Based on the weather forecast this week, Rocket Lab has set a new no earlier than launch date for the upcoming mission from Rocket Lab Launch Complex 2 in Virginia for Capella Space. Here are the details.
Stronger Together
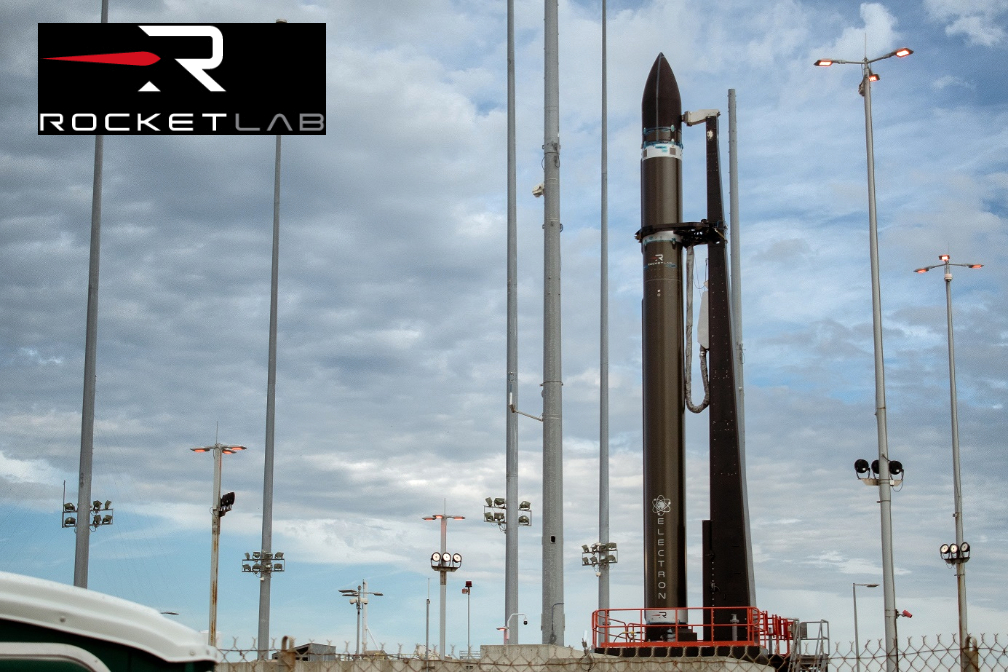
- Launch date: Wednesday March 15
