Axiom Space has revealed that the company will launch the first of two Orbital Data Center (ODC) nodes to LEO, by year’s end. These nodes will lay the foundation for space-based cloud computing, addressing growing needs for users around the world.
ODCs will provide secure, scalable, and cloud-enabled data storage and processing, and artificial intelligence/machine learning (AI/ML) solutions directly to satellites, constellations, and other spacecraft in Earth’s orbit, with the capability to operate independently of terrestrial infrastructure. This innovative approach reduces reliance on Earth-based systems and also enhances resiliency and security of emerging mesh networks in orbit but also enhances real-time operations of space assets by providing lower latency and higher availability cloud capabilities. Axiom Space’s ODCs will transform space operations, especially in the context of defense and security.
Use cases for ODCs include:
On-orbit and real-time processing, exploitation, and dissemination (PED) of data from multiple national security and commercial satellites
Lower-latency multi-sensor fusion for terrestrial or Space threat detection and tracking
AI/ML and Large Language Models (LLM) to enable real-time and autonomous or semi-autonomous decision making for satellites and other space assets
Earth-independent endpoint detection and response (EDR) capabilities to enhance the cyber security of the thousands of national security, commercial, and civil space assets
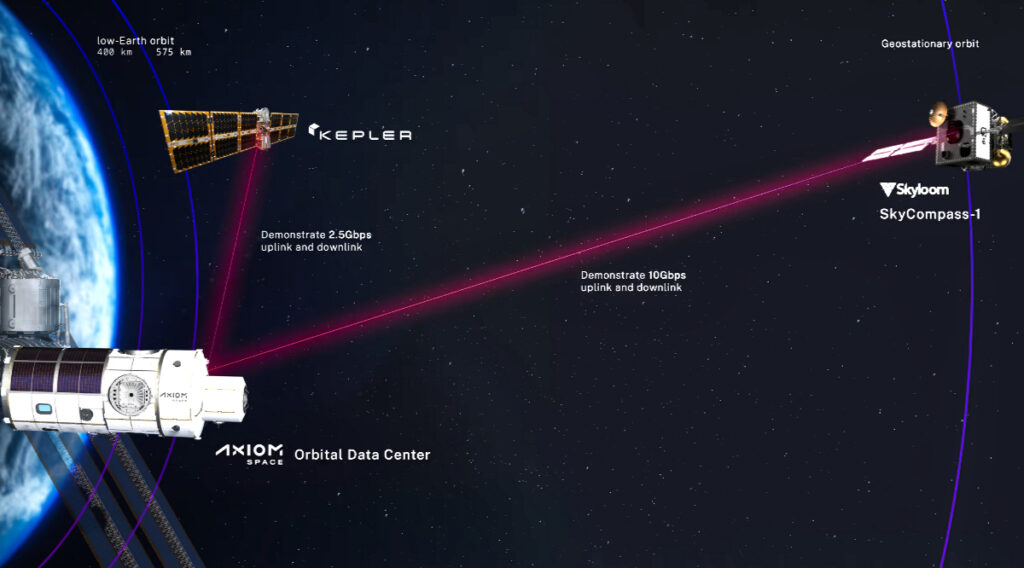
ODC Nodes 1 and 2 will be part of the Kepler Communications optical relay network constellation scheduled to launch by the end of the year. Axiom Space and Kepler Communications have been collaborating since 2023 on the integration of Optical Intersatellite Links (OISLs) with Axiom Space’s ODCs to enable high-speed data connections directly between ODCs and commercial and government spacecraft and networks on-orbit.

These ODC Nodes will feature high-speed, 2.5 Gbps-capable optical links to other Kepler Communications optical relay assets in LEO or other satellites, constellations and spacecraft that are compatible with the Space Development Agency’s (SDA) Tranche 1 optical communications standards. Data transfer will also be possible between the ground and the ODC nodes via optical or radio frequency links. SDA-compatible optical communications terminals will make these initial ODC nodes, and future nodes, interoperable with national security, other government, and commercial satellite networks.
Axiom Space will have options to purchase additional payloads on Kepler’s constellation to increase ODC capacity. The two companies will jointly collaborate on extending network and ODC services to national security, civil, commercial, and international customers.
As the rapid development of digital technology, driven by the proliferation and adoption of AI/ML, continues to transform industries, the limitations of terrestrial data centers — such as energy consumption, cooling, real estate, regulatory licensing and permitting, and exposure to human or natural disruptions — are becoming increasingly apparent, globally. Axiom Space is at the forefront of mitigating these challenges by developing a modular and scalable network of ODC nodes that will offer enhanced global digital sovereignty, security, and resilience to customer data and AI/ML needs, doing so by leveraging the abundant energy and domain of space.
Looking ahead, Axiom Space is committed to expanding its Docs network in the years to come, significantly increasing capacity and capability from kilowatts to megawatts of processing power on-orbit to provide customers with a viable alternative to resource-intensive terrestrial data centers.
We have been developing ODC capabilities since 2022with the launch of an AWS Snowcone to the International Space Station (ISS), followed by an array of demonstrations in Earth-independent cloud solutions from the station,” said Jason Aspiotis, global director of in-space data and security, Axiom Space. “In 2023, we announced our initial plans for an ODC Tranche 1 on Axiom Station, and in March, we shared news of the launch of a prototype data processing unit – AxDCU-1 – with Red Hat to the ISS this spring. ODC Nodes 1 and 2 are an acceleration of our plans to deploy a multitude of free-flyer ODC nodes in LEO to meet the rapidly emerging demand from users around the world, especially for defense applications where real-time, and cyber and quantum-secure data processing, AI/ML, and autonomous decision-making solutions are critically needed.”
Aspiotis continued, “Free-space optical communications have come a long way in the past few years, with significant investments by commercial entities, the Department of Defense, and NASA in advancing OISL capabilities. We plan to integrate emerging 10Gbps+ OISL and space-to-ground optical communications capabilities into our future ODC nodes, as they become available to facilitate connections to more satellites, more constellations, more ground sites, and ultimately Tbps-worth of data flow in the foreseeable future.”
Kam Ghaffarian, CEO, Executive Chairman, and Co-founder of Axiom Space, said, “Our ODC nodes will soon be open for business. We have agreements in place with users around the world to deploy initial, space-based cloud services, not just demonstrations of capabilities. We are also closely monitoring national security needs, especially the U.S. Golden Dome initiative, and how our evolving ODC infrastructure can support U.S. and allied capabilities in space-based data storage, processing, cybersecurity, and AI/ML. ODCs are integral to Axiom Space’s vision of era-defining space infrastructure, unlocking transformational capabilities and economic growth.”
About Axiom Space
Axiom Space is building the world’s first commercial space station – Axiom Station. Serving as a cornerstone for sustained human presence in space, this next-generation orbital platform fosters groundbreaking innovation and research in microgravity, and cultivates the vibrant, global space economy of tomorrow. Today, driven by the vision of leading humanity’s journey off planet, Axiom Space is the principal provider of commercial human spaceflight services to the International Space Station and developer of advanced spacesuits for the Moon and low-Earth orbit. Axiom Space is building era-defining space infrastructure that will empower our civilization to transcend Earth for the benefit of every human, everywhere.




 . The IQSat is AI-enabled and includes Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI) ML) from Intuidex, Inc. incorporated in Intuidex’s Watchman for Space
. The IQSat is AI-enabled and includes Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI) ML) from Intuidex, Inc. incorporated in Intuidex’s Watchman for Space











 ) with SatixFy’s space grade chips and communications systems
) with SatixFy’s space grade chips and communications systems