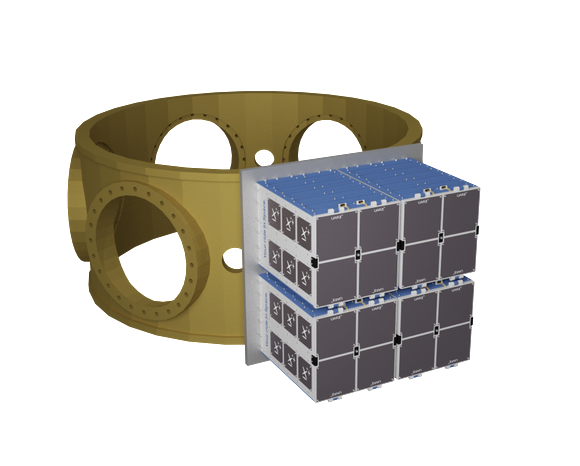
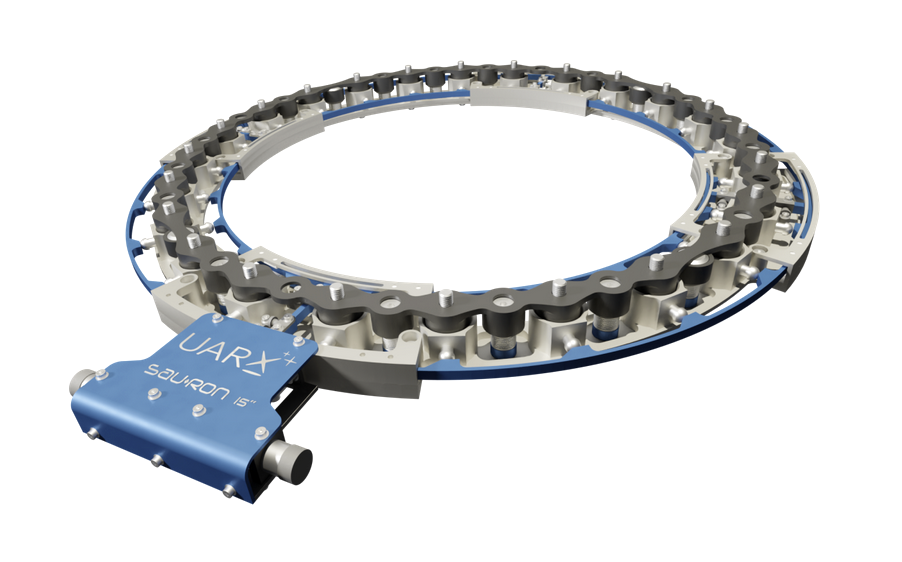
Exobotics and Simera Sense are collaborating to engineer and integrate a hyperspectral imager into one of their smallsat platforms that is scheduled to be launched into LEO later this year.

The hyperspectral imager will perform high resolution imaging, at less than 5 meters per pixel in the 450 to 900 nm. range, allowing for the collection of a variety of space related data which can be used across sectors both within and beyond the space industry. Potential use cases for the hyperspectral imaging technology include monitoring and forecasting crop health, measuring the emissions of pollutants, object detection, and more.
Exobotics has developed a bespoke payload support system to enable the image to work with a wide range high-speed radios in S-, X- and Ka-bands to improve performance and flexibility in space. The manufacturing of the hyperspectral image is part of a wider collaboration which will later focus on turn-key integrated satellite platforms in order to improve accessibility to space for customers.
Nadeem Gabbani, Founder of Exobotics, said, “We are delighted to be working with Simera to produce and integrate the hyperspectral imaging payload which will provide high-resolution imagery for a variety of use cases for our customers. Reducing the barriers to entry for space is vital for the growth of the wider economy, and many sectors, such as FinTech, mining and agriculture, need to be made aware of the benefits space can bring at an affordable cost. Access to space needs to be cost effective, easy and fast, which is why we oversee the end-to-end design, manufacturing and testing phases for payloads and nano-satellite platforms, which can be achieved in 9 to 12 months through our fast track program.”
Ana-Mia Louw, General Manager at Simera Sense, said, “Simera and Exobotics have great synergy, and by working collaboratively, exciting solutions are in the pipeline. We look forward to a successful hyperspectral mission launching later this year, and future collaboration with Exobotics, continuously making leading earth observations missions effortless for our clients.”


 or Thales VesseLINK
or Thales VesseLINK