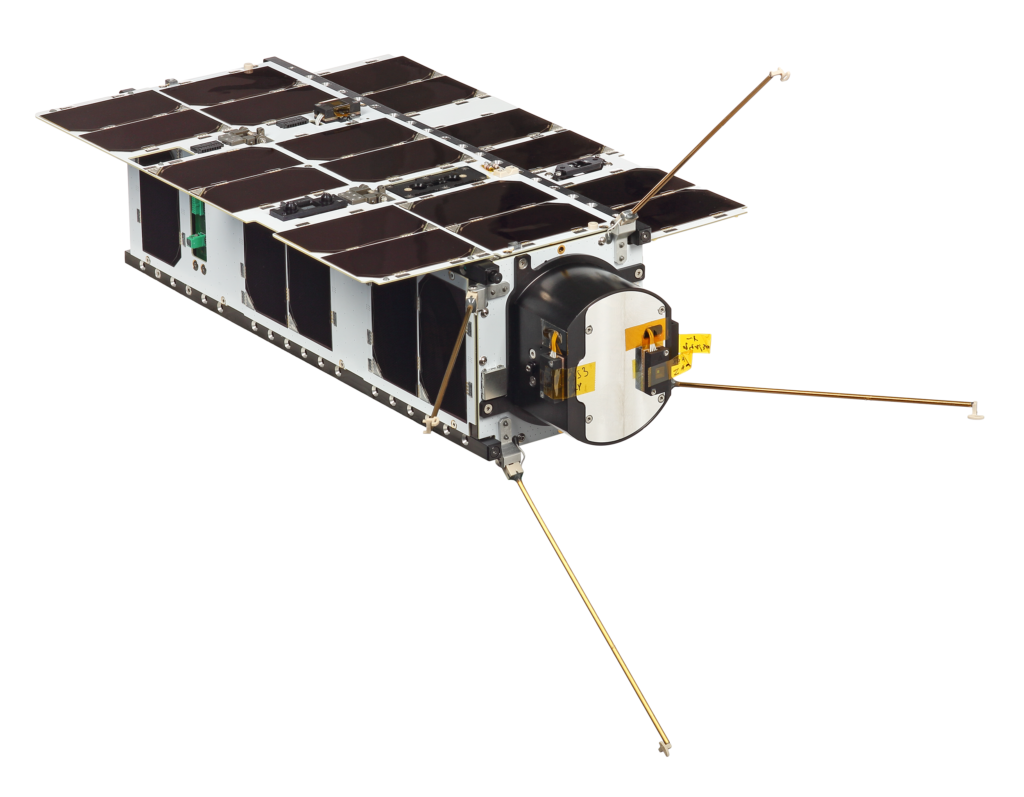
Swarm’s satellite modem, the Swarm Tile, is designed to be embedded into a circuit board design. It connects IoT devices to Swarm’s network, providing two-way data transfer. Compact, lightweight, and low power, the Swarm Tile is ideal for low-bandwidth, battery-powered use cases.
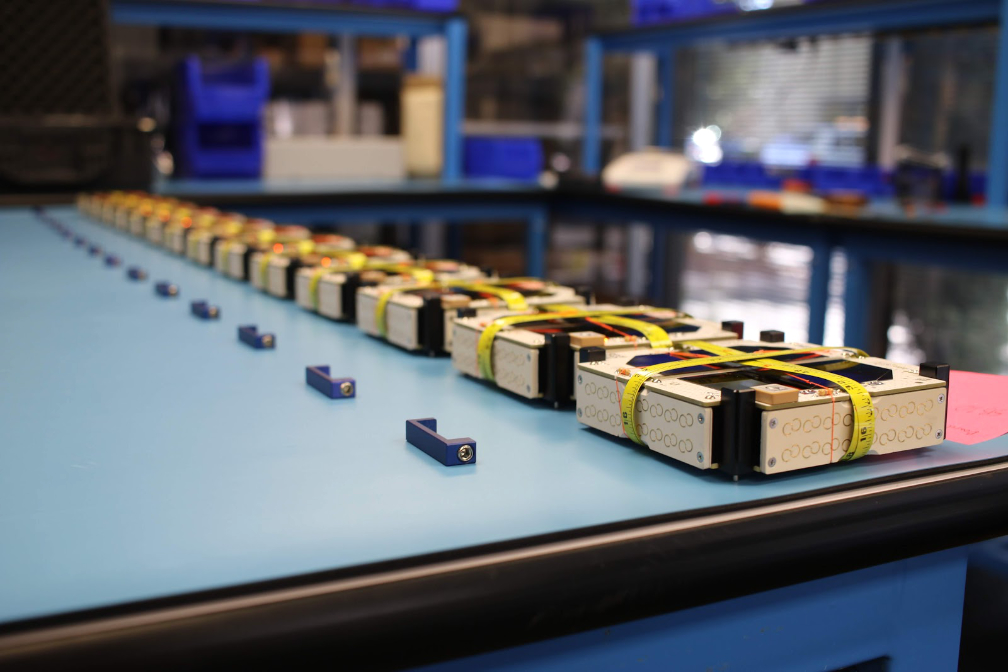
Swarm Technologies designs and prototypes all of their user terminal technology in-house, ensuring 100% quality control of all components and that customers receive the latest state-of-the-art technology. The company then works with contract manufacturers to produce Swarm Tiles at massive scale.
