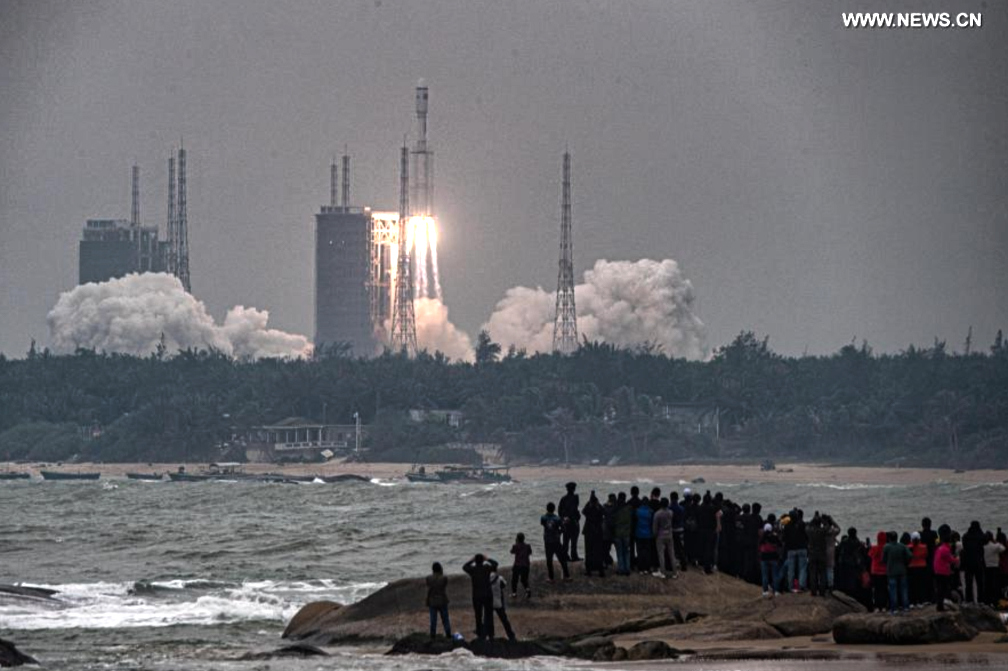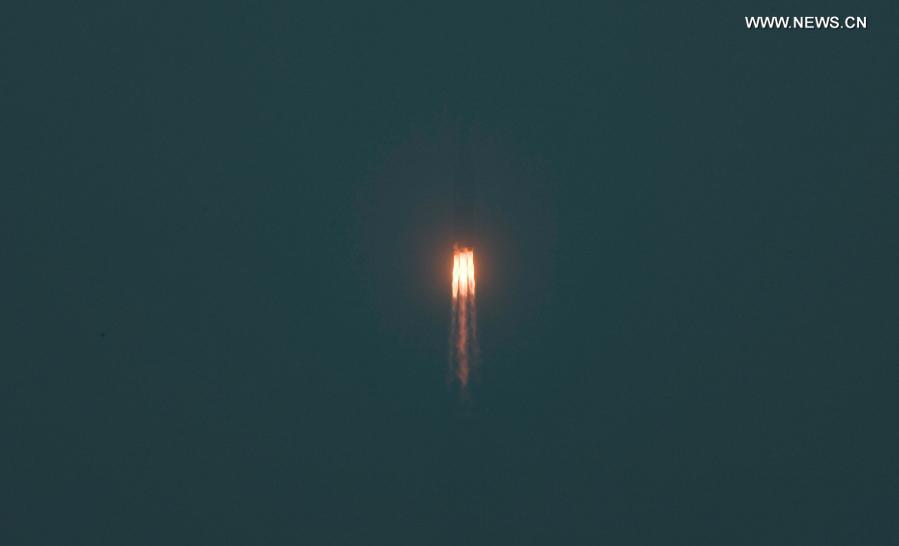
2020 was the time when the space scene was lively again, with the Thai government pushing for space-activity-related legislation and creating mechanisms to promote and support both the government and the private sector to develop the space industry together. This is one of the target industries in the new S-curve that will increase Thailand’s investment capacity and its role in developing the space industry and ultimately add value to the Thai economy.
