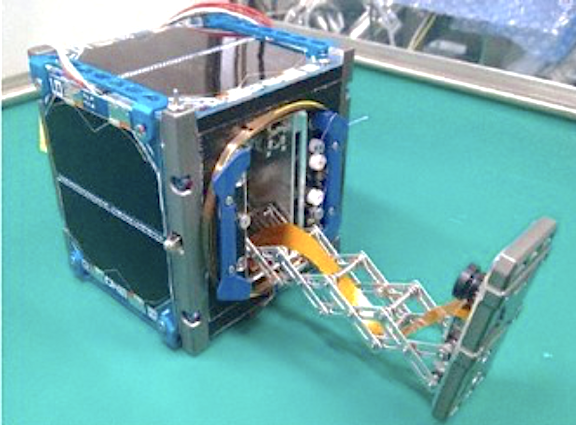
Sateliot will rely on The Space Alliance formed by Thales Alenia Space (TAS) and Telespazio for the development of a constellation of smallsats to ensure the company’s IoT connectivity is compatible with the 5G standard.

Acting as telecommunications cell towers in space, the plan envisages 16 satellites by 2025 with an investment of around 100 million euros will enable the deployment of IoT services in sectors such as maritime, logistics, energy, agri-food, infrastructures and environmental monitoring.
Sateliot has reached an agreement with Thales Alenia Space in Spain and France to coordinate the design and development of the technologies required to offer the envisaged IoT services with 5G coverage starting in 2022.
TAS will ensure the viability of the entire technical phase, including engineering activities and the definition of the mission and end-user needs, with the objective of guaranteeing coverage extension services to European, American, South American and even African telecommunications operators from 2022.
The agreement between Sateliot and Telespazio will promote the development of the IoT market. In particular, Sateliot will leverage Telespazio’s experience and penetration in the international space services market to assess the main needs of customers in different sectors. Telespazio will use Sateliot’s capabilities to boost its offering in an IoT sector that already includes global hybrid coverage based on the integration of LTE/WiFi/Lora/Satellite technologies.
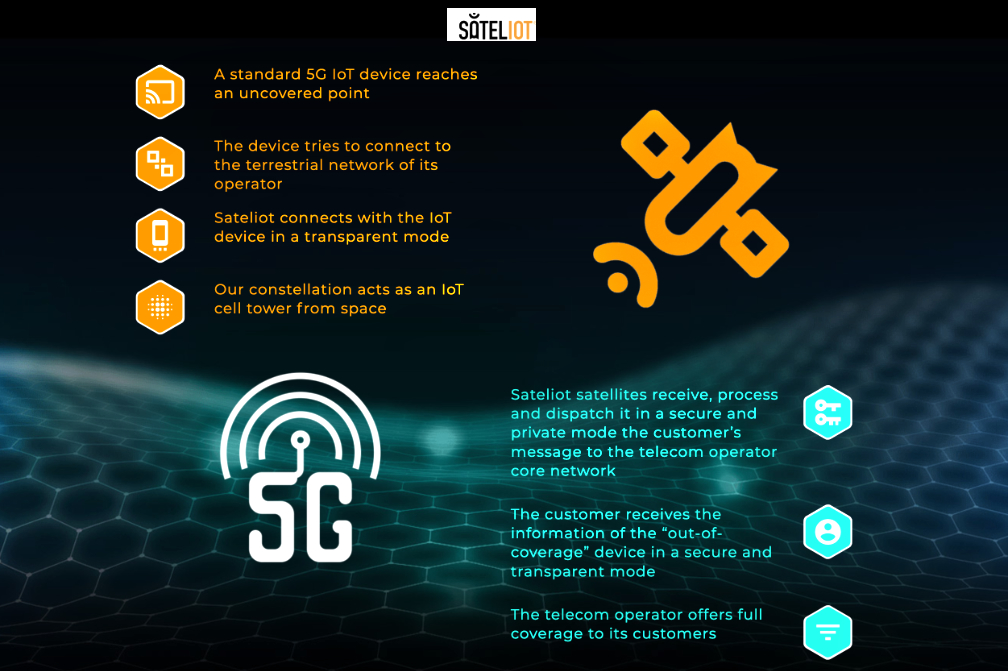
This agreement will allow Telespazio and Sateliot to develop new IoT services in sectors such as seaborne freight, agriculture, infrastructure management and telecommunications. In the freight sector, for example, IoT sensors connected via satellite are able to offer information about the load status, allowing transport monitoring and enhanced security, while in the agricultural sector, they can provide real-time data to promote sustainable crop management. IoT sensors are also one of the most promising solutions for infrastructure monitoring and management, maintenance management, traffic status control and rescue operations management after accidents.
