Lockheed Martin (NYSE: LMT) has announced that the firm’s In-space Upgrade Satellite System (LM LINUSS ) accomplished a successful, on-orbit demo, proving how smallsats can serve an essential role in sustaining critical space architectures. This is accomplished by regularly upgrading existing constellations with new capabilities and extending spacecraft design lifecycles.
) accomplished a successful, on-orbit demo, proving how smallsats can serve an essential role in sustaining critical space architectures. This is accomplished by regularly upgrading existing constellations with new capabilities and extending spacecraft design lifecycles.
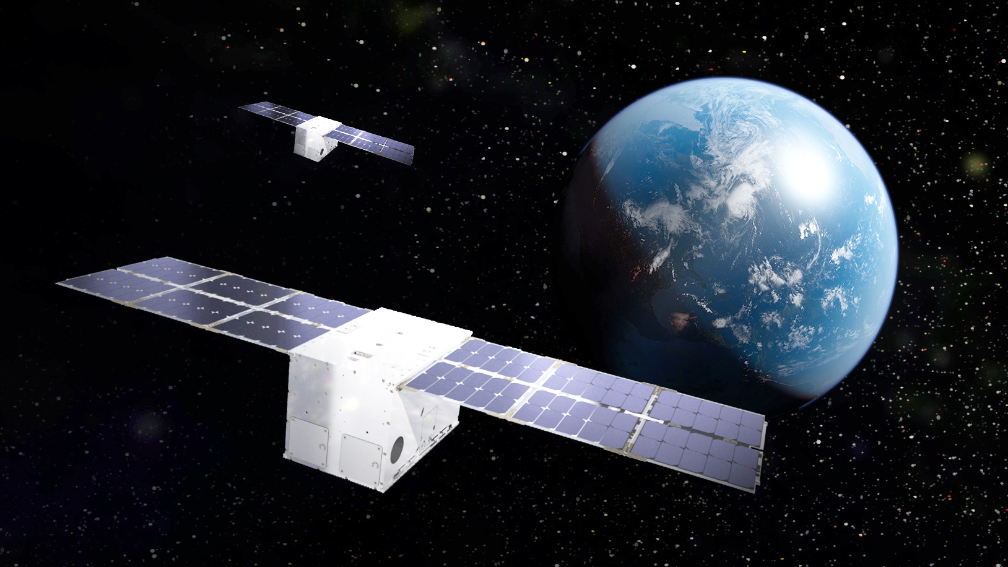

LM LINUSS, a technology demo funded internally by Lockheed Martin, is comprised of two, LM 50 12U CubeSats. While on-orbit, the system demonstrated highly-automated, rendezvous and proximity operations (RPO) that enables complicated — yet precise — maneuvering across multi-satellite constellations. This allows on-orbit servicing coordination and upgrades at scale in any orbit. The RPO demonstration was part of Lockheed Martin’s mission to validate essential maneuvering capabilities for future space upgrade and servicing missions.
12U CubeSats. While on-orbit, the system demonstrated highly-automated, rendezvous and proximity operations (RPO) that enables complicated — yet precise — maneuvering across multi-satellite constellations. This allows on-orbit servicing coordination and upgrades at scale in any orbit. The RPO demonstration was part of Lockheed Martin’s mission to validate essential maneuvering capabilities for future space upgrade and servicing missions.
During the demo, one of the LM LINUSS CubeSats acted as the designated servicing vehicle, navigating a flightpath toward the second CubeSat, which represented the resident space object (RSO). As the servicing vehicle approached the RSO, on-board guidance algorithms made final real-time adjustments to complete its rendezvous operations. The culminating success was declared when the CubeSats maneuvered in a proximity of one another, demonstrating high confidence in conducting future, on-orbit servicing missions for customers.
In addition to RPO, these smallsats also accomplished additional technology demonstrations while on-orbit…
- Performing automated maneuvers and using artificial intelligence to fly coordinated flightpaths, supporting a variety of operational conditions.
- Using Lockheed Martin’s Horizon
 2.0 command and control (C2) software and advanced RPO software.
2.0 command and control (C2) software and advanced RPO software. - Maintaining connection with a secure cloud-based architecture for mission telemetry, tracking and control.
- Showcasing the company’s advanced SmartSat
 software.
software. - Demonstrating miniaturized Space Domain Awareness capabilities.
- Validating new onboard high-performance processing, low-toxicity propulsion, inertial measurement units, machine vision, and 3D-printed components.
LM LINUSS could be considered the most capable pair of CubeSats in geosynchronous Earth orbit today, based on customer community feedback. The spacecraft have higher bus density, payload accommodation and on-orbit processing than any other CubeSat, which helps enable revolutionary mission capabilities in the future. Part of Lockheed Martin’s LM 50 smallsat family, it is the collaborative integration of the company’s mission electro-optical payload deck with a next-generation bus from Terran Orbital Corporation. LM LINUSS and other Lockheed Martin pathfinders are helping create a more sustainable future, safely adding mission life and more.
“The LM LINUSS pathfinder is an excellent example of how Lockheed Martin is investing in innovation in the real world. Agile development, cloud-based operations, and smallsat platforms came together at speed and in orbit, where the real test of technology occurs. Through the accomplishments of LM LINUSS, Lockheed Martin is pioneering how future small and medium class missions will be upgraded on-orbit, and continuing to develop critical, breakthrough technologies that keep our customers ahead of ready.” — Johnathon Caldwell, Lockheed Martin, vice president and general manager, Military Space
“This LM LINUSS demonstration was a success for many reasons, including the fact that our team navigated the inherent challenges of a novel technology and validated our software for future missions. We will leverage what our team learned from LM LINUSS’ design, development, and operations to continue advancing Lockheed Martin’s innovative vision for on-orbit satellite servicing and upgrades.” — David Barnhart, a technology director at Lockheed Martin Space