The private sector also plays an important role in developing the economy and stimulating investment in the space industry. This year, mu Space and Advanced Technology Public Company Limited (mu Space Corp.) attracted investors from several industries and businesses to invest in the space industry, such as TOT Public Company Limited, executives from Dow Chemical Group, SCG, as well as the current investors, including Nice Apparel Group, B.Grimm Group, Majuven Fund, a private business group as well as a group of other minor investors, i.e., executives from the UCLA Foundation. The value of ‘mu Space’ has increased to more than $100 million through a Series B fundraising.

‘mu Space’ CEO, Varayuth Yenbamroong, on December 25th, 2020, stated during a soft opening event of the first spaceship factory in Thailand that “the fund recently raised will be used on quickly build a large-scale factory to produce and assemble the first spaceship of Thailand, along with satellite parts and commercial spaceships for domestic affairs, communications, national security such as creating a locally made GPS (Global Positioning System), robotic testing, autonomous system testing for unmanned vehicles to be used on the Moon mission. The factory will be equipped with the 5G communication system. It will also serve as a platform to develop “Space IDC” technologies, with a plan to test the “Space IDC”(Space Internet Data Center) simulation in the first quarter of 2021.”
“Space IDC,” or Space Internet Data Center services, is a project jointly created by ‘mu Space’ Corp. and TOT Public Company Limited that aims to provide a data center service with a server, both located in space.
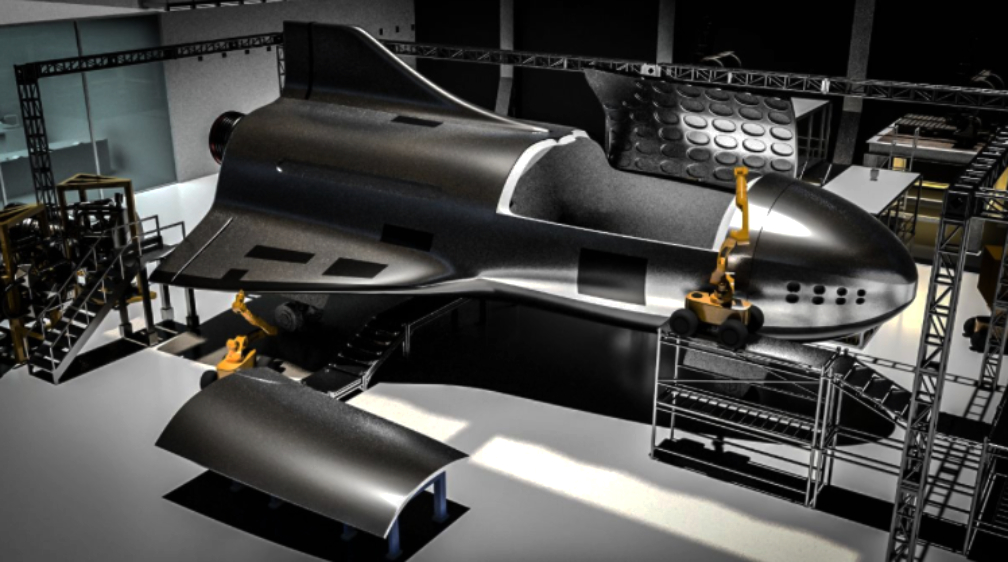

“mu Space’ is planning to build 11 gateway stations initially in Bangkok to operate the upcoming LEO satellite while preparing to propose as many as 8 projects from US National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) at the start of 2021. ‘mu Space’ has gains a lot of experience and has grown significantly from submitting 7 space technology development projects, with its Tipping Point Solicitation Project passing the first hearing. “There is a good chance that ‘mu Space’ will be awarded with the project contract,” said Varayuth.
Despite the presence of COVID-19 pandemic, ‘mu Space’ is planning to hire about 100 positions, starting with the first 50 positions in Q1 2021 to create skilled laborers, in line with the national space technology and industry development plan.