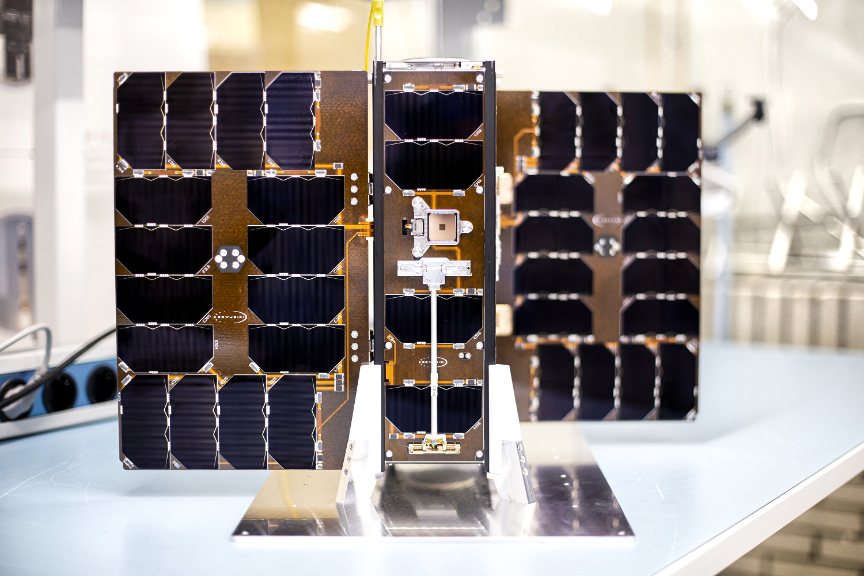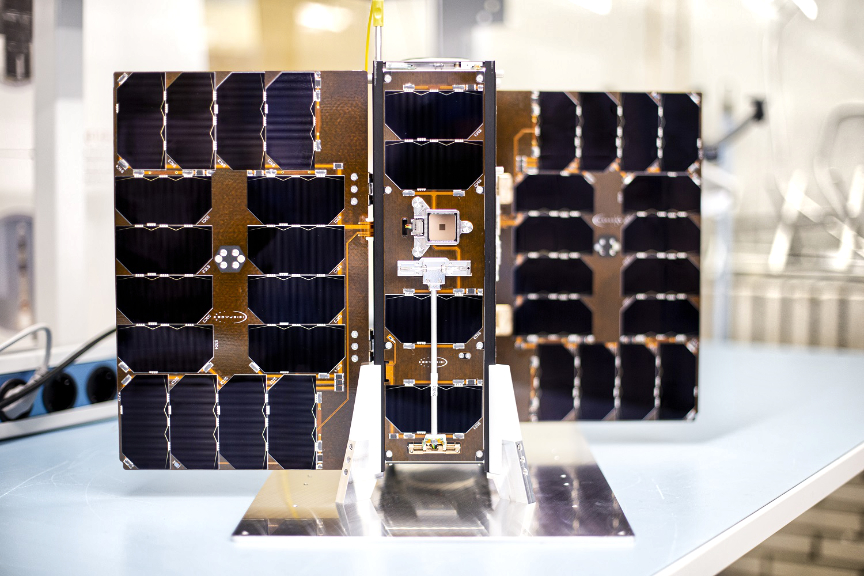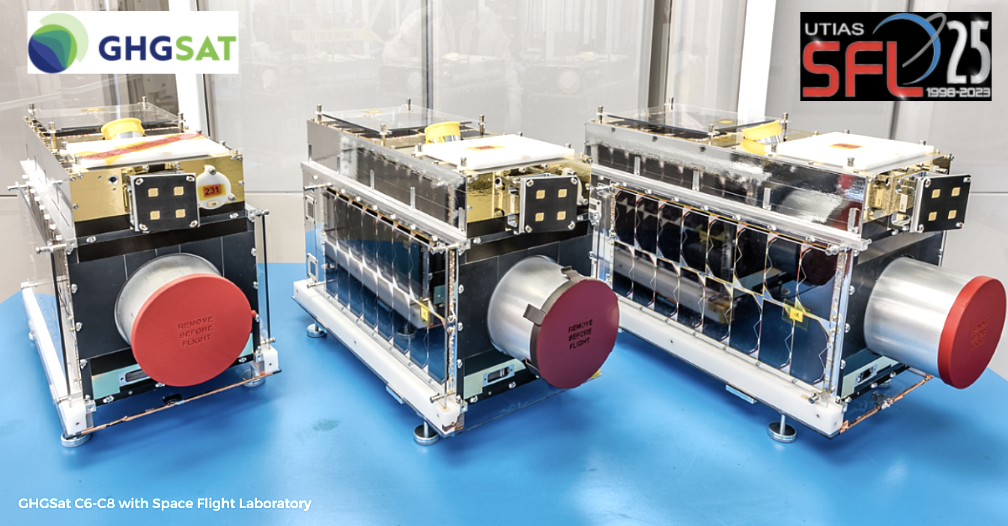
GHGSat will be launching six additional satellites in 2023 — the first three are GHGSat satellites, named Mey-Lin (C6), Gaspard (C7) and Océane (C8) and they will travel into orbit this spring onboard SpaceX’s Transporter-7 rideshare mission.
GHGSat’s satellite methane sensors have set the standard for performance with an industry-leading combination of low detection threshold and high resolution. The timely and frequent insight the monitoring constellation provides is used by industry, governments and financial services worldwide to proactively drive reductions in emissions.
The demand for data is increasing as awareness of the benefits of addressing methane emissions continues to grow, and nations turn their focus to meeting the commitments made as part of the Global Methane Pledge. With 12 spacecraft in orbit by the end of the year, GHGSat will be doubling its capacity to make more than 1.5 million facility measurements in 2023.
Named after the children of GHGSat team members, as per company tradition, Mey-Lin, Gaspard, and Océane completed testing in December and will travel to their launch site in California later this month. All three proprietary payloads feature the same proven, patented high-resolution interferometer currently on-orbit, tuned to precisely detect and measure the specific ‘signature’ of methane in the atmosphere.
GHGSat-C9, C10, and C11 are hosted payloads currently in the final stages of assembly and testing, and will soon be shipped for integration with third-party satellites, as announced on September 15 of last year. GHGSat-C10 is the world’s first commercial CO2 hosted payload, reaffirming GHGSat’s leadership position in the monitoring of greenhouse gases at industrial facilities from space.
An announcement regarding launch dates will follow in due course.
Stephane Germain, CEO at GHGSat, said, “Every year since our demonstrator satellite Claire was launched in 2016, we’ve pushed the boundaries of emissions monitoring from space. We are driven by our ambition to fight climate change by continuing our role as an independent purveyor of the best methane emissions insight in the world, and as a trusted partner to industry, government and financial services customers. The new satellites mean we can dramatically ramp up the number of locations and emissions we can monitor worldwide, including increasing daily monitoring over key oil and gas production sites.”











 on SpaceX Transporter-9 later this year. Along with launching in 2023, the new agreement adds two additional flights in 2024 and two flights scheduled for launch in 2025, each of which are on upcoming Transporter missions.
on SpaceX Transporter-9 later this year. Along with launching in 2023, the new agreement adds two additional flights in 2024 and two flights scheduled for launch in 2025, each of which are on upcoming Transporter missions.