Mangata Networks has selected Scotland as the location for the company’s research and development activities, as well as satellite manufacturing, space systems and core network operations.

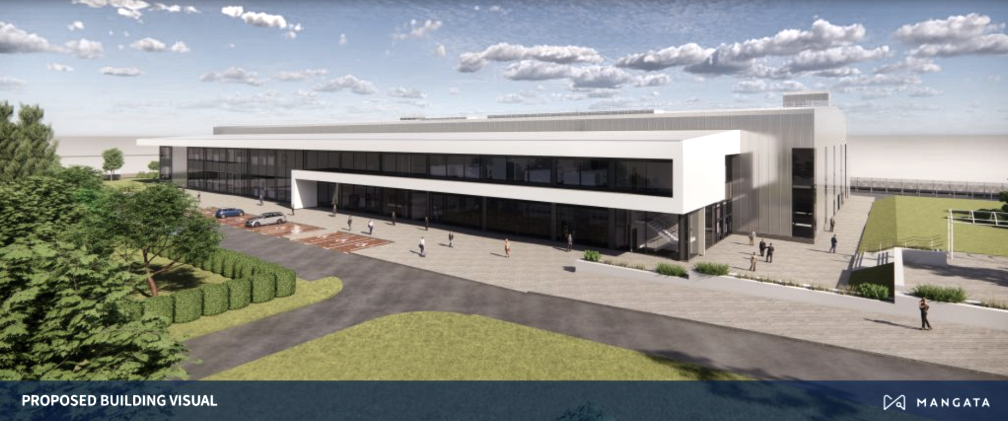
Over the coming years, as many as 575 new jobs will be created as part of Mangata’s state-of-the-art engineering and operations hub for satellite manufacturing and operations at the Prestwick International Aerospace Park in Ayrshire.
The hub is supported by an innovative funding and assistance package from public sector partners, totaling more than £83.7 million from Scottish Enterprise, Scottish Government, UK Government and South Ayrshire Council. This funding comprises £54.5 million from Scottish Enterprise and £29.2 million from the Ayrshire Growth Deal provided on commercial terms (i.e., this is not grant funding) that will see this funding repaid over the next 15 years.
Mangata’s new facility will produce and test more than 24 medium class satellites every three months, becoming a significant focal point and asset for the Scottish and UK space sectors as well as a centerpiece for technology and innovation. The facility is capable of qualifying, integrating and testing satellites up to 1500kg in size for the space and launch environments. From this engineering hub, the company will establish an operations center that will manage its satellite systems and global network.
The majority of the new jobs will be highly paid, highly skilled technical engineering positions in product development, designing and manufacturing satellites, and operating the system end-to-end. Construction will begin in early 2023, with manufacturing and operations teams set to move in from late 2024.
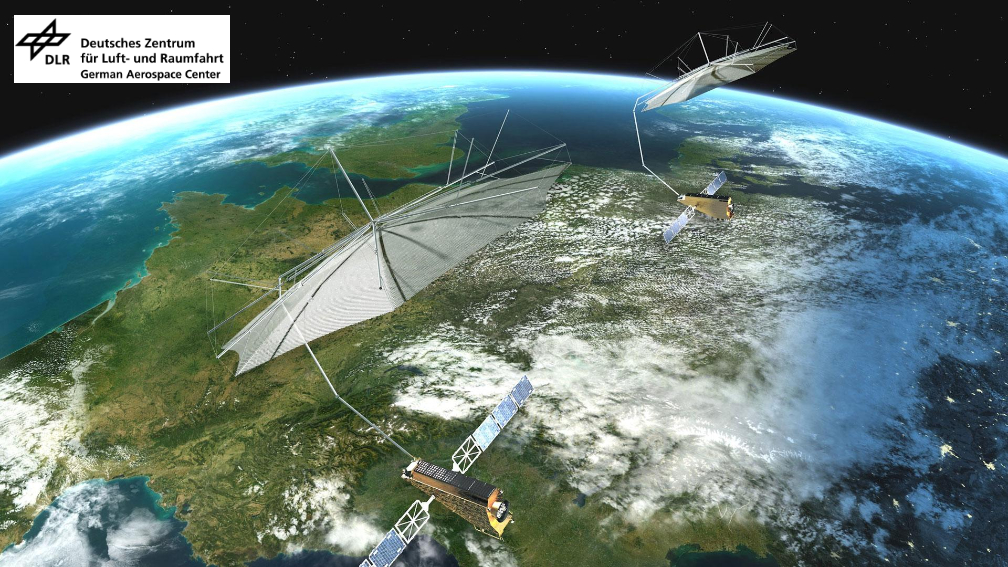
Mangata is building a global satellite telecommunications network with sustainable, cutting-edge technology. It is designed to reach and connect any community, anywhere on Earth, removing barriers and inequalities for the up to four billion people without adequate internet access. It will support the creation of local content and enable sharing on a global basis.
