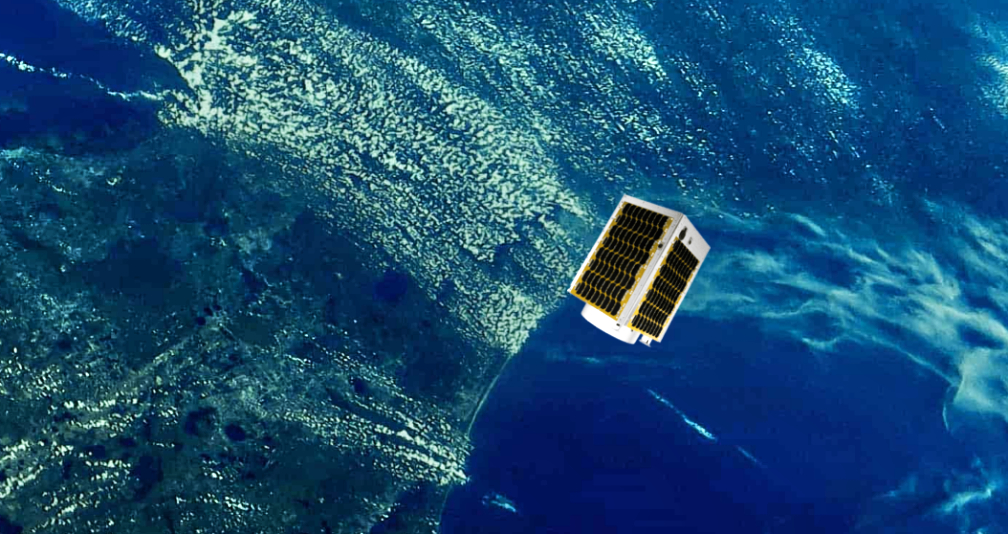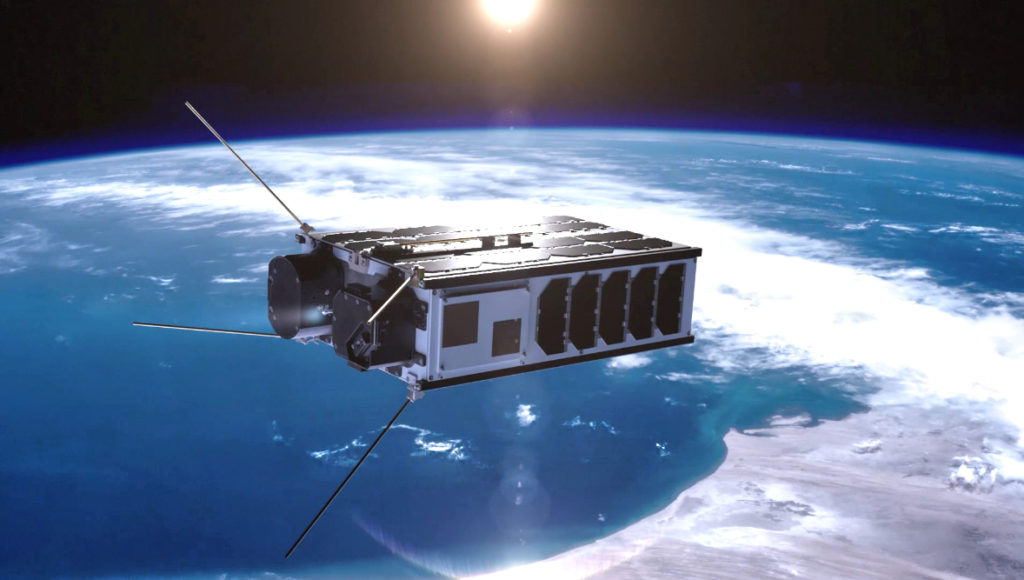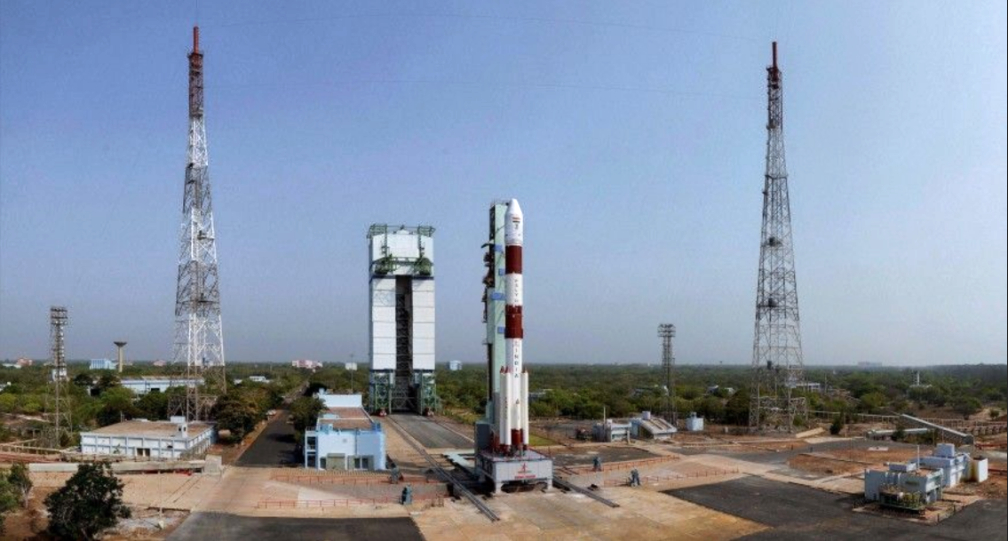
Exolaunch is arranging the launch and providing technical mission management for four of Spire Global’s Lemur-class 3U cubesats aboard a Soyuz rocket mission scheduled for September 28.
Spire Global operates the world’s largest commercial constellation of smallsats making radio occultation measurements, alongside other Earth Observations (EO) that serve the maritime, weather and aviation industries.
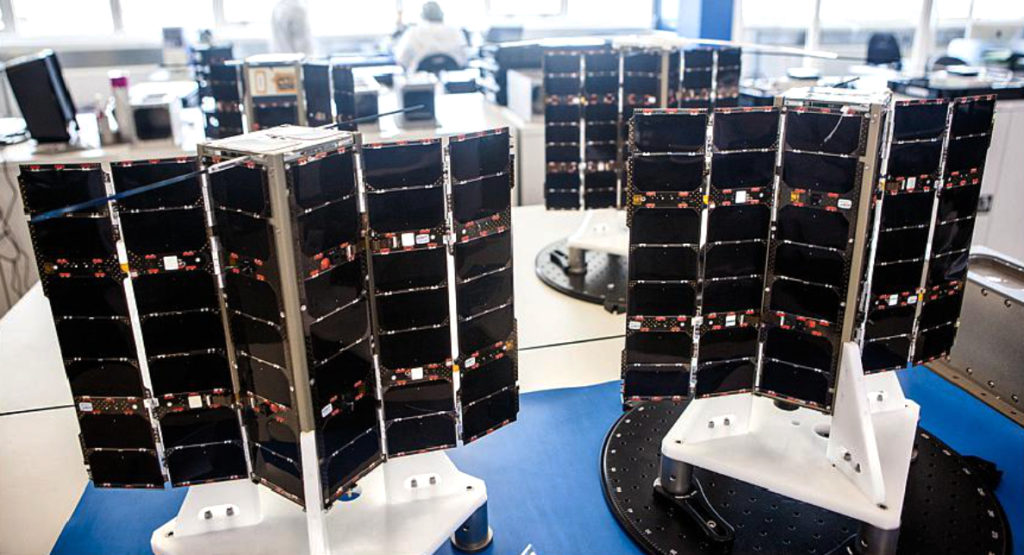

To date, Spire has launched more than 100 satellites that operate across a broad range of orbits. Exolaunch has helped deploy approximately one-third of Spire’s satellite constellation since 2016 when the launch service partnership started between the companies. The ongoing cooperation between Exolaunch and Spire has become a cornerstone for pioneering the latest advancements in small satellite launch systems and services.
As it has done on previous rideshares, Exolaunch will arrange launch services and mission technical support for Spire using its advanced cubesat deployment system, the 12U EXOpod. It will also utilize the EXObox deployment sequencer to control the safe and precise separation of Spire’s satellites.