- Launch timing: 6:00-8:00 p.m. Eastern, with lift-off targeted for 6:00 p.m.
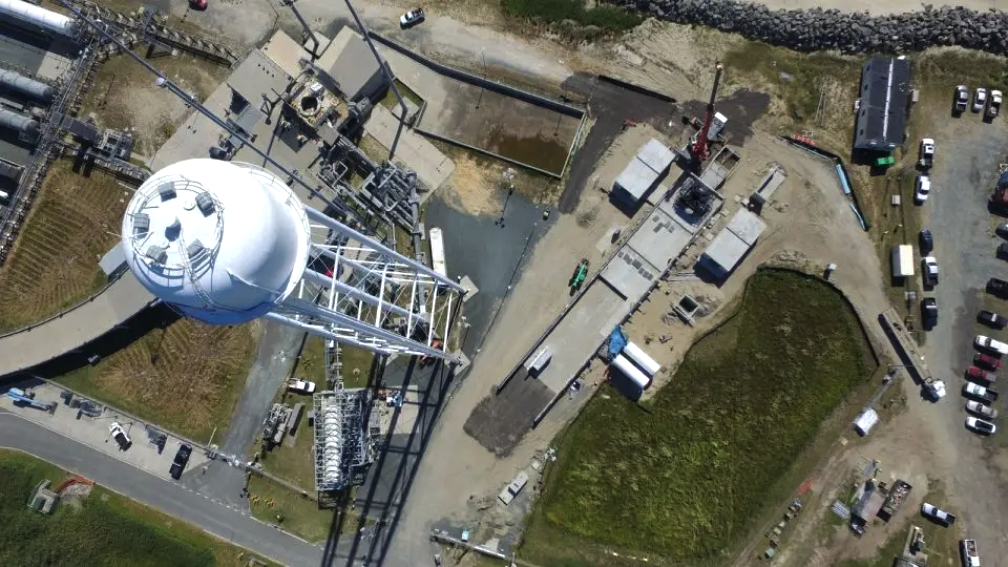
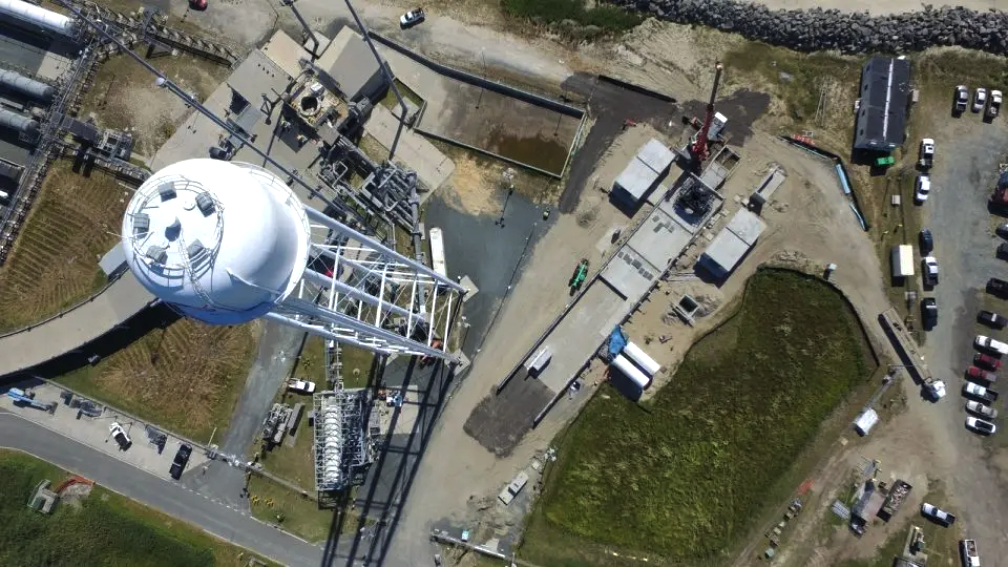
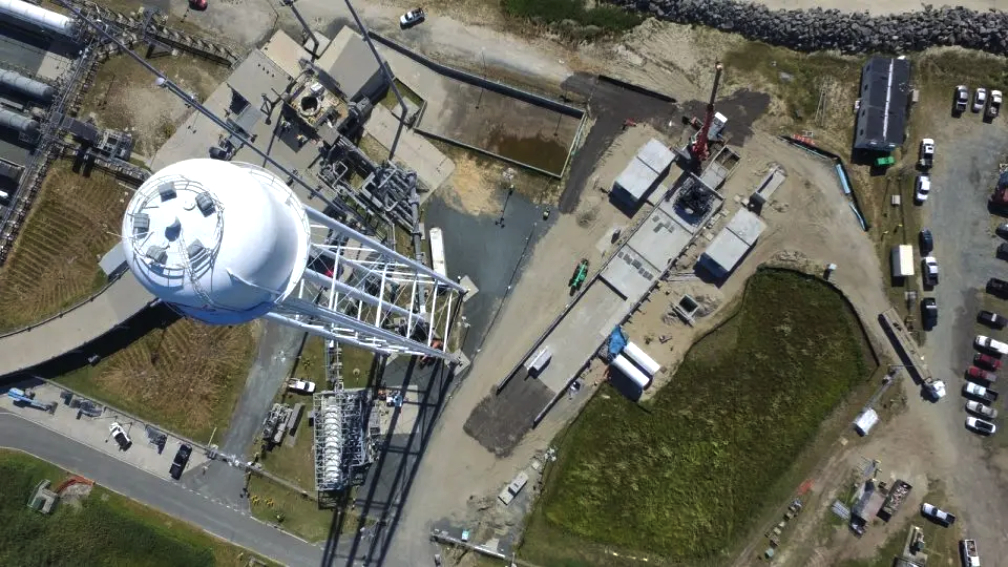
Launch location: Rocket Lab Launch Complex 2, Wallops Island, Virginia.
