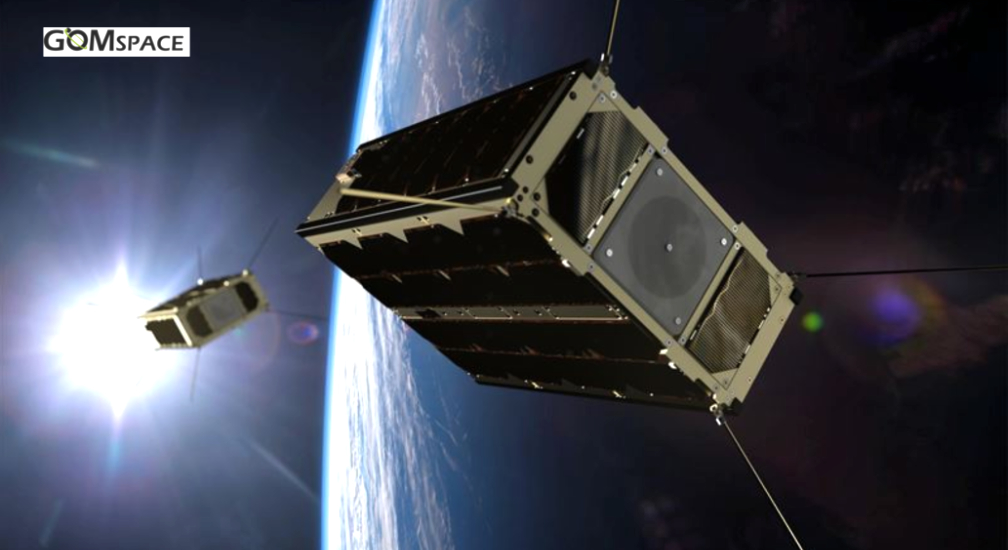
GomSpace and J.P. Morgan have successfully used the GOMX-4 satellites for an in-orbit demonstration (IOD) and tested tokenized value transfer in space.

The IOD from GomSpace enabled J.P. Morgan to test the world’s first bank-led, tokenized value transfer in space, executed via smart contracts on a blockchain network established between satellites orbiting the Earth.
GomSpace and J.P. Morgan successfully executed a transaction between two LEO satellites, which validated the approach towards a decentralized network where communication with Earth is not necessary. This breakthrough opens the door to a potential peer-to-peer DvP (data versus payment) satellite marketplace in the long term, as private companies prepare to launch their own constellations.
The project was made possible due to GomSpace’s GOMX-4 satellites already on-orbit and which are highly reconfigurable. This allows GomSpace to provide rapid on-orbit demonstrations, such as this project, as a service to the firm’s customers exploring new uses of space technology and the company’s smallsats.
“We are proud to have supported J.P. Morgan as they explored this novel use case of a space-based payment infrastructure utilizing blockchain technology,” said Niels Buus, the CEO of GomSpace.











 FF3/S Sat Phone geolocation system (and ancillary items) from a UAE prime contractor for use on a surveillance aircraft to monitor critical infrastructure in the region.
FF3/S Sat Phone geolocation system (and ancillary items) from a UAE prime contractor for use on a surveillance aircraft to monitor critical infrastructure in the region.
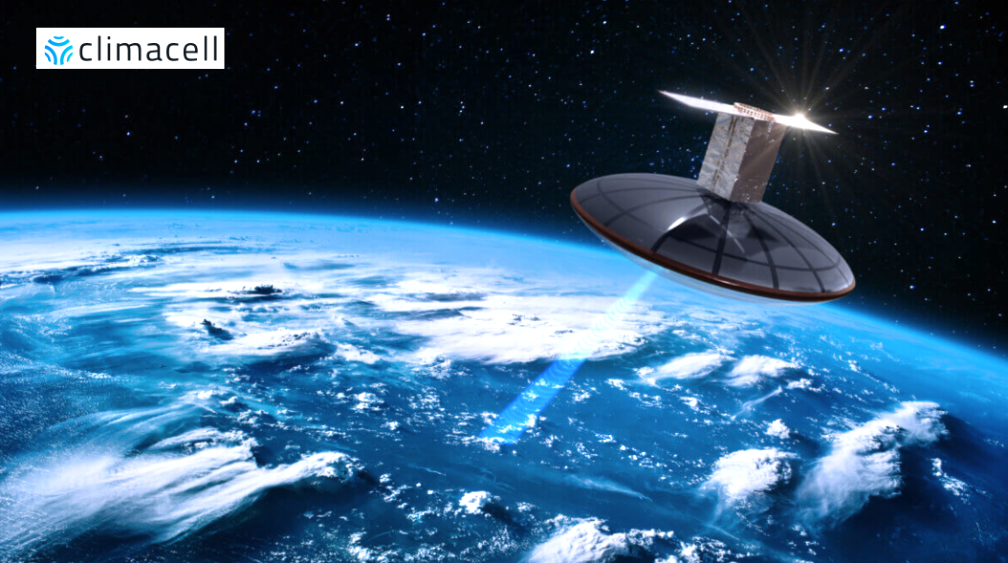





 that is fully customizable to any industry impacted by the weather. Customers around the world including Uber, Delta, Ford, National Grid, and more use ClimaCell to dramatically improve operational efficiency. The company was built from the ground up to help teams predict the business impact of weather, streamline team communication and action plans, improve productivity, and optimize profit margins.
that is fully customizable to any industry impacted by the weather. Customers around the world including Uber, Delta, Ford, National Grid, and more use ClimaCell to dramatically improve operational efficiency. The company was built from the ground up to help teams predict the business impact of weather, streamline team communication and action plans, improve productivity, and optimize profit margins.