Following the successful lift-off of the first launch of the SR75 rocket on May 3, 2024, HyImpulse has now firmly integrated the Southern Launch Australian launch site in Koonibba into the company’s global launch site strategy.

This MoU secures further launch opportunities in the southern hemisphere for HyImpulse’s commercial launch vehicle program. This marks a significant expansion of its launch capabilities in Australia.
This MoU with Southern Launch encompasses additional launches of the SR75 single-stage suborbital rocket at the Koonibba site and also includes the development of a new launch site in Whaler’s Way for the SL1 orbital rocket, currently under development. The SL 1 rocket, standing at 32 meters tall, is designed to reach an orbital altitude of 500 km in LEO and features a three-stage, bundled hybrid propulsion system using paraffin (candle wax) and liquid oxygen, capable of transporting payloads of up to 600 kg payload in its initial configuration.
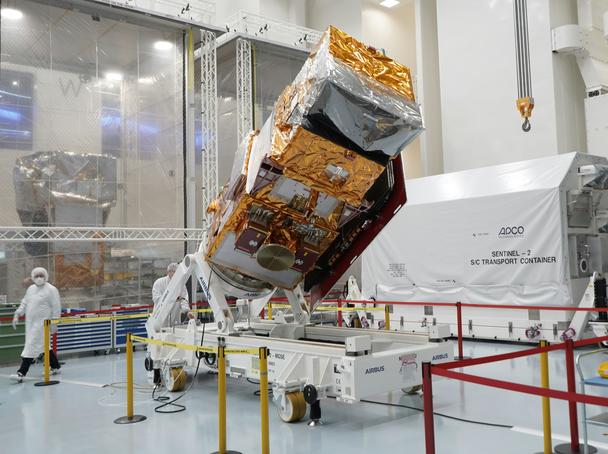
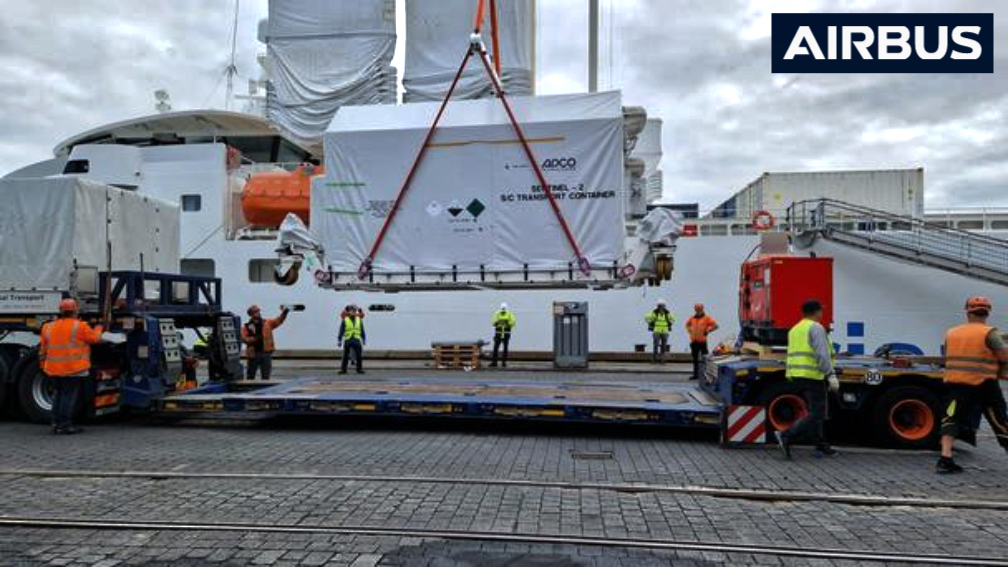
The SL1 is aimed at providing cost-effective transportation of small satellites into space, with its first launches scheduled for the end of 2025. The SL75 suborbital rocket, successfully launched from Koonibba on May 3rd is currently en route back to Germany by sea, having been recovered nearly intact. The rocket is expected to arrive at the HyImpulse laboratories in Neuenstadt am Kocher in Baden-Württemberg, Germany, by the end of August. Upon arrival, data will be extracted, and comprehensive analyses will be initiated to evaluate the inaugural test launch and advance the rocket and propulsion technology.
In addition to Koonibba, HyImpulse has also signed agreements with the Saxa Vord launch site in the UK and is collaborating with the French space agency CNES to access the small launcher site at the Guiana Space Centre in Kourou, French Guiana.
Dr. Christian Schmierer, Co-founder and Co-CEO of HyImpulse, said, “Sovereign access to space is crucial for the economies of Germany and Europe. This includes not only the development of reliable commercial launch vehicle systems, but also access to launch sites capable of reaching all relevant Earth orbits. Our partnership with Southern Launch secures further launch opportunities for both our suborbital and three-stage orbital rockets.”