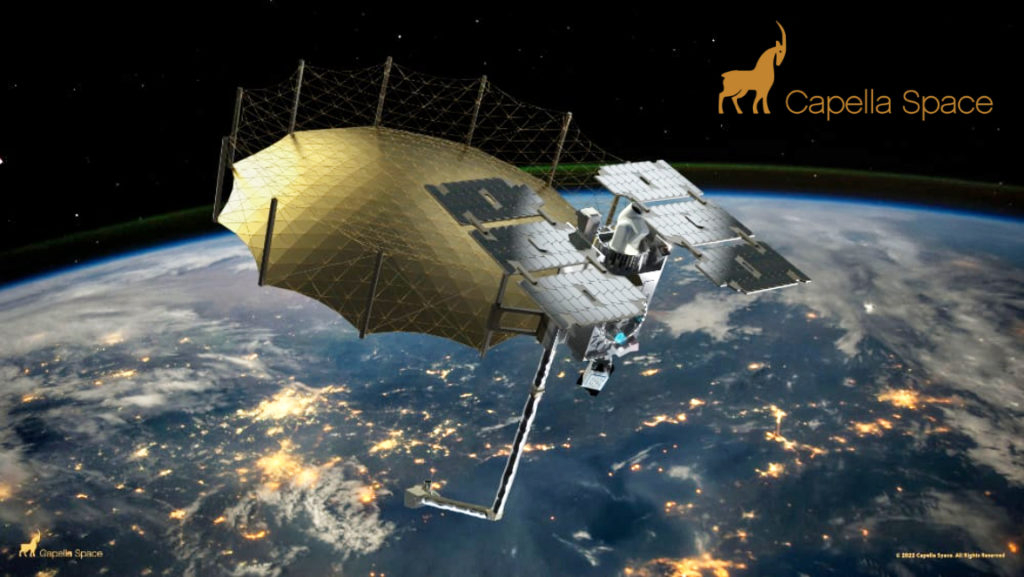
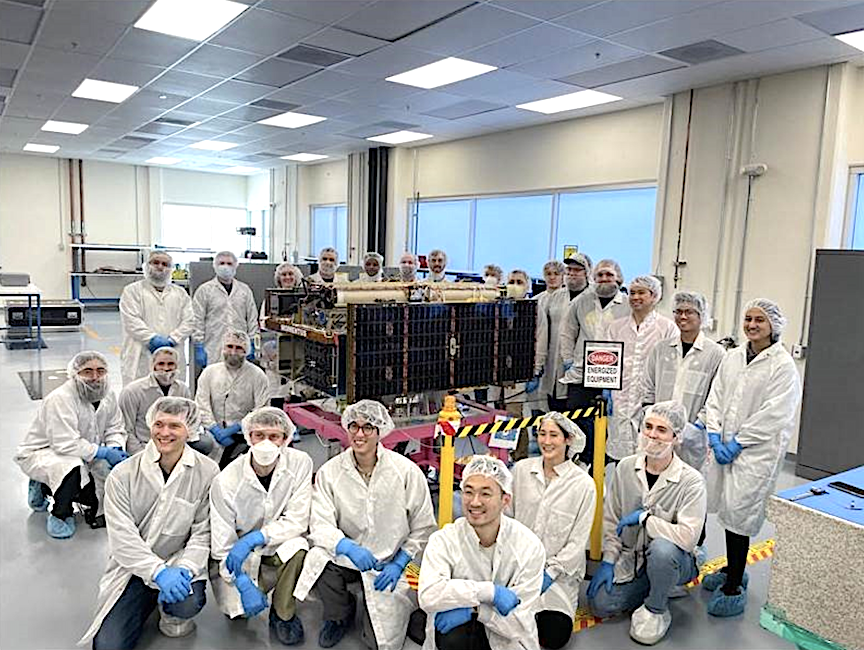
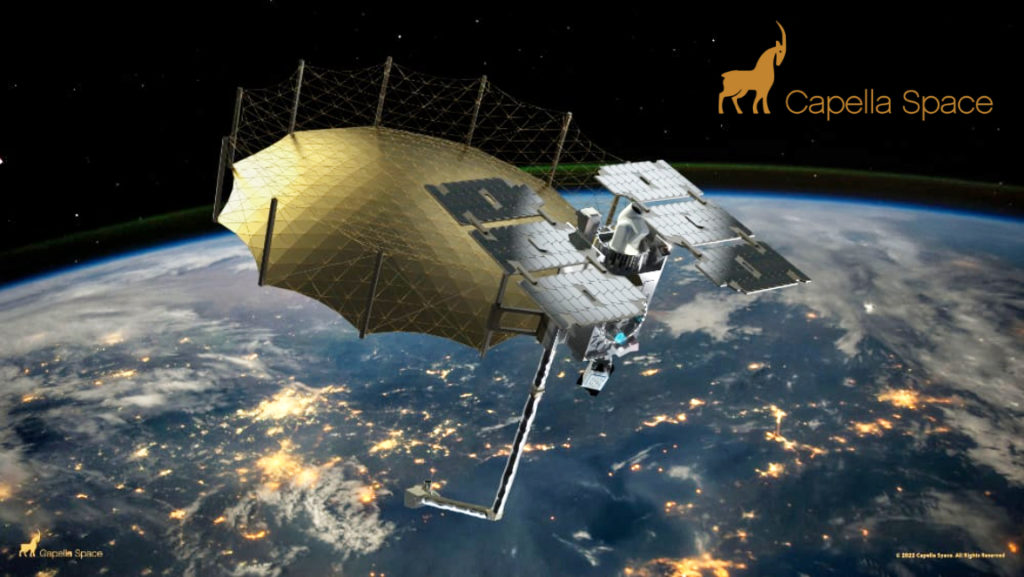
The mission will be Rocket Lab’s second Electron launch from Launch Complex 2 on Wallops Island, Virginia. Stronger Together will carry two 100-kg class satellites for Capella Space, a leading provider of commercial Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) imagery.
Previous update posting…
