The HANBIT-TLV will carry onboard the payload SISNAV, an inertial navigation system being developed by DCTA and other institutions.
INNOSPACE, a South Korean space startup for small launch vehicles, signed an agreement with the Brazilian Department of Aerospace Science and Technology (“DCTA”) to launch SISNAV, an inertial navigation system project supported by Finep and AEB.
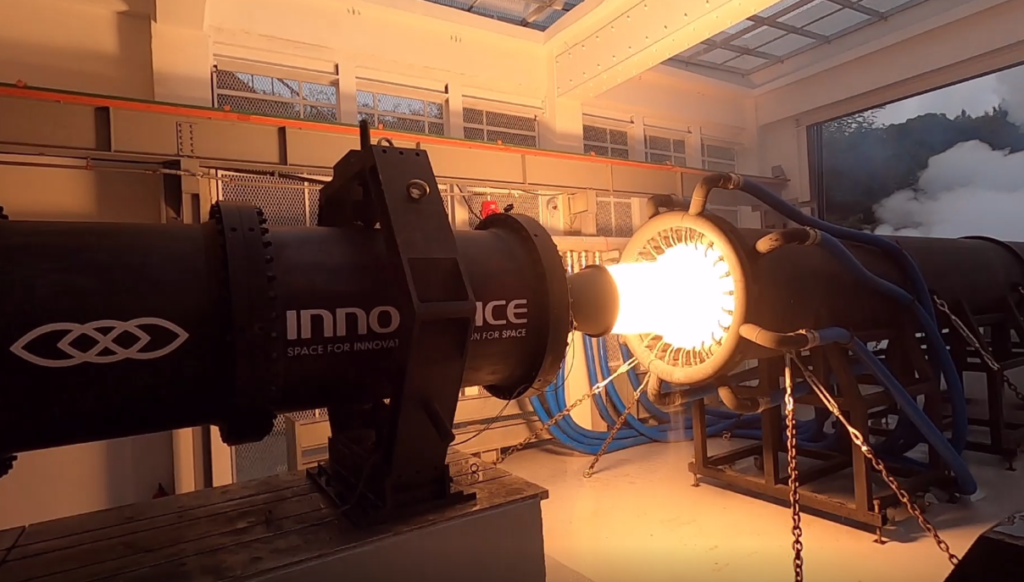
INNOSPACE is currently developing HANBIT, a small satellite launcher powered by its hybrid rocket engines, and the first test flight of HANBIT-TLV is scheduled for the fourth quarter of 2022 at the Alcântara Launch Center in Brazil, which is an equatorial launch site. It will be the first suborbital test flight to validate the first stage engine of HANBIT-Nano, which is a 2-stage small satellite launcher capable of carrying a 50kg payload.

With this agreement, INNOSPACE expects to be able to verify the launch vehicle’s performance capability and obtain recognition in the aerospace sector at the same time by launching the payload despite a test flight. HANBIT-TLV is a 15-ton thrust single stage hybrid rocket with a height of 16.3m, 1-meter-diameter, and weight of 9.2-ton.
The HANBIT-TLV will carry onboard the payload SISNAV, an inertial navigation system being developed by DCTA and other institutions. They will verify that SISNAV operates well in specific environments such as vibration, shock, and high temperature that occur in the entire process from takeoff and during the transatmospheric flight.
“This agreement is meaningful in that INNOSPACE and DCTA have been committed to mutual technical and operational development and continued partnership. We hope that INNOSPACE will enter the small satellite launch service market with the successful first test launch of HANBIT-TLV in the fourth quarter in Brazil,” said Soo Jong Kim, CEO of INNOSPACE.
