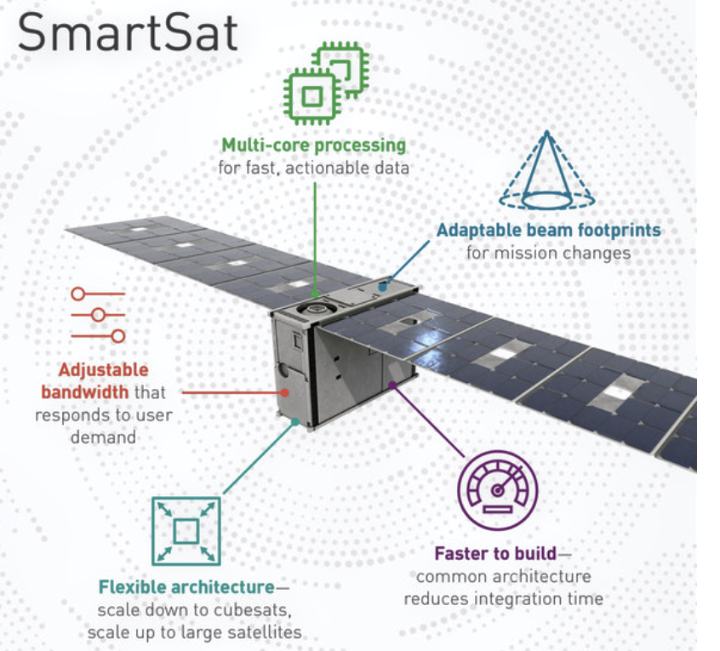
T4i and Spacety Luxembourg have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to set the framework for several intended collaborations regarding Electric Propulsion and flight opportunities.

T4i (Technology for Propulsion and Innovation) is an Italian rocket company that specializes in in-space and access-to-space propulsion systems, tailored for smallsats, offering an array of technologies that match the mission’s requirements of satellite operators.
T4i conducted an extensive research on several propulsion systems and different propellants. Among them, T4i scientific research along the iodine propellant as ground-breaking source of energy in space, opens certain interesting outcomes in response to the new constellation market demand.
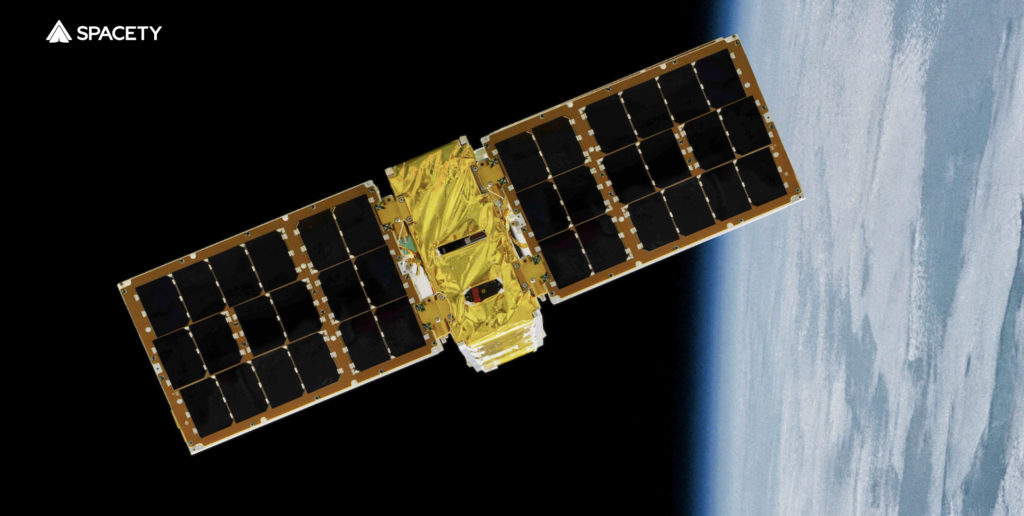
Spacety Luxembourg is a commercial space company involved in the design, manufacturing, launching, operation of satellites, and providing space flight services to its clients worldwide to flight test or demonstrate their technologies or science in space. Spacety has built and launched its first SAR satellite, the world’s first miniaturized C-band SAR satellite with a phased-array antenna, and plans to build, deploy, and operate a mega SAR constellation with 300+ satellites to provide near real time SAR data services to the world.
There are common fields of interests between the two companies. T4i is developing plasma thrusters in different sizes to accommodate the entire spectrum of smallsats, while Spacety Luxembourg is both offering flight opportunities for T4i IOD missions and looking for innovative, robust, and reliable iodine-based electric propulsion systems for their SAR constellation. In addition, this agreement formalizes the mutual interest in collaborating for future space missions and the possibility for T4i to capture the growing demand arising in the Chinese constellations market through this partnership with Spacety.
“Propulsion is an important subsystem of satellites for constellation. As more constellations are deployed for EO and telecommunications, the market for electric thrusters will expand rapidly. However, an electric thruster is a complicated system and it needs to be tested and verified in space before being used for any operational satellite mission. T4i has developed advanced propulsion technologies for small and micro satellites. Spacety has frequent flight opportunities and extensive experience of technology IOD/IOV missions. The collaboration of the two companies will produce innovative space products, which will be needed by many satellites, including Spacety’s,” said James Zheng, CEO of Spacety Luxembourg.
“We are honored to have the opportunity to cooperate with such a trustful partner as Spacety and eager to expand T4i’s market reach,” said Daniele Pavarin, T4i co-founder and CEO.