According to Jaume Sanpera, the Founder and CEO of Sateliot, “This strategic agreement with The Space Alliance, formed by Thales Alenia Space and Telespazio, underpins our business plan focused on two growth paths. On the one hand, through a transversal strategy with telecommunications operators. And, on the other, through a vertical business line, aimed at end customers, to whom we will facilitate the monitoring of different variables in real time for profitable decision making for their businesses.”
The objective of Sateliot’s business plan is to close 2025 with a turnover of around 236 million euros and a total workforce of more than 100 people. To make this possible, Sateliot has completed two capital increases and is negotiating a new round of financing with various international funds.
Sateliot is the first satellite telecommunications operator that will provide global and continuous connectivity to all the elements that will make up the universe of the Internet of Things (IoT) -such as the connected car or home- under the 5G protocol. Thanks to a constellation of state-of-the-art nanosatellites, located at low altitude that act as mobile cell towers, Sateliot is the perfect complement to large telecommunications companies by providing the necessary infrastructure where terrestrial technologies do not reach. More information in our web, Twitter and LinkedIn.
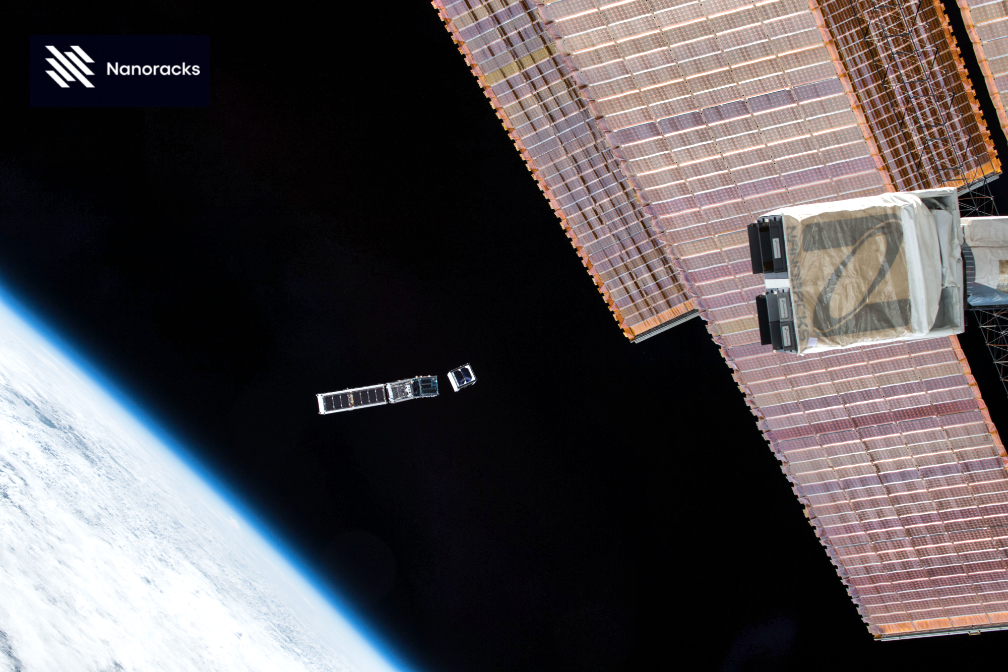
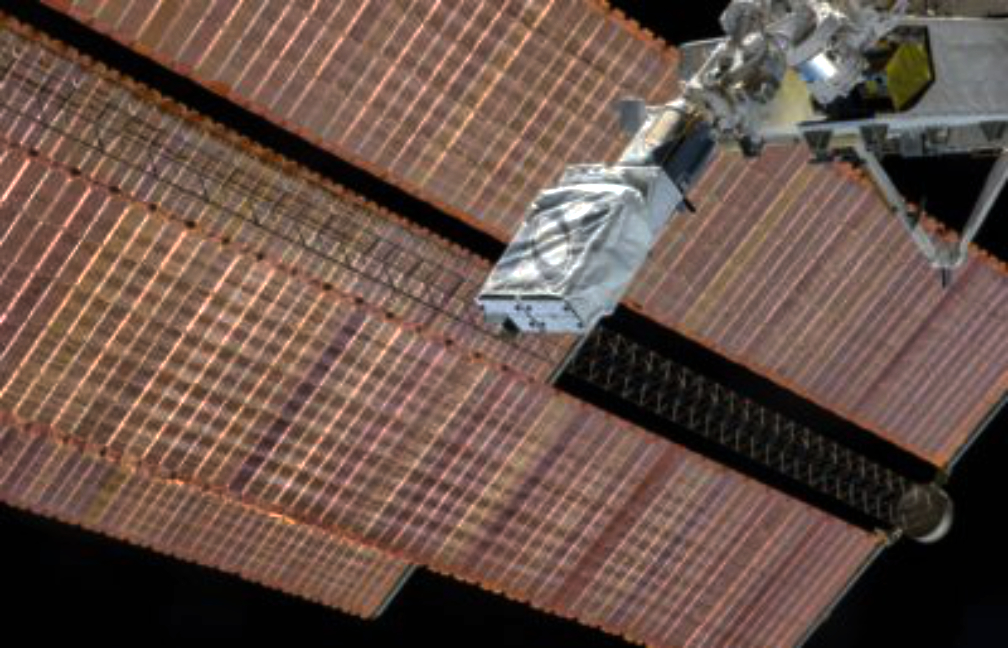
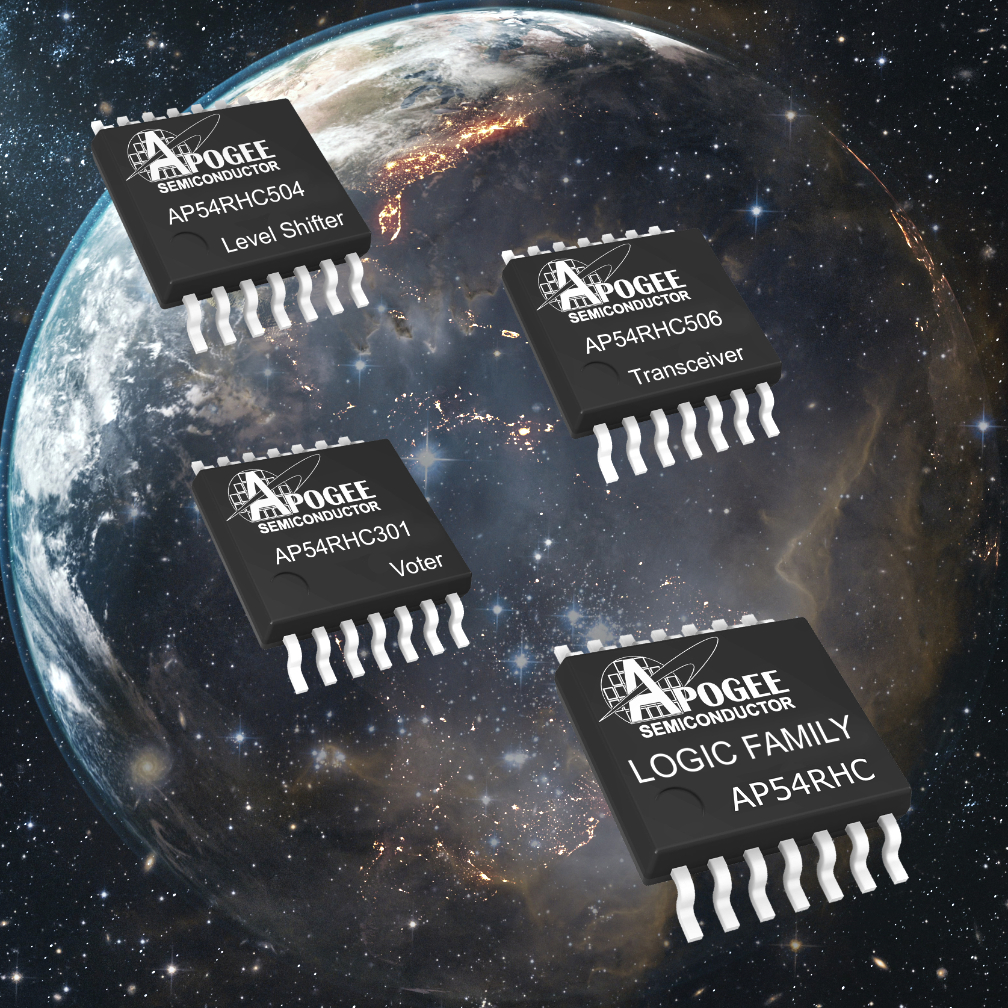







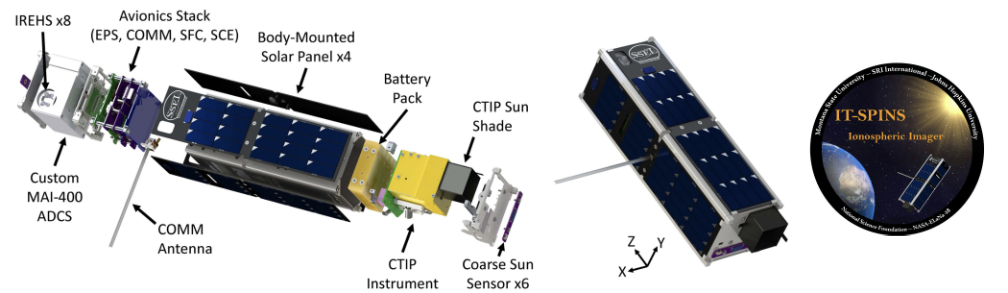
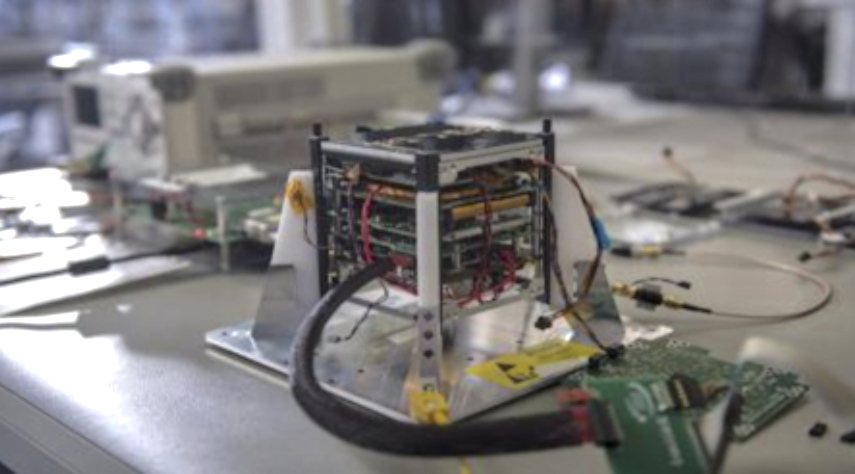





 ) design methodology that improves the radiation performance of commercial process technologies, enabling the rapid creation of rad-hard designs in a fraction of the time and effort.
