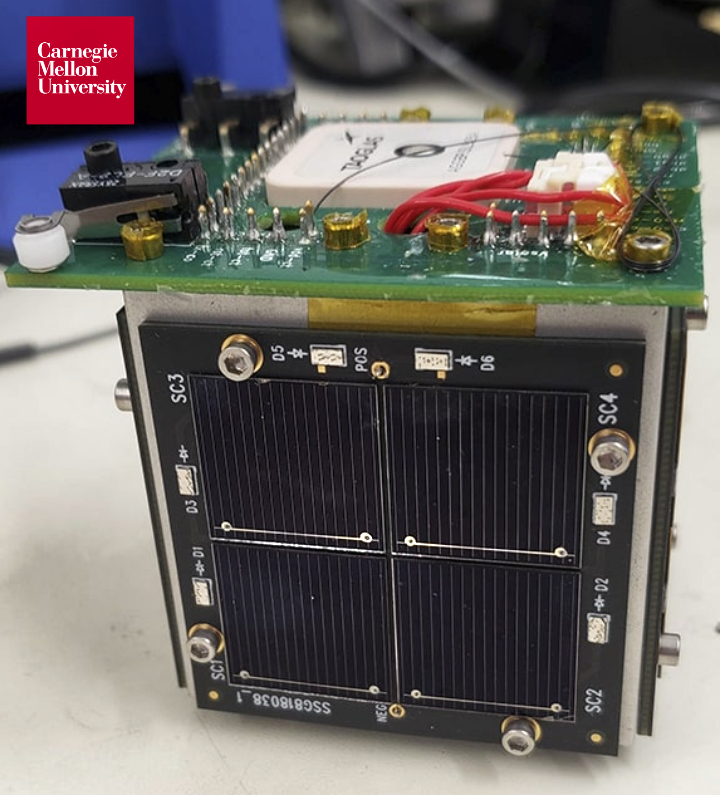
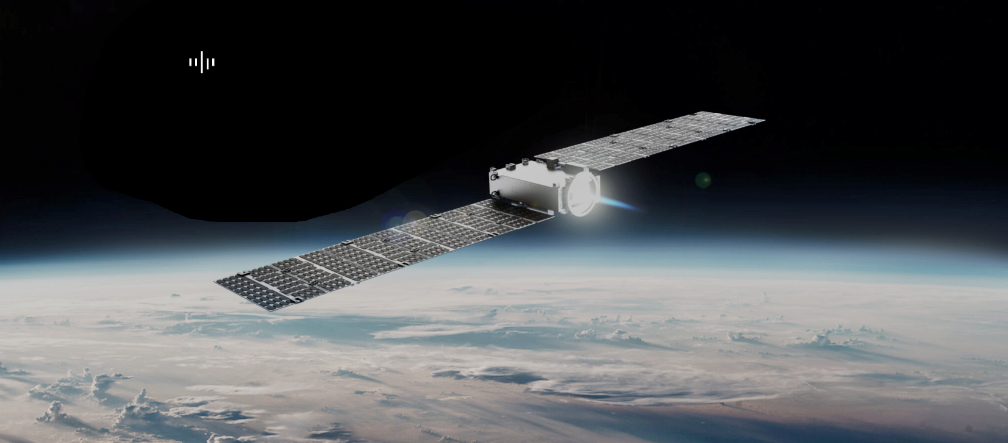
SayariLabs, first Kenyan space company, provider of satellite services and space-based solutions to governments, industries, and academic institutions in Africa and beyond, and EnduroSat, a provider of software-defined smallsats and space services for business and academia, have signed a commercial agreement to launch TAIFA-1 (“one nation” from Swahili), the first Kenyan, 3U, software-defined smallsat.

TAIFA-1 will get to orbit on SpaceX`s Falcon 9 — the launch is scheduled for Q4, 2022.
In the past decade, East Africa has been hit with heavy droughts and wildfires, causing water crisis, and damages of local agriculture and food supplies. TAIFA-1 will be loaded with a hyperspectral, Earth Observation (EO) camera that will capture environmental, wildlife, agricultural and land use mapping, all in the battle to halt the calamities in the region.
EnduroSat and SayariLabs also signed an MOU, which is another milestone for this partnership and the upcoming, joint space projects of the two companies. EnduroSat organized a two-week educational training program, dedicated to space systems and engineering and covering all aspects of mission analysis, design, and space craft assembly for the engineering team of SayariLabs.

“Over the past decades, space and satellite industries have been reserved for the wealthy and mighty. SayariLabs is on a mission of democratizing these industries for all interested players in the African region and in making Kenya a space giant in the next generation. With the advancement of technology this fantasy is quickly becoming a reality. Our partnership with EnduroSat, a leading company in this industry, is a major game-changer and it strengthens our hope and belief of being a major space and satellite solution provider in Kenya, the African region and other parts of the world,” said Aaron Nzau, the Founder and CEO SayariLabs
“I am really proud to have the opportunity to support SayariLabs in their efforts to bring space closer to thousands of people in Kenya. Working alongside their team has been an amazing experience for us and I cannot wait to see the innovations and the positive impact that they plan to have, realized in practice. EnduroSat has been for long time a true believer in open, responsible and accessible space and this is yet another step in this direction,” said Raycho Raychev, Founder and CEO of EnduroSat
EnduroSat provides software-defined smallsats and space services for business, exploration, and science teams. Its focus is on the development of next generation space commercial services and exploration programs. With an annual growth of 250%+, it is one of the fastest growing space companies in Europe. Proud member of the International Astronautical Federation (IAF), EnduroSat’s team exceeds 100+ talented developers, engineers, and scientists, currently serving more than 120+ clients worldwide. Customers for the Shared Satellite Service include 1) commercial space companies focused on IoT, remote sensing, meteorology, and Earth observation, and 2) research organizations: space agencies, universities, and institutes.
SayariLabs is the first Kenyan space startup company established in 2020 to provide satellite services and space-based solutions to governments, industries, and academic institutions in Kenya, as well as in the African region and other parts of the world. the company’s focus is on being the commercial market leader for satellite manufacture and space exploration activities in Africa and beyond. We are honored to be the first Kenyan satellite manufacturing startup company to be supported by the Kenya Space Agency, and partnering with EnduroSat from Bulgaria, in achieving our first satellite mission – TAIFA – 1. With our team of eight dedicated and talented Kenyan engineers, SayariLabs intends to grow and serve customers in several technology areas including the IoT industry, remote sensing, meteorology, earth observation and build more partnerships with research organizations, academic institutions, and MDA’s (Ministries, Departments and Agencies) within governments.