
The STAR VIBE mission, which is the product of a collaboration between the Wrocław-based company Scanway Space and the German company German Orbital Systems, was launched into orbit on board a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket during the Transporter 6 mission.

This a demo mission of two proprietary systems — a small EO telescope called STAR and a system for self-inspection of satellite status called VIBE. The objective of the mission is to test the STAR telescope and the VIBE technology under space conditions, as well as to raise the level of technological readiness level to the highest, ninth level. To this purpