
Terran Orbital Corporation (NYSE: LLAP) has concluded the bus commissioning for the CENTAURI-5 satellite with nominal health and status checkouts.

Tyvak International SRL, Terran Orbital’s wholly-owned international subsidiary, designed and built this LEO satellite for Fleet Space Technologies.

CENTAURI-5 adds capacity, reduces signal delay, and provides additional network redundancy. The 3D printed metal patch antenna satellite is traveling to an expected altitude of 330 miles where it will orbit in the existing Centauri constellation operated by Fleet Space and Terran Orbital.
Upgrades from the CENTAURI-4 payload include enhancements that mitigate the effects of radiation in LEO as well as direct communication links to ground stations and an extended S-band range, allowing uplink at standard ground station frequencies.
The Centauri constellation is set to become one of the world’s most advanced, low-power, satellite networks, securing global coverage for internet of things (IoT) devices by using its in-house smallsat technology. Satellites within the constellation will each perform a specific function. CENTAURI-5 will focus on improving data transfer and communication in the energy, utilities and resource industries.
“Terran Orbital is thrilled yet another of our Transporter-5 satellites has achieved bus commissioning shortly after launch,” said Terran Orbital Co-Founder, Chairman, and Chief Executive Officer, Marc Bell. “The data and insight gained from CENTAURI-5 will improve IoT operations in ways we can only begin to imagine. The quality-of-life implications here on Earth are endless. Terran Orbital will continue to design, build, integrate, and operate cutting-edge satellite solutions for clients like Fleet Space as we usher in the New Space Industry.”
“Fleet’s mission is to unlock the extraordinary power of global connectivity by launching constellations of LEO satellites,” said Fleet Space Technologies Founder, Flavia Tata Nardini. “The applications, from aiding more sustainable approaches to finding rare earth minerals to exploring worlds beyond ours, have true benefit for the whole of our planet. This work requires the very best technical minds and partners. Terran Orbital is a leader in their field collaborating with a global team of space technology pioneers to deliver one of the most advanced networks of low-power satellite networks ever launched.”
Terran Orbital is a leading manufacturer of small satellites primarily serving the United States and Allied aerospace and defense industries. Terran Orbital provides end-to-end satellite solutions by combining satellite design, production, launch planning, mission operations, and in-orbit support to meet the needs of the most demanding military, civil, and commercial customers.
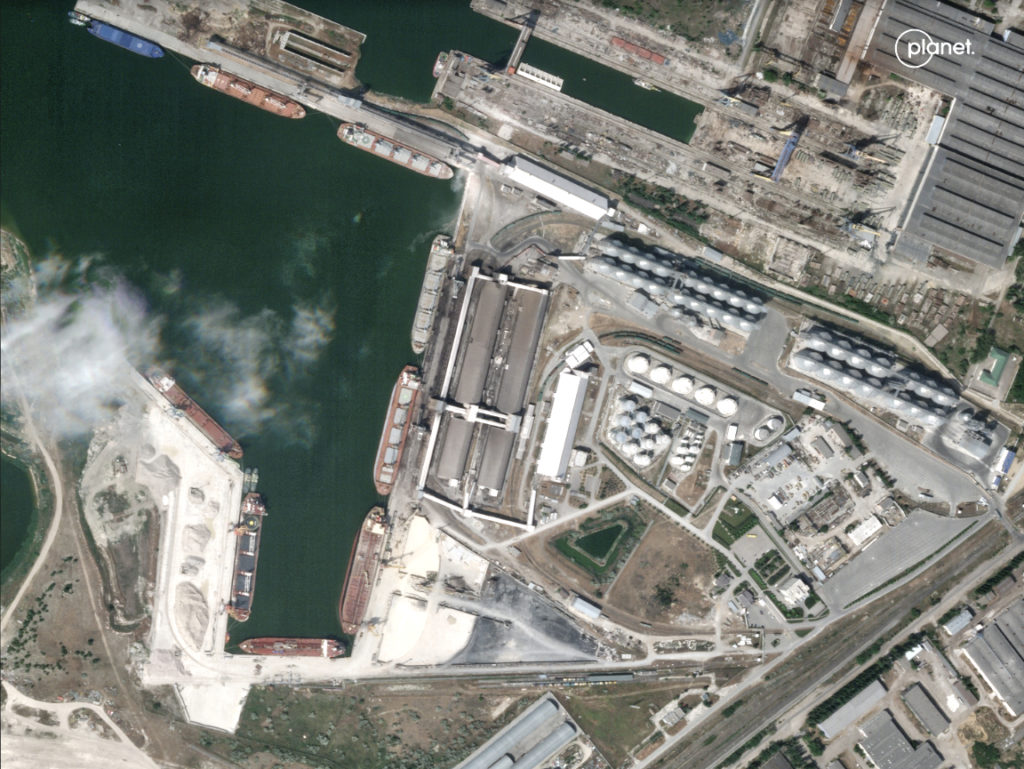
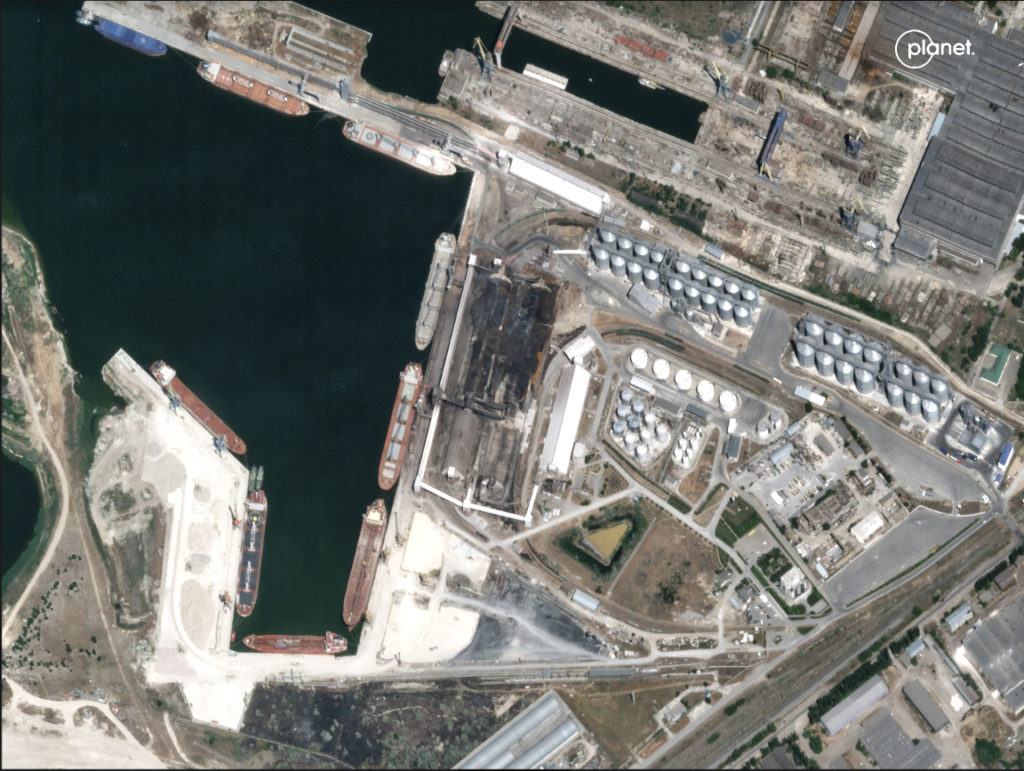




















 and OnTime
and OnTime