Rocket Lab USA, Inc. (Nasdaq: RKLB) has been selected to launch NASA’s Advanced Composite Solar Sail System, or ACS3, on thir Electron launch vehicle.
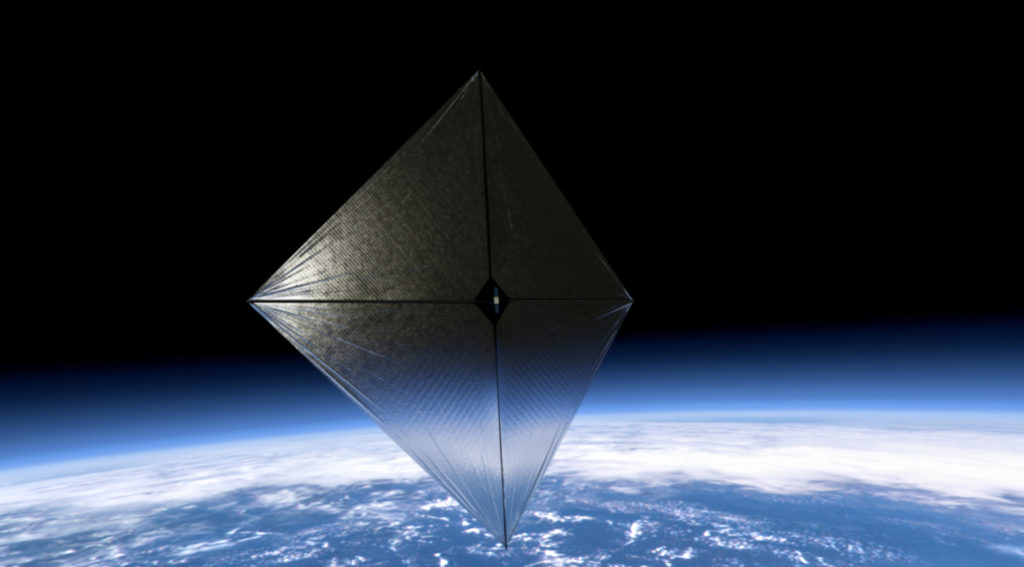
NASA’s ACS3 technology demonstration uses composite materials – or a combination of materials with different properties, in its novel, lightweight booms that deploy from a cubesat to support a solar sail. Just as a sailboat is powered by wind in a sail, solar sails employ the pressure of sunlight for propulsion, eliminating the need for conventional rocket propellant.
Data obtained from the ACS3 demonstration will guide the design of future larger-scale composite solar sail systems that could be used for space weather early warning satellites, near-Earth asteroid reconnaissance missions, or communications relays for crewed exploration missions.
ACS3 will launch as part of a rideshare mission, scheduled for lift-off from Rocket Lab Launch Complex 1 in mid-2022. The ability of the Electron launch vehicle’s Kick Stage to deploy individual satellites to unique orbits, even when flying as part of a rideshare, was a key factor in Rocket Lab being selected as the launch provider.

ACS3 requires a higher altitude than the other rideshare payloads launching on the same mission, so after deploying the first payloads, the Kick Stage will perform another burn with its 3D printed Curie engine to raise the orbit and deploy ACS3. Rocket Lab’s Kick Stage has demonstrated orbit raises across 18 missions to date, and also successfully conducted inclination changes and orbit lowering, providing customers with proven, flexible, and precise in-space transportation.
“We are thrilled to be NASA’s launch partner for this innovative mission,” said Rocket Lab founder and Chief Executive, Peter Beck. “It seems fitting to launch NASA’s Advanced Composite Solar Sail System on Electron, the world’s first full carbon composite orbital launch vehicle. We’re excited to see composites used yet again to unlock new capabilities in space.”
ACS3 Mission Partners:
NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, is designing ACS3’s deployable composite booms and solar sail system. NanoAvionics of Columbia, Illinois, is designing and building the 12U cubesat for the ACS3 technology demonstration. NASA’s Ames Research Center in California’s Silicon Valley is managing the ACS3 project and will oversee final integration of the solar sail payload and cubesat. The Santa Clara University’s Robotics Systems Lab in Santa Clara, California, will provide cubesat operations support for the ACS3 technology demonstration. NASA’s Small Spacecraft Technology program within the agency’s Space Technology Mission Directorate is sponsoring the ACS3 project and is providing the funding for the launch . NASA’s Game Changing Development program within the agency’s Space Technology Mission Directorate is developing ACS3’s deployable composite boom technology.