Vaya Space will create a Brazilian subsidiary as part of their strategic plan to expand operations into South America. Vaya Space anticipates creating 200 direct jobs in Brazil over the next two years and plans an initial manufacturing footprint of approximately 10,000 square meters.

The final location for Vaya Space manufacturing operations within Brazil remains in negotiation, with several areas vying for consideration. Previously, a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) was signed with the Investment and Trade Promotion Agency (INDI) for the state of Minas Gerais, Brazil. Vaya Space is also considering locations in the aerospace cluster located within the state of São Paulo, in the city of São José dos Campos, which according to a 2020 ranking by the Financial Times Magazine, is the third best city in the world for aerospace sector strategic investment.
Jack Blood, Vaya Space Vice President, commented on the favorable business climate that exists in Brazil, government policy to facilitate commercial space efforts, and the opportunity for public-private partnering and said, “The US-Brazil Technological Safeguards Agreement (TSA) protects sensitive space technology exports to Brazil for launch from the Alcântara Launch Center. This ensures compliance with US export control requirements, and allows us to take advantage of the excellent location of this spaceport, which can support a wide range of launch azimuths, from equatorial to polar,” stated Blood. “The Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation (MCTI) under the leadership of Marcos Pontes has been a strong advocate of bringing commercial launch business to Brazil. Other considerations included the ability to generate turn-key solutions with the National Institute for Space Research (INPE), which has robust capabilities to support development of small satellite technologies, particularly earth observation and space and atmospheric sciences; along with Brazilian Space Agency (AEB) alignment with FAA best practices. Taken as a whole, all these factors create an excellent environment in Brazil for commercial space operations, and for Brazil to assume a leadership role of the space industry in South America.”
Vaya Space President Rob Fabian summarized, “We are excited about standing-up our Brazilian subsidiary. We look forward to partnering with Brazilian companies; developing local, regional, and global supply chains, supporting a strong and diversified customer base, and contributing to the creation of a vibrant commercial space economy.”
Vaya Space is a hybrid rocket propulsion and SmallSat launch company leveraging advances in additive manufacturing to redefine the cost, performance, and safety of space access. With a build, integrate, and launch-ready cycle of less than 30 days, Vaya Space is capable of launching payloads greater than 1,000 kg into Low Earth Orbit (LEO), and payloads greater than 600 kg into Sun Synchronous Orbit (SSO). Positioned to serve the global market, Vaya Space is now accepting launch reservations for 2023.






 data service.
data service.
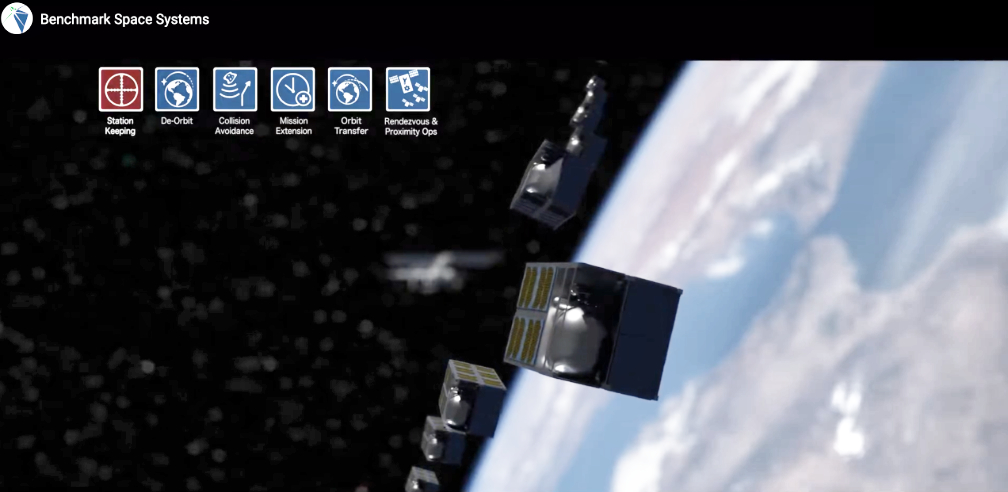





 tanker, to optimize spacecraft control accuracy in preparation for the first-ever tanker maneuvers in space during simulated docking demonstrations.
tanker, to optimize spacecraft control accuracy in preparation for the first-ever tanker maneuvers in space during simulated docking demonstrations.