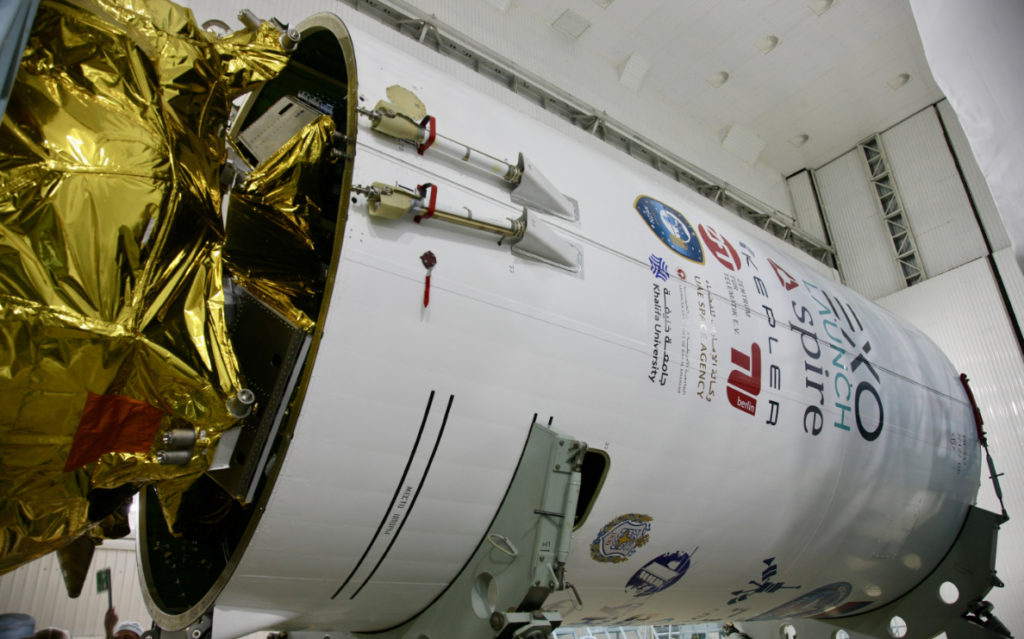

The Spire satellite launch is part of a September Soyuz rideshare mission that is manifested by Exolaunch to realize the launch plans of its international small satellite customers. The mission is named Wanderlust, Desire to Travel, which symbolizes both the ever-increasing importance of sustainable access to space for smallsats and longing for travel that was recently restricted.
Executive Comments

“Our long-time partnership with Spire has been extraordinarily valuable not only in driving Exolaunch to continually refine its solutions, but also in helping to propel the smallsat and space industry to new heights,” said Jeanne Medvedeva, Exolaunch VP of Launch Services. “We look forward to supporting Spire on this latest rideshare launch and stand ready to facilitate the ongoing expansion of their satellite constellation.”

“The experience and comfort we have working with the Exolaunch team has enabled Spire to continue with this launch campaign despite the challenges of a global pandemic. The combination of Exolaunch’s trusted deployment hardware, launch expertise, and customer focus has made them one of our more trusted launch partners,” said Robert Sproles, Senior Director, Constellation Planning and Operations at Spire. “Exolaunch has been instrumental in enabling Spire to set the industry-standard in the commercial aerospace sector as we work with our customers to tackle ever more frequent and extreme weather events in this era of Climate Change.”
Exolaunch has excellent heritage flying international customers on Soyuz, having launched more than 85 smallsats on Soyuz missions to date. This mission marks Exolaunch’s 7th with Soyuz. On this mission, Exolaunch will deploy a cluster of 15 smallsats into a sun-synchronous orbit for its customers Kepler Communications, the UAE Space Agency, the Würzburg Center for Telematics, the Technische Universität Berlin and several European commercial companies. The company is set to provide its market-leading separation systems – EXOpod for cubesats and CarboNIX for microsats – as well as its EXObox sequencers, to ensure timely deployment of smallsats into their target orbit.

 OneWeb wants 3 less rocket launches. Each will carry 34 to 36 OneWeb satellites and the full OneWeb constellation should be in orbit by the end of 2022.
OneWeb wants 3 less rocket launches. Each will carry 34 to 36 OneWeb satellites and the full OneWeb constellation should be in orbit by the end of 2022.