) design methodology that improves the radiation performance of commercial process technologies, enabling the rapid creation of rad-hard designs in a fraction of the time and effort.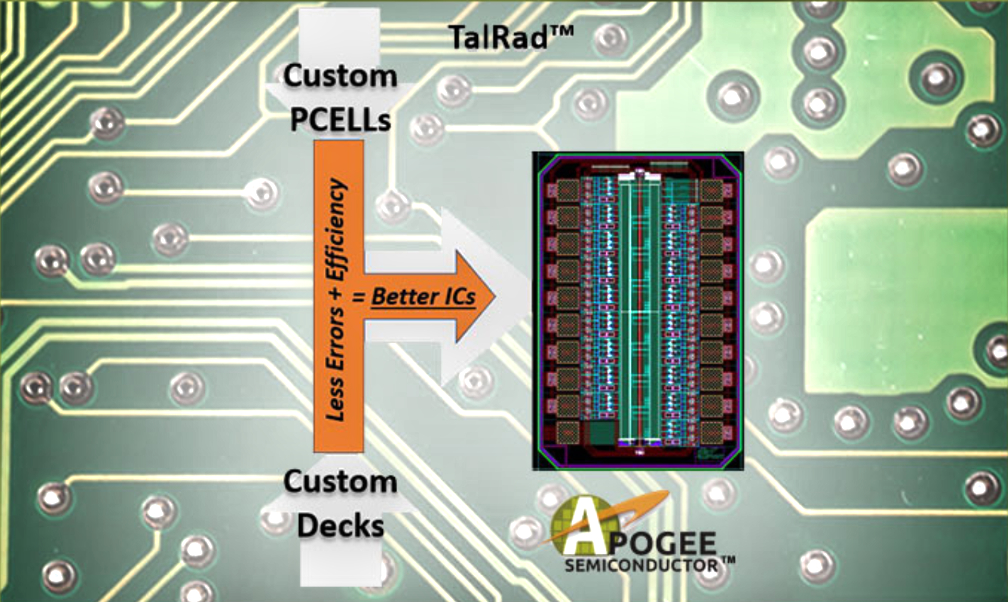

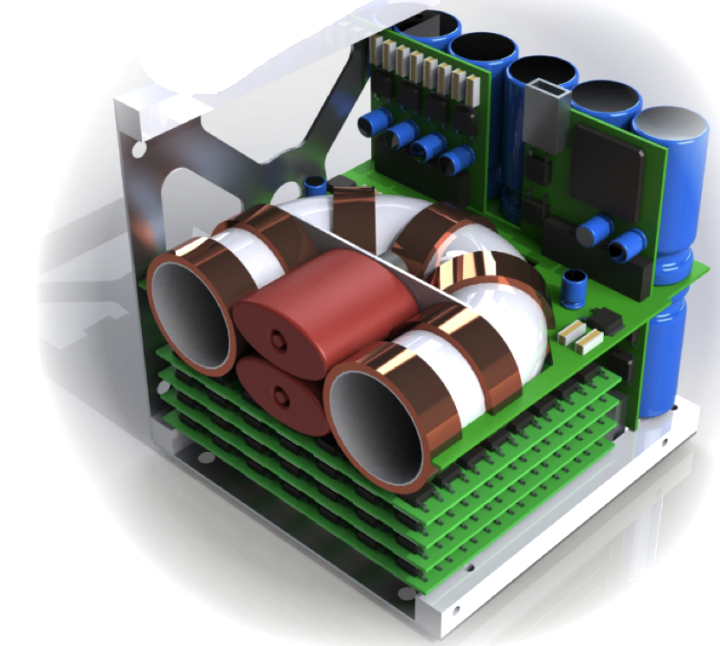


 Software Defined Radio (SDR) for new U.S. Space Force programs for smallsats. The contract, “Modular Software Defined Radio for Resilient SATCOM”, requires Space Micro to assess future Department of Defense (DoD) requirements for advanced SATCOM.
Software Defined Radio (SDR) for new U.S. Space Force programs for smallsats. The contract, “Modular Software Defined Radio for Resilient SATCOM”, requires Space Micro to assess future Department of Defense (DoD) requirements for advanced SATCOM.