Access to Swarm’s data network will be available through an annual subscription with no setup or hidden fees. Data can be delivered to the Swarm dashboard, via email, or to any third party application via an easy-to-use REST API.
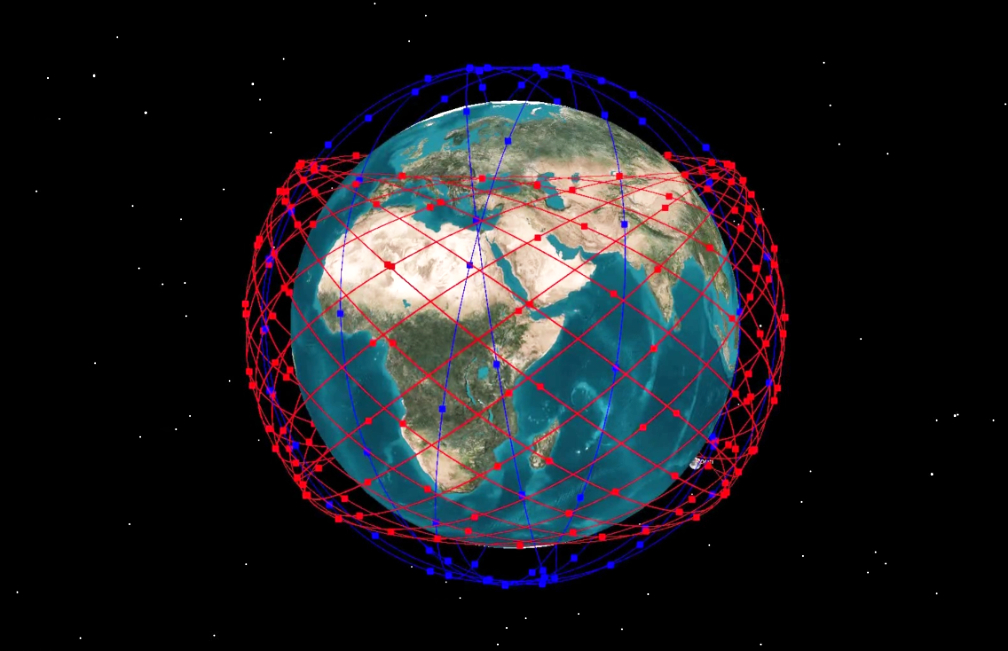
Swarm’s full satellite constellation will provide 24/7 network coverage for all points on Earth, providing reliable, globa,l data services.
According to the firm, Swarm’s hardware and data services are a fraction of the cost of legacy satellite data providers, often 1/10th the cost of existing satellite solutions, — that opens up new markets for connectivity that previously could not afford to do so. Target companies for Swarm include precision agriculture, vehicle tracking and telematics, maritime and fishing, energy, and logistics industries.
Ford Motor Company’s pilot program with Swarm is one example of how accessible satellite connectivity can improve efficiency and safety in the mobility industry. In a letter of support to the FCC in July 2020, Ford wrote, “Swarm is a critical Ford technology partner that is capable of providing the ‘anywhere and everywhere’ transmission medium for the connected vehicles of the future… [Swarm] will help ensure that Ford has the necessary coverage and throughput to serve connected vehicles even in the most remote locations, both in the United States and globally.”
More than 200 companies have already signed up for early access to join the Swarm network when commercial services start later this year.



















 A study into global broadband retail prices from
A study into global broadband retail prices from 




