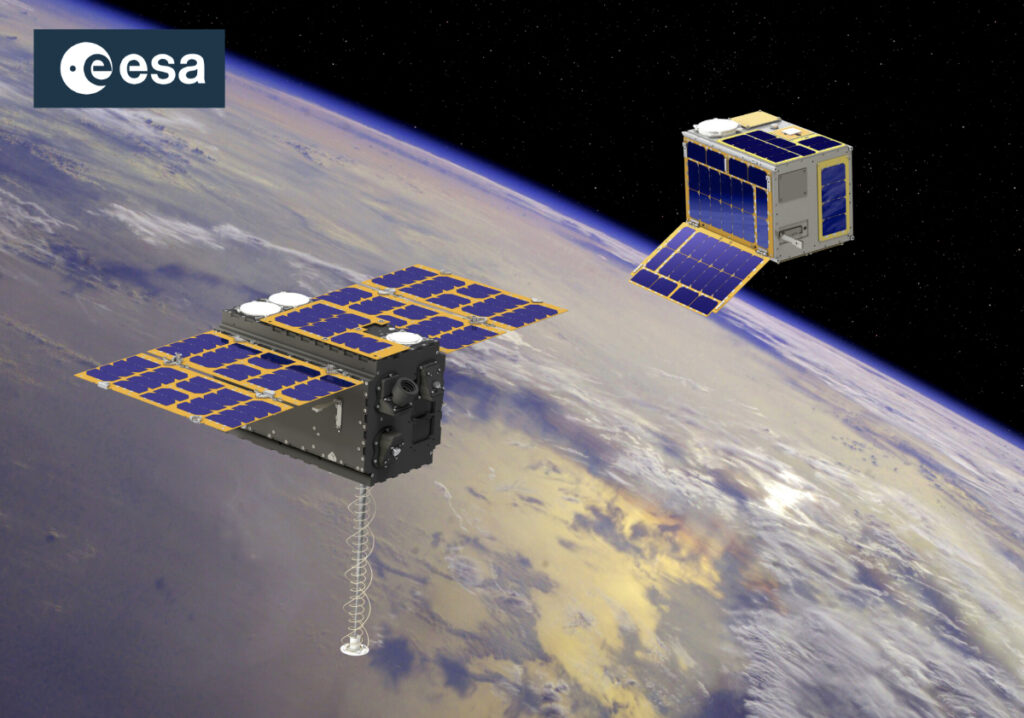
Xona Space Systems has launched Pulsar-0, the first production-class satellite in the company’s LEO constellation that will bring accuracy and affordable resiliency to industries across defense, construction, agriculture, mining, critical infrastructure, logistics, and automotive environs. The company believes introducing this technology will unlock an entirely new category of innovation by providing a new way to localize hardware in this physical world.
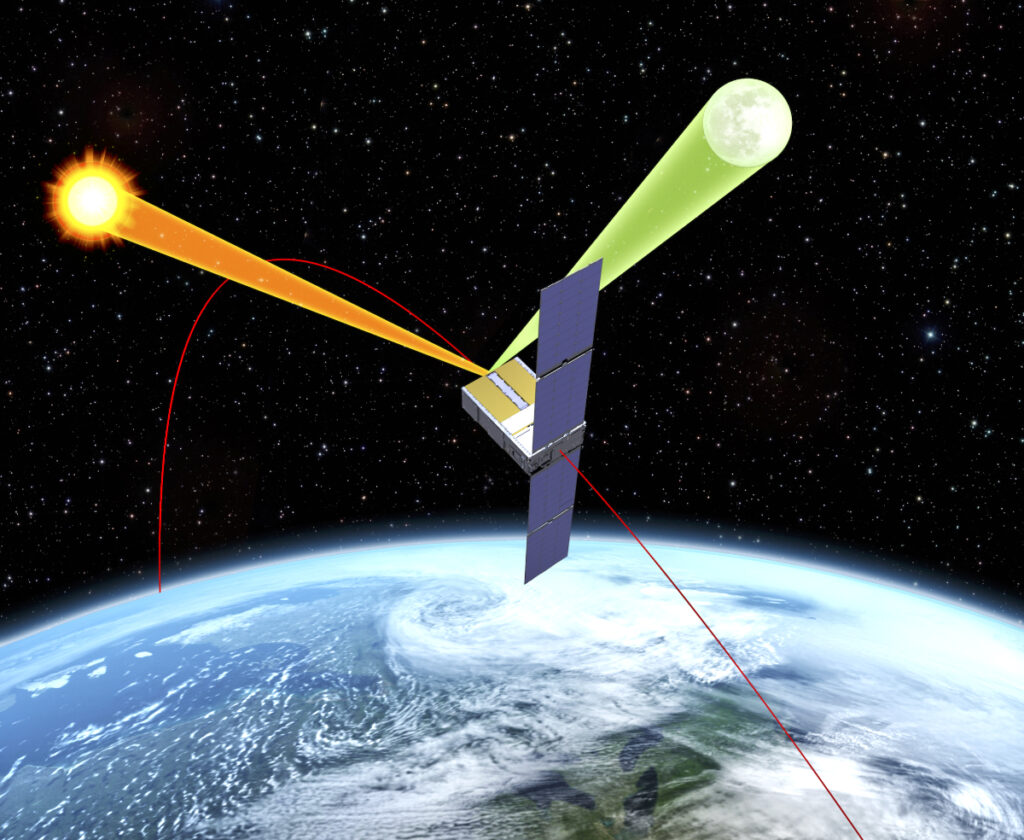
Critical infrastructure, civil aviation, and financial systems rely on positioning, navigation, and timing (PNT) services from aging government satellites to function. But they are vulnerable and easy to manipulate. The need for resiliency in this infrastructure is urgent, and Pulsar will be a key part in closing this gap. We’ve heard from leaders across private and public sectors alike that there is no time to waste.
Pulsar-0 entered orbit aboard the SpaceX Transporter-14 mission and will begin broadcasting signals to Earth after the smallsat completes spacecraft commissioning. The primary mission is to validate Xona’s technology and unlock live sky testing with the firm’s early customers, charting the path for more frequent launches as the constellation gows and starts commercial operations.
Building hardware is difficult. Building hardware for space is even harder. Along the way, difficult decisions had to be made to preserve momentum in the face of supply chain volatility. One of those decisions was to proceed with launching Pulsar-0 without a propulsion system onboard, a tradeoff that reduces the mission capability and lifetime from our initial plans but has enabled the company to remain on track for launch and to initiate testing quickly. In a world where resilient PNT is needed now more than ever, launching sooner means real-world implementation can start sooner.
Over the coming months, Pulsar-0 will demonstrate:
- Precise location: Making progress towards delivering on our partnership with Trimble, Pulsar-0 will broadcast real-time precision location with accuracy greater than 10cm. By broadcasting GNSS corrections from low Earth orbit, Pulsar can provide improved positioning before our full constellation is operational while users benefit from stronger signals that reach more places.
- Range authentication: Legacy GPS signals are open and unencrypted, opening the door for malicious actors to generate counterfeit signals that are perceived as real. Pulsar will show a new way to verify the authenticity of our signal in action, providing protection against spoofing attacks.
- Jamming resistance: Today, contested environments are frequently jammed, blocking legacy GPS signals which disrupts civilian life and military operations. With a received signal strength 100 times stronger than that of legacy GPS, Pulsar will outperform in denied domains where jammers and other interference might be present.
- Signal penetration: Environments occluded from open sky have long been a challenge for legacy GPS to reach. We expect to show Pulsar excelling in these environments, bringing reliable connection to traditionally denied spaces inside reinforced buildings, urban canyons, and more.
Pulsar-0 is a milestone for Xona Space Systems and the company will now be focusing on building the capacity to launch more satellites faster and to grow the constellation to achieve persistent and redundant coverage everywhere on Earth.