Unfavorable weather conditions required Rocket Lab to cancel the March 11th launch of the Capella Space SAR smallsats… a new launch date will be announced shortly and the company has an open window for such activity throughout this coming week.
Original information posting…
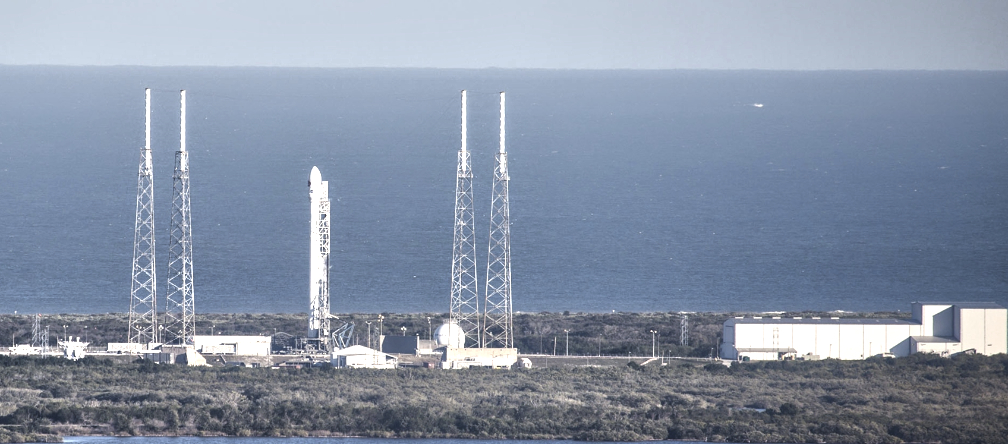
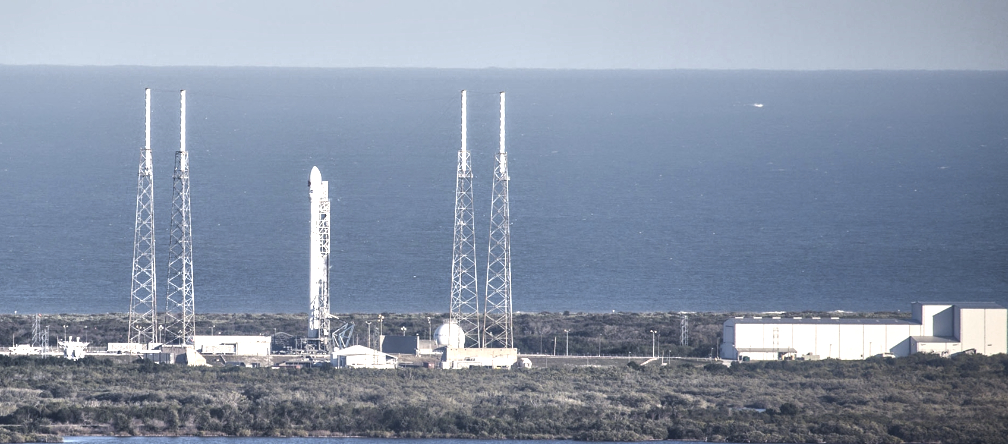
Rocket Lab USA, Inc. (Nasdaq: RKLB) has scheduled their next Electron launch from Virginia during a launch window that opens on March 11, 2023, ET.
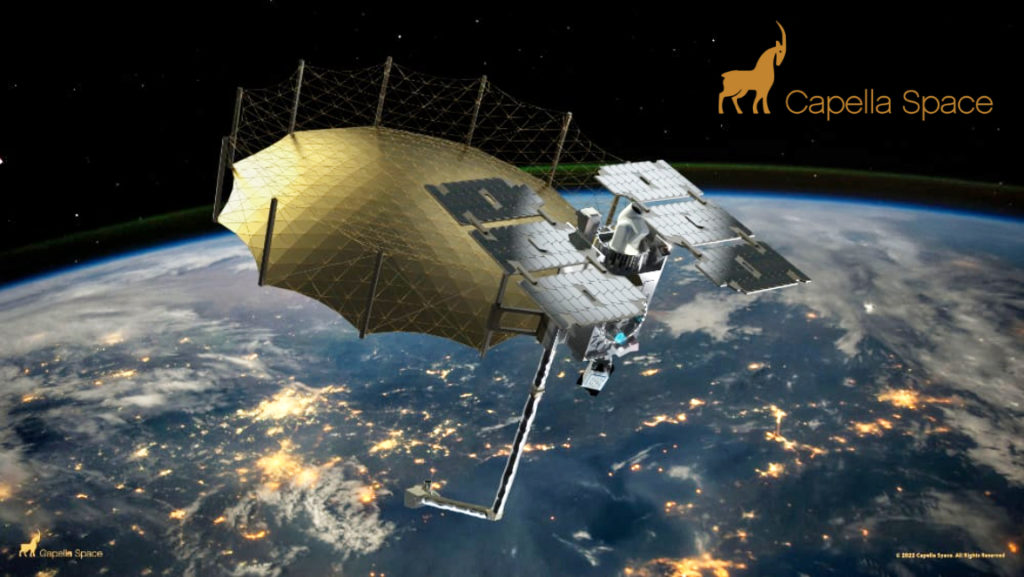

The “Stronger Together” mission is scheduled to launch from Rocket Lab Launch Complex 2 (LC-2) on Wallops Island, Virginia, for Capella Space, a provider of commercial Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) imagery. The mission will be Rocket Lab’s second launch from the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport at NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility following on the Company’s successful inaugural mission from LC-2 on January 24, 2023.

