Mynaric and Cloud Constellation have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to use Mynaric’s laser communication products to connect Cloud Constellation’s LEO satellites via highly secure, high-performing Optical Inter-Satellite Links (OISLs).

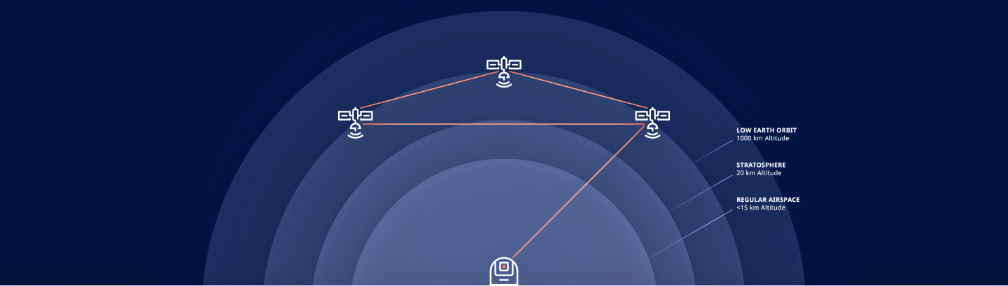
Cloud Constellation is developing an LEO constellation known as SpaceBelt to provide Data-Security-as-a-Service (DSaaS) and further secure cloud storage and management services, while leveraging laser communications technology to move data securely between the satellites. OISLs are a cornerstone of the SpaceBelt architecture and a requirement for high-speed, reliable communications to transfer cloud-stored data in space to anywhere on the globe.
The MoU outlines the next steps of the planned partnership between both companies, which would include, in a first phase, Mynaric delivering all OISL terminals required for the first ten satellites of the SpaceBelt constellation to be built by its selected prime of choice LeoStella. Mynaric’s CONDOR product is a perfect fit for SpaceBelt’s requirements, given its high performance, delivery schedule and full compliance with the Space Development Agency’s (SDA) OISL Standard, which is of critical importance to Cloud Constellation’s plans to serve the U.S. Government and other security-sensitive commercial enterprise customers. Further selection criterion was Mynaric’s industrialized approach toward the production of OISL terminals.
Cloud Constellation Corporation’s SpaceBelt is a patented, high-speed global cloud storage network of space-based data centers, each seamlessly interconnected together to provide exclusive and secure cloud infrastructure to service providers, enterprises and governments around the world.
is a patented, high-speed global cloud storage network of space-based data centers, each seamlessly interconnected together to provide exclusive and secure cloud infrastructure to service providers, enterprises and governments around the world.
“Mynaric is excited to support Cloud Constellation and work with its satellite prime contractor, LeoStella. SpaceBelt provides a truly unique satellite service to its diverse customer set. We are confident that the use of Mynaric’s CONDOR terminals within the SpaceBelt network architecture enhances the overall value proposition of this service offering. It is great to see Mynaric’s laser products contribute to yet another powerful use case that will benefit security-sensitive customers in the U.S. Government and beyond,” said Tina Ghataore, CCO Mynaric.
Mynaric (Frankfurt Stock Exchange: M0Y, ISIN: DE000A0JCY11) produces the optical fiber for the skies and, as a pioneer of laser communication, enables extremely fast and secure wireless data transmission between aircraft, drones and satellites. Globally, the need for fast, secure and ubiquitous network connectivity is advancing inexorably. Data networks such as the internet are now largely based on infrastructure on the ground which cannot be expanded arbitrarily for legal, economic or logistical reasons. The future, therefore, calls for an expansion of the existing network infrastructure into air and space. Mynaric pioneers this growth market with an industrialized approach to wireless laser communication products.