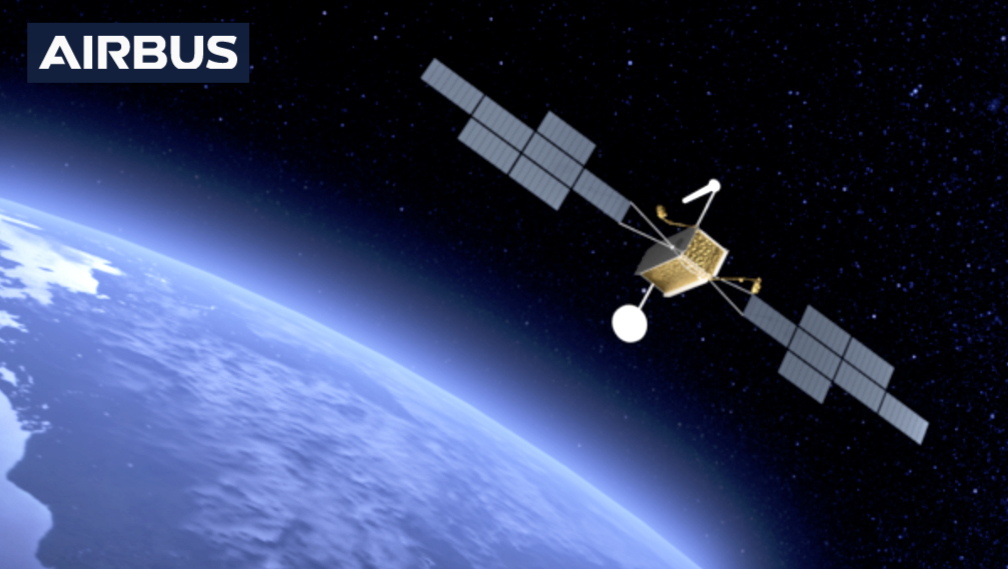
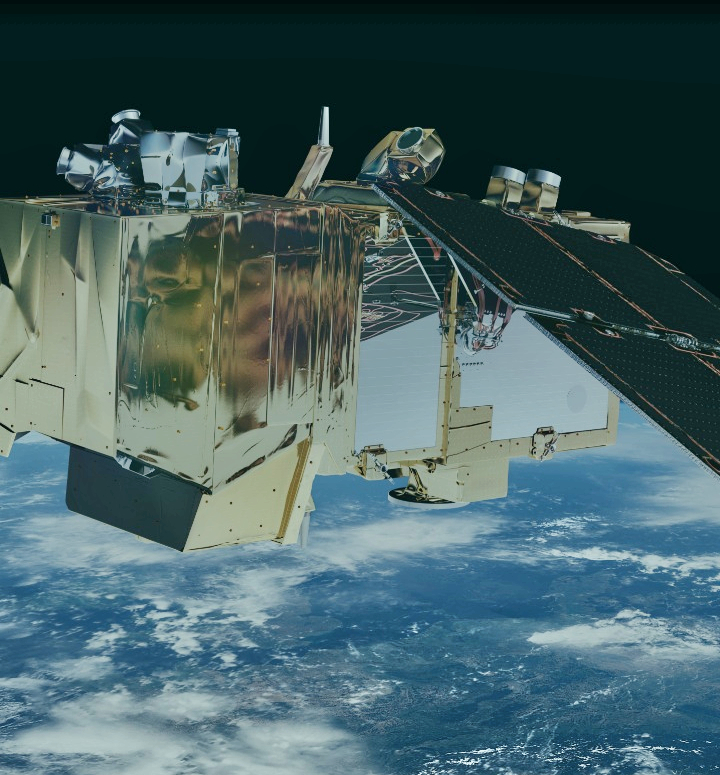
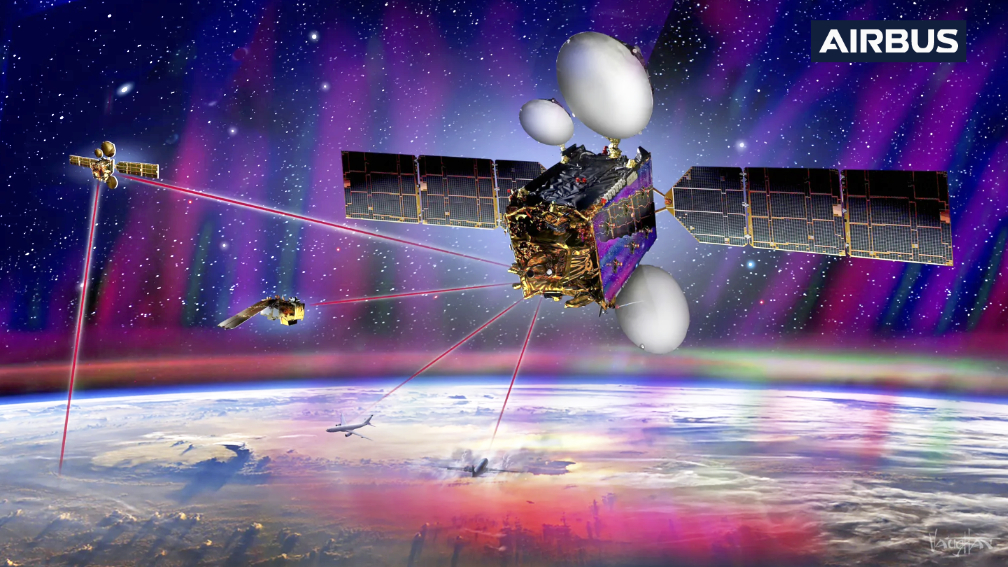








 (SDH) is a public-private partnership between ESA (European Space Agency) and Airbus. The SpaceDataHighway service uses the Airbus-owned and operated European Data Relay System (EDRS) laser communication infrastructure to provide this high bandwidth capability for both LEO satellites and airborne platforms.
(SDH) is a public-private partnership between ESA (European Space Agency) and Airbus. The SpaceDataHighway service uses the Airbus-owned and operated European Data Relay System (EDRS) laser communication infrastructure to provide this high bandwidth capability for both LEO satellites and airborne platforms.