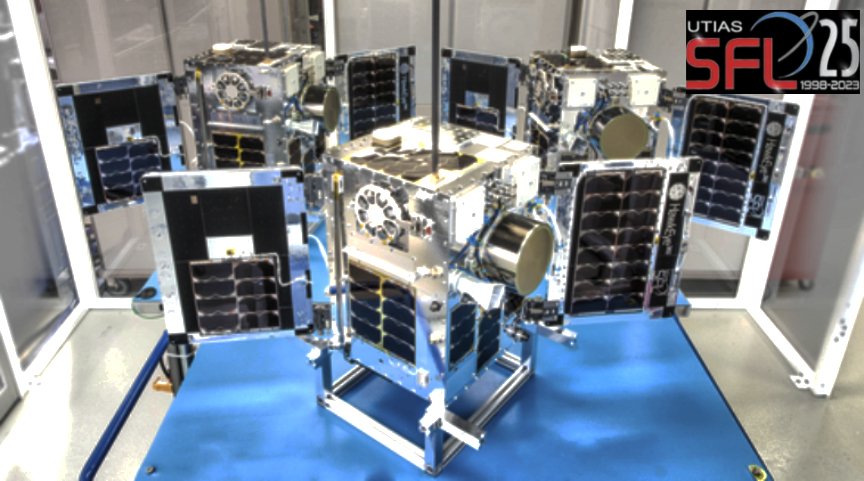
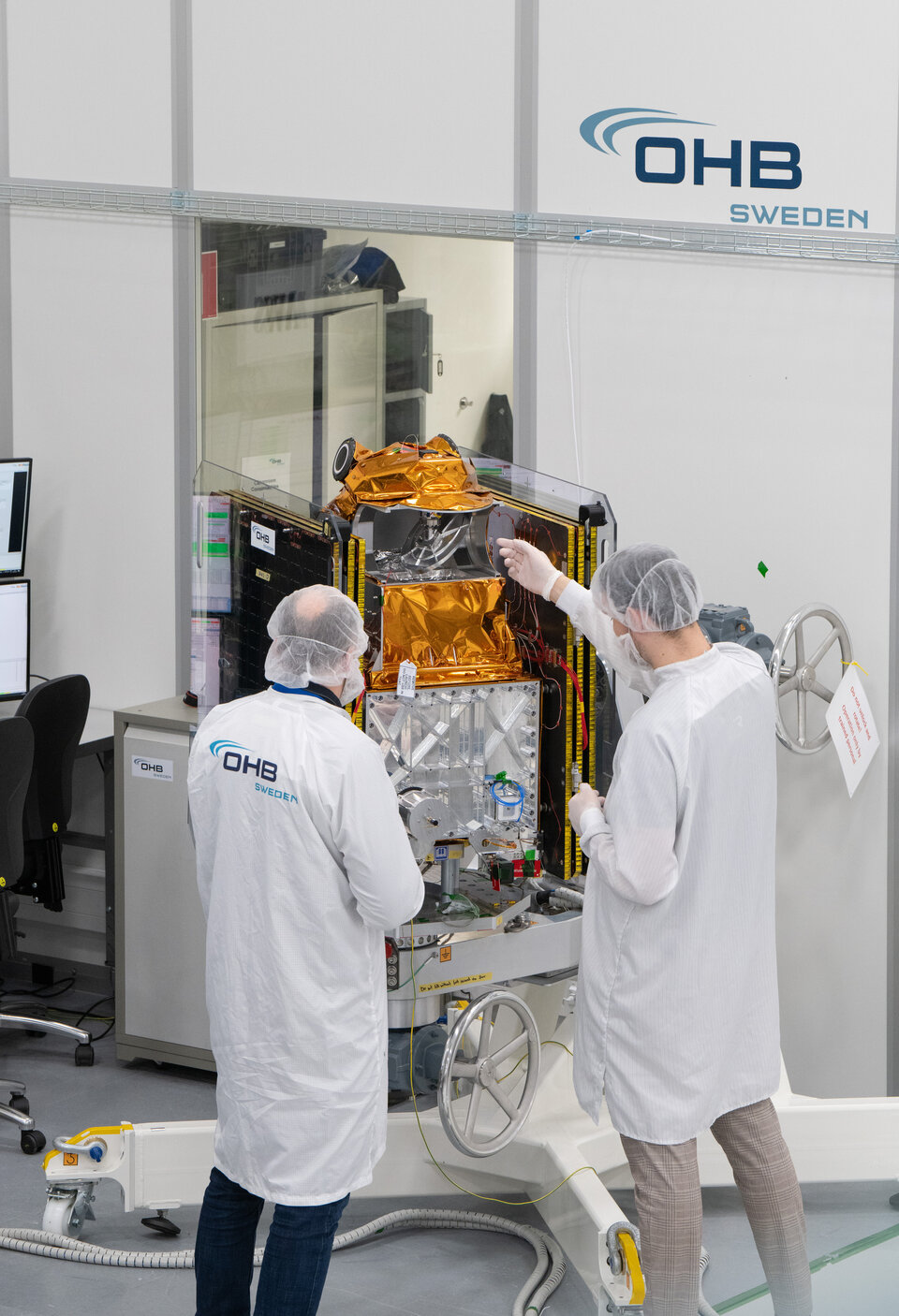
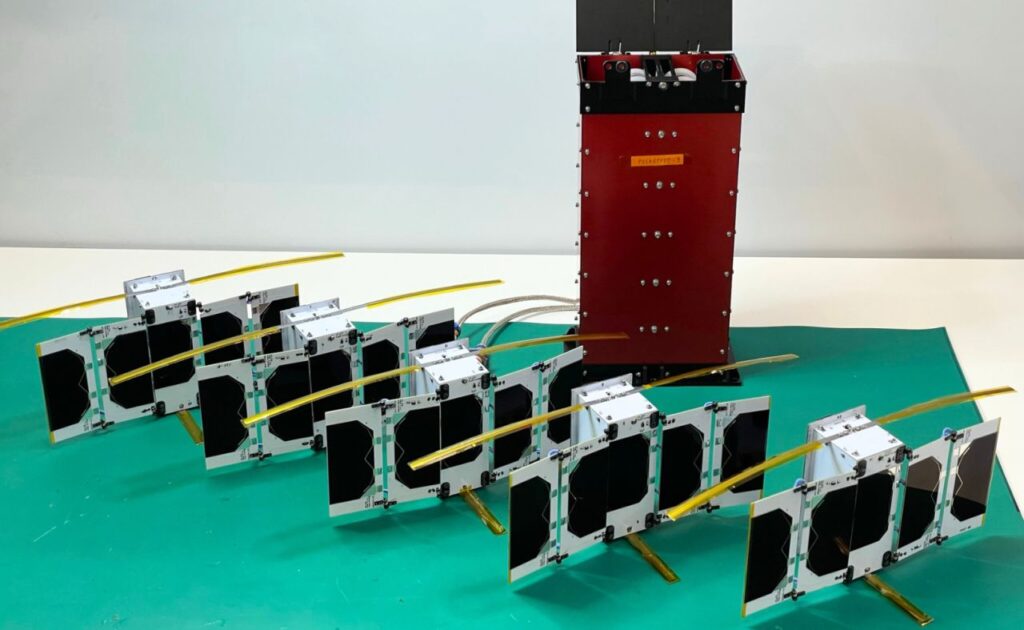
Space Flight Laboratory (SFL) has confirmed that six radio frequency geolocation smallsats developed for HawkEye 360 have successfully communicated with ground control — the HawkEye 360 Cluster 8 and 9 satellites were launched from Florida aboard the SpaceX Bandwagon-1 Rideshare mission.

The two new three-satellite clusters bring to 27 the total number of geolocation microsatellites developed by SFL for HawkEye 360, which integrated Cluster 8 at its own plant in Virginia under SFL’s Flex Production Program. For Cluster 9, which represents the next evolution and includes updated payload and platform features, SFL handled the entire process, including development, integration, and testing, at its Toronto facility.

HawkEye 360 selected SFL to develop its satellites due to the importance of attitude control and formation flying by multiple spacecraft for accurate RF signal geolocation. SFL has innovated compact, low-cost formation-flying technology at a maturity and price point that, according to the company, no other smallsat developer can credibly offer.

SFL built the HawkEye 360 Pathfinder satellites on its 15 kg NEMO platform. All subsequent clusters have been developed on the larger 30 kg SFL DEFIANT bus.
The HawkEye 360 constellation detects, characterizes and geolocates RF signals for a variety of communications, navigation, and security applications. Clusters 8 and 9 were launched in mid-inclination orbits to increase coverage over the busiest maritime traffic corridors at mid-latitudes, including the Indo-Pacific region, according to HawkEye 360.
Established in 1998, SFL has developed 76 operationally successful smaller satellite missions totaling more than 300 cumulative years in orbit. Another 20 missions are now under development by SFL, which offers a complete suite of nano-, micro- and small satellites – including high-performance, low-cost CubeSats – that satisfy the needs of a broad range of mission types from 3 to 500 kilograms. For a comprehensive list of SFL high-performance satellite platforms, please access this direct infolink…
“SFL is proud to play a key role in the development of HawkEye 360’s space assets as it continues to expand and enhance its unparalleled space-based RF data detection and analytics capabilities,” said SFL Director Dr. Robert E. Zee.
About Space Flight Laboratory (SFL)
SFL generates bigger returns from smaller, lower cost satellites. Small satellites built by SFL consistently push the performance envelope and disrupt the traditional cost paradigm. Satellites are built with advanced power systems, stringent attitude control and high-volume data capacity that are striking relative to the budget. SFL arranges launches globally and maintains a mission control center accessing ground stations worldwide. The pioneering and barrier-breaking work of SFL is a key enabler to tomorrow’s cost-aggressive satellites and constellations.