 rideshare mission in LEO.
rideshare mission in LEO. 
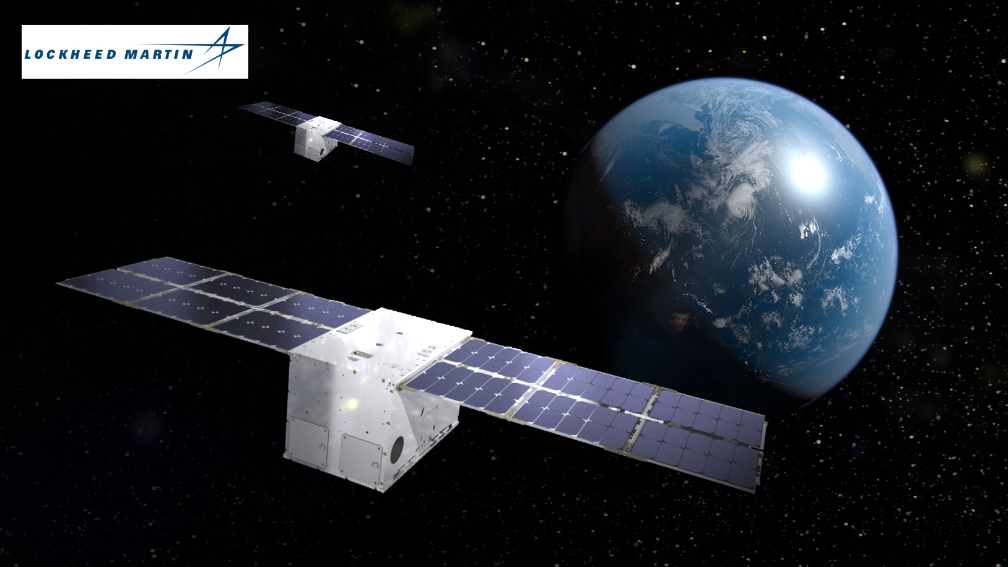





 12U cubesats — each about the size of a four-slice toaster — designed to demonstrate how smallsats can serve an essential role in sustaining critical space architectures in any orbit. Developed using internal funding, LINUSS will be two of the most capable cubesats in Geosynchronous Earth Orbit (GEO).
12U cubesats — each about the size of a four-slice toaster — designed to demonstrate how smallsats can serve an essential role in sustaining critical space architectures in any orbit. Developed using internal funding, LINUSS will be two of the most capable cubesats in Geosynchronous Earth Orbit (GEO).