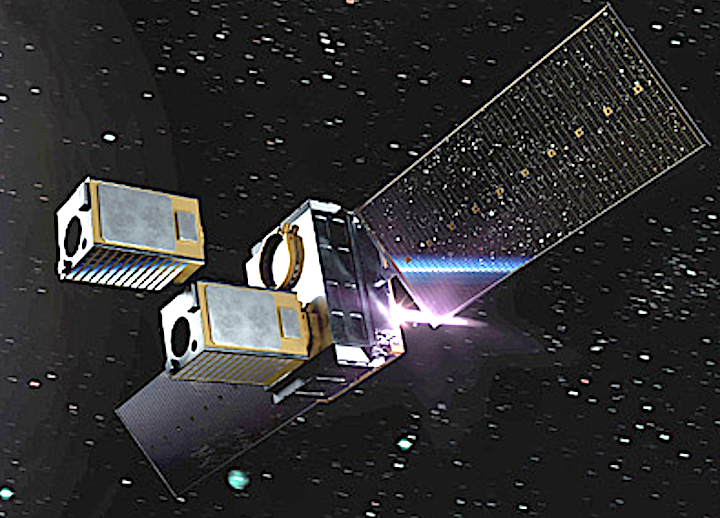
“Stronger Together” will deploy two,100 kg class satellites to LEO and expand the existing Capella Space SAR constellation, increasing imaging capacity to meet growing customer demand. Capella Space SAR satellites are able to gather images of Earth any time of the day, in any weather as well as penetrate conditions that include clouds, fog, smog, darkness and smoke.
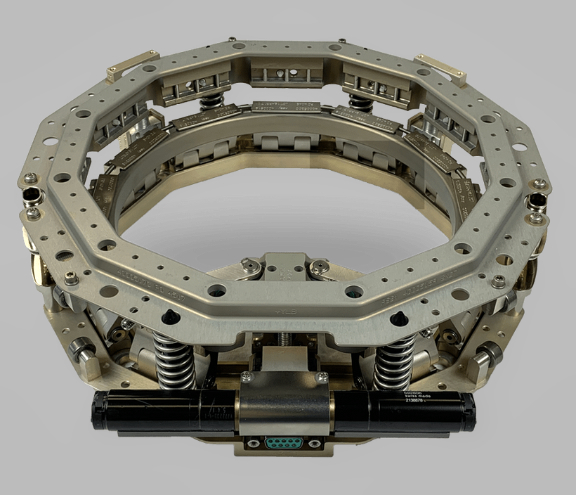
Supporting Rocket Lab’s vertical integration strategy, Rocket Lab will also supply Capella Space with two of the Company’s own Motorized Lightbands; separation systems designed to separate the Capella satellites from Electron once in orbit. Rocket Lab has launched for Capella previously with the “I Can’t Believe It’s Not Optical” mission in August of 2020, when Electron successfully deployed to orbit Capella’s first satellite in that firm’s SAR constellation.
This upcoming launch is one of five missions for Capella Space scheduled to start launching on Electron this year, following the recently-announced multi-launch deal securing four rapid succession launches for Capella from Rocket Lab Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. However, there is the option for Capella to move any of these missions to Launch Complex 2 should that be needed to meet Capella’s requirements – the type of responsive and flexible launch solution that Rocket Lab can provide by operating three orbital launch pads across two continents.
Members of the public wanting to watch Electron’s upcoming launch from Virginia can visit nearby viewing locations in Accomack County, Virginia, such as Robert Reed Park and Curtis Merrit Harbor on Chincoteague Island. The Virginia, Maryland and Delaware Atlantic beaches also provide good viewing locations.
A live launch webcast will also be available at this direct link from around T-20 minutes.