Prestwick is already home to Scotland’s largest and most established aerospace cluster, and, through the £80 million investment from the Ayrshire Growth Deal, is now focused on taking advantage of the burgeoning global commercial space market to become the leading center for aerospace and space in the UK.
This technology will be deployed within Scotland where the created network can be tested with customers and used to incubate Scottish startups. These startups will benefit from exposure to Mangata’s investors and will have the opportunity to showcase their own technologies and applications, potentially exporting them on a global basis, through Mangata’s network.
Deputy First Minister of Scotland, John Swinney, said, “The fact that Mangata has chosen to base its new satellite manufacturing facility in Ayrshire is a huge boost for the region, for the space and manufacturing sectors, and for Scotland as a whole. As well as the substantial, high-skilled job opportunities, this will open up new pathways for the satellite manufacturing supply chain and help position Scotland as a leading centre for space and manufacturing innovation – while supporting the aims of our space strategy.”
Brian Holz, Chief Executive Officer of Mangata Networks, said, “Scotland, Ayrshire, the local regions, and the UK have expressed a lot of confidence in our system and mission. We are very grateful to be able to locate Mangata’s core product development, satellite manufacturing, and network operations teams in a state-of-the-art facility in Prestwick. We will be using this facility to bring our satellite connectivity and intelligent Edge compute solutions to enterprises globally. Today, our customer base has already committed to over 1.5 Tbps pre-launch, nearing full capacity of our initial 32 satellites. As the business grows, Mangata’s network can scale to over 750 satellites. This factory will be a key enabler, allowing us to scale and deliver cost-effective space technology into markets that really need it.”
Adrian Gillespie, Chief Executive of Scottish Enterprise, said, “This investment has the potential to be a real game-changer in helping unlock economic opportunities from the global commercial space sector. Mangata’s decision to locate this project in Ayrshire is a strong endorsement of our ability to support and nurture global industries of the future. Not only will it bring hundreds of new quality jobs for the people of Scotland, but it will be a catalyst for a new supply chain, opening up opportunities and partnerships both domestically and internationally. We look forward to working closely with Mangata to bring its state-of-the-art advanced manufacturing facility to fruition at Prestwick International Aerospace Park.”
Juliette Neu, Chief Experience Officer at Mangata Networks, said, “All the Scottish organizations involved have been incredibly supportive of our efforts to bridge the gap in global connectivity and access. Mangata is passionate about connecting humanity all around the world, using the systems we will develop in Scotland. We saw this same spirit to serve in the local and global community in our interactions in Scotland. They are so committed to helping each other. That drive is at the core of our shared values and mission.”
Leader of South Ayrshire Council, Martin Dowey, said, “We are delighted Mangata has chosen to locate in Prestwick and have great pleasure in welcoming them to South Ayrshire. We very much look forward to working with them and seeing the many benefits they bring to our local communities, beginning with hundreds of jobs. This really is fantastic news, as Mangata is exactly the kind of company we want to attract to South Ayrshire. The global satellite market is booming, and we aim to be right at the centre of that with a vibrant and thriving space sector. This will create high value jobs and exciting future careers for our young people, particularly in STEM-related opportunities, but also in wider support roles. The Council has now secured approval for a significant investment program to deliver commercial workspace at Prestwick. This comprehensive and bold approach gives companies like Mangata the confidence that we can build Prestwick as a global space cluster. We are already anticipating the first satellite launches from Prestwick Spaceport from spring 2024 and, through our highly ambitious space programme, are set to become Europe’s premier space hub.”
Larry Schwartz, Chief Operating Officer at Mangata Networks, said, “Our Prestwick facility will include a satellite operations center to operate our satellites following their launch. Our facility will also feature a network operations centre to operate our end-to-end global communications network as well as an R&D center to develop our intelligent microEdge data centres. Having all of these operations under one roof makes us extremely efficient across all aspects of our technology development and operational networks. This is key to bringing our customers a cost-effective, state-of-the-art network that includes an intelligent Edge compute and cloud service solutions. We are looking forward to working with local universities and companies, creating partnerships and integrating technology into our network and product solutions. We will develop those capabilities in Scotland and help those partners scale globally, using our network.”
UK Government Minister for Scotland, Malcolm Offord, said, “The creation of this space manufacturing hub will deliver jobs and investment to Ayrshire and put Scotland at the forefront of an innovative industry. The UK Government is investing £10 million towards these cutting-edge facilities as part of our £32 million support for Ayrshire’s space and aerospace program.”


 ’s integrated system architecture which includes the LizzieSat
’s integrated system architecture which includes the LizzieSat