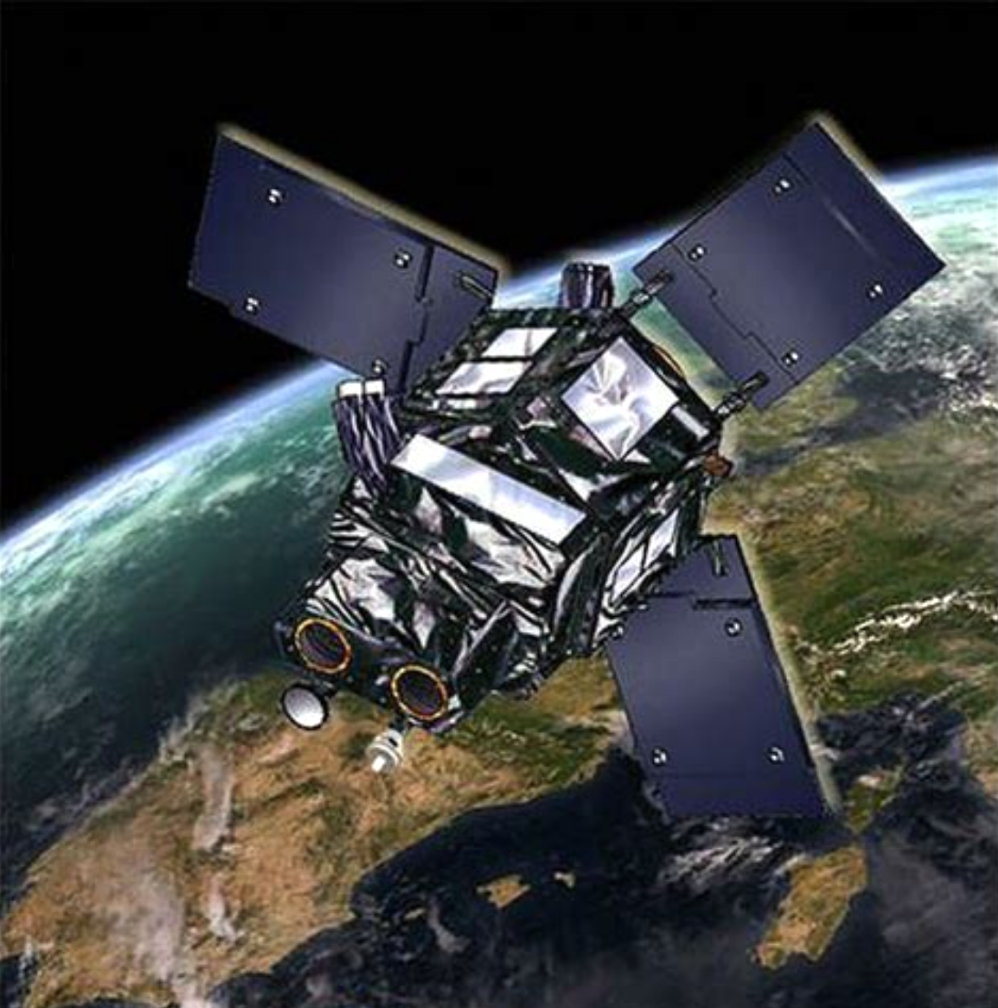
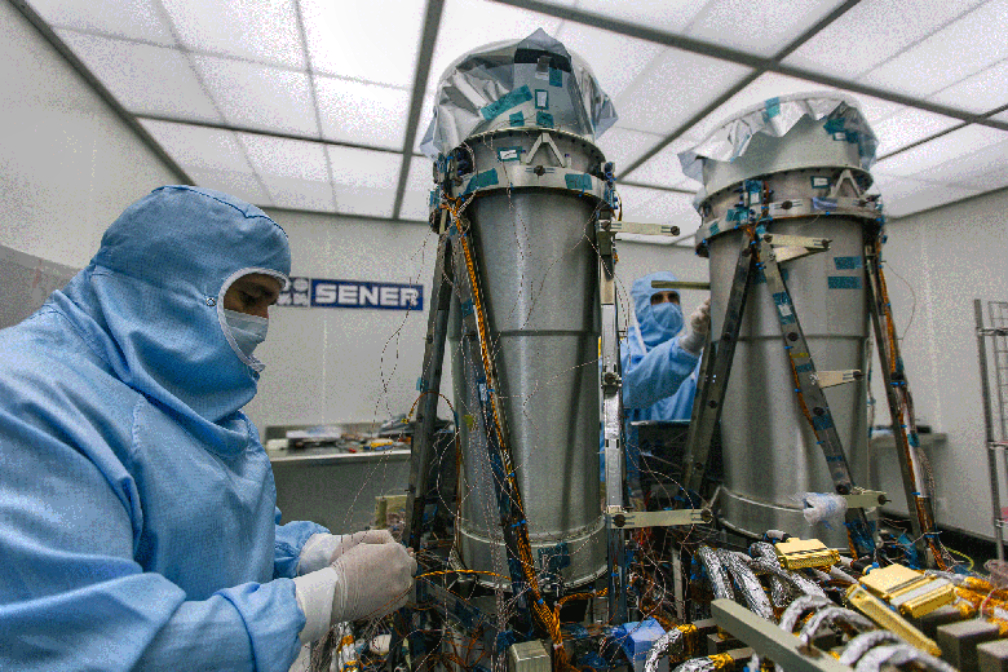
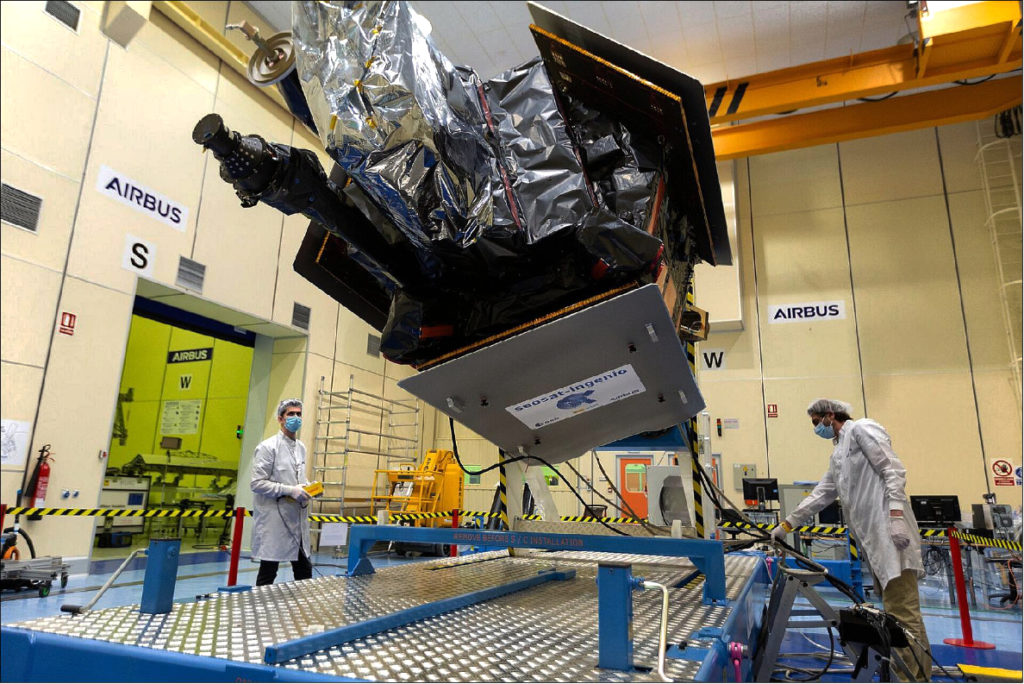
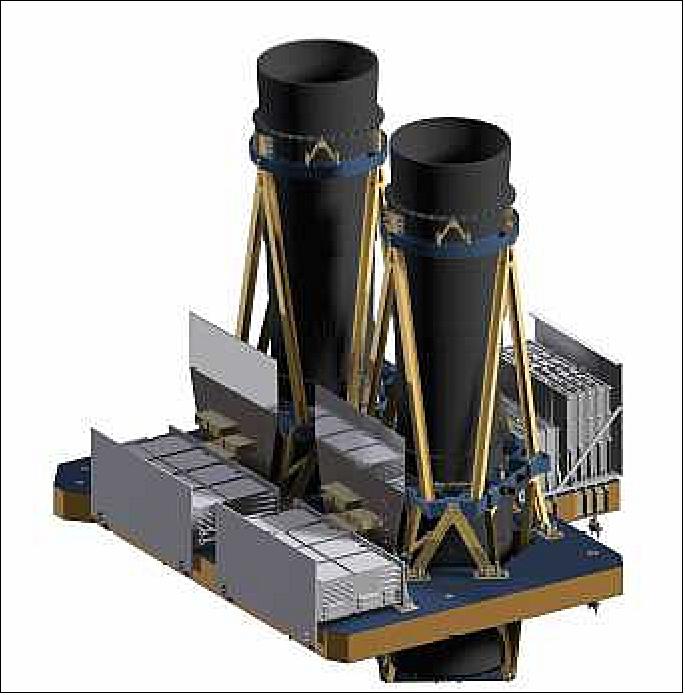
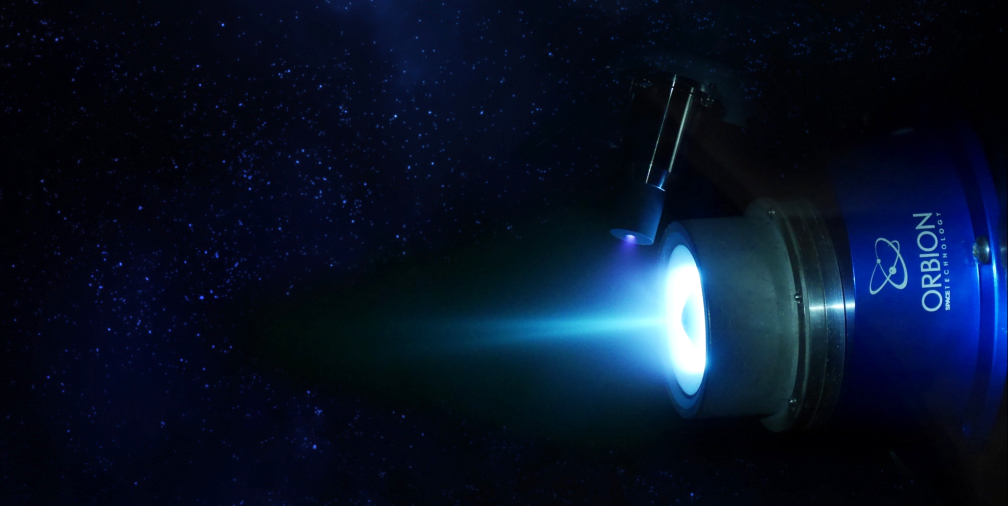
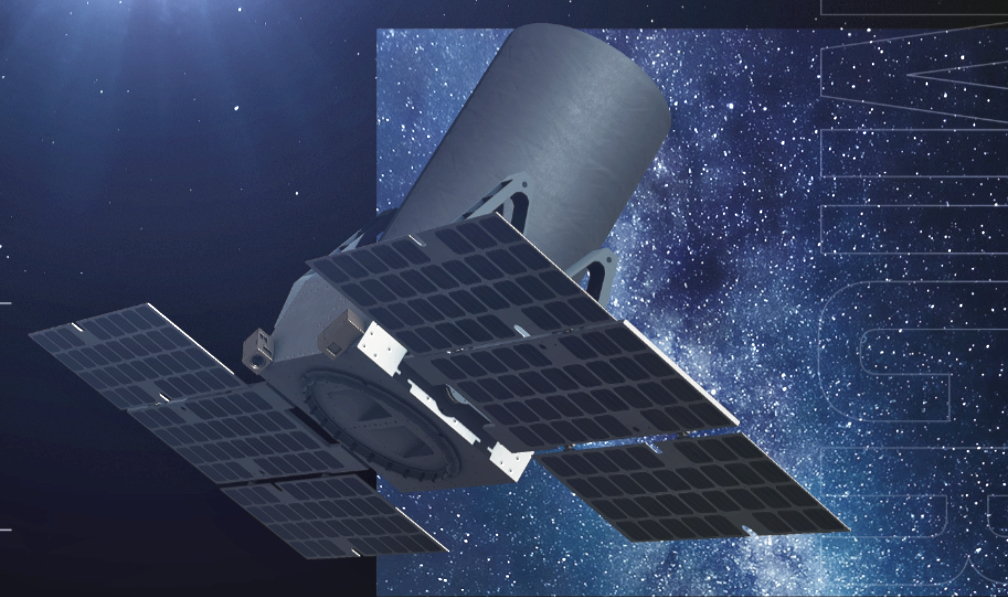





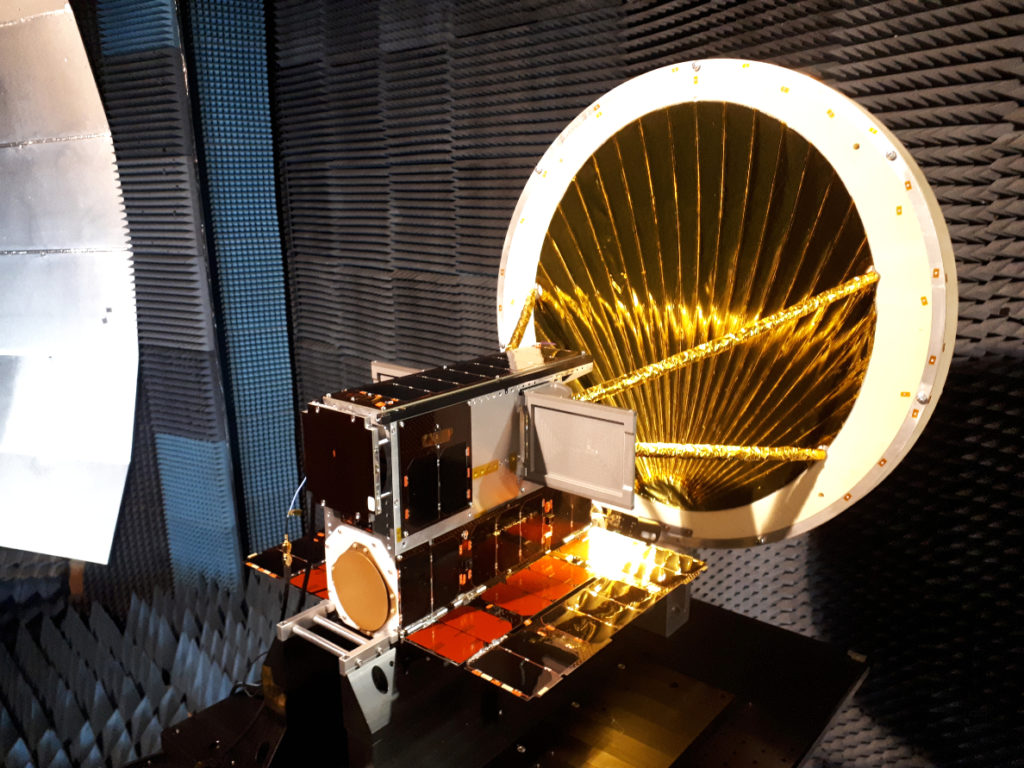


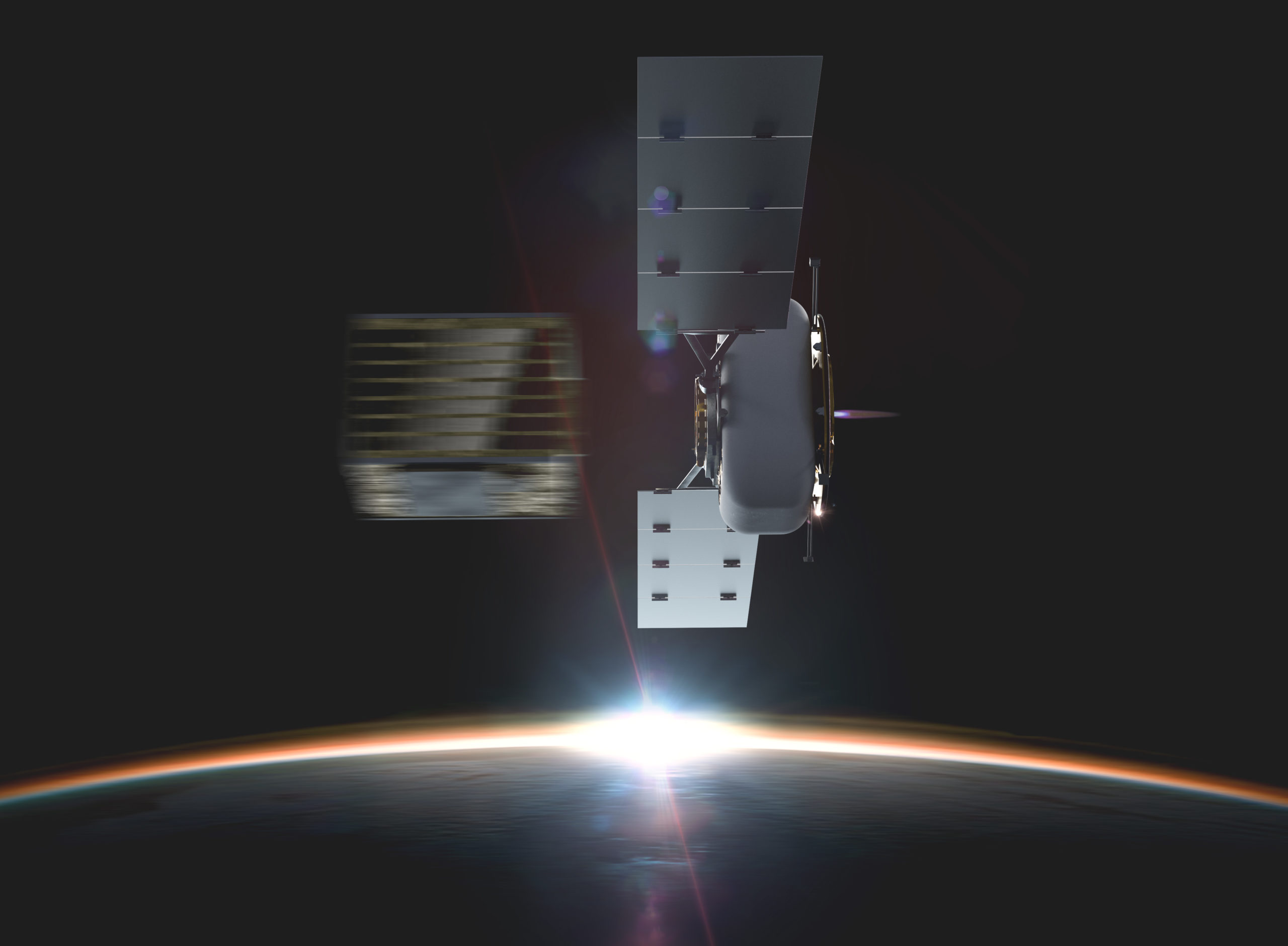







 The goal of the Blackjack Program is to demonstrate that a constellation of LEO satellites meets Department of Defense (DoD) performance and payload requirements, at a significantly lower cost, with shorter design