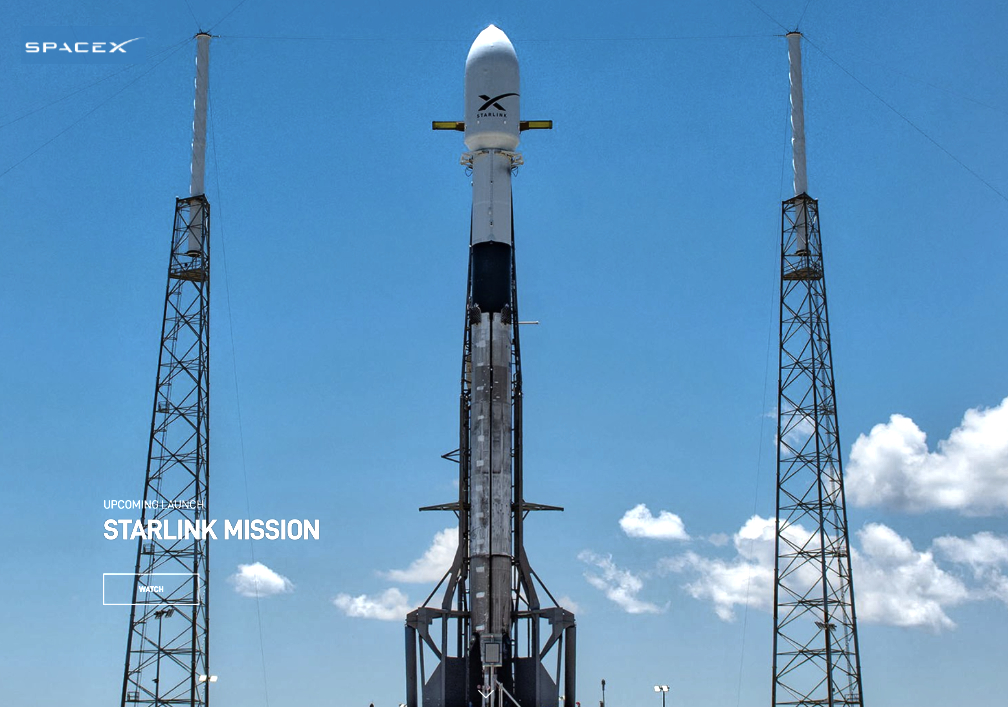
The first SpaceX launch of the day and this one occurred on Tuesday, June 12th., at 3:10 a.m. ET (07:10 UTC) and a Falcon 9 carried 53 Starlink satellites to LEO from Space Launch Complex 40 (SLC-40) at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.

The first stage booster supporting this mission previously launched SES-22, ispace’s HAKUTO-R Mission 1, Hispasat Amazonas Nexus, CRS-27, and four Starlink missions.
Following stage separation, the first stage landed on the Just Read the Instructions droneship stationed in the Atlantic Ocean.