cycles and with easier and more frequent technology upgrades. The spacecraft will be delivered on a rapid timeline to support the critical DARPA demonstration schedule with the first spacecraft to be delivered in mid-2021.
The goal of the Blackjack Program is to demonstrate that a constellation of LEO satellites meets Department of Defense (DoD) performance and payload requirements, at a significantly lower cost, with shorter design cycles and with easier and more frequent technology upgrades. The spacecraft will be delivered on a rapid timeline to support the critical DARPA demonstration schedule with the first spacecraft to be delivered in mid-2021.



 Earth-imaging company Planet has nine of their latest generation SuperDove satellites booked on the mission for deployment to a 500 km morning-crossing Sun Synchronous Orbit (SSO). Each of the nine SuperDoves will be integrated with and deployed from Rocket Lab’s Maxwell dispensers, the industry’s lightest cubesat dispenser in its class.
Earth-imaging company Planet has nine of their latest generation SuperDove satellites booked on the mission for deployment to a 500 km morning-crossing Sun Synchronous Orbit (SSO). Each of the nine SuperDoves will be integrated with and deployed from Rocket Lab’s Maxwell dispensers, the industry’s lightest cubesat dispenser in its class.  The 10th and final payload aboard this mission, Canon Electronics Inc.’s CE-SAT-IIB, was arranged by satellite rideshare and mission management provider Spaceflight Inc. CE-SAT-IIB is a technical demonstration microsatellite developed by Canon Electronics Inc. It has a middle-size telescope equipped with an ultra-high sensitivity camera to take night images of the Earth and small size telescopes which are suitable for CubeSat use.
The 10th and final payload aboard this mission, Canon Electronics Inc.’s CE-SAT-IIB, was arranged by satellite rideshare and mission management provider Spaceflight Inc. CE-SAT-IIB is a technical demonstration microsatellite developed by Canon Electronics Inc. It has a middle-size telescope equipped with an ultra-high sensitivity camera to take night images of the Earth and small size telescopes which are suitable for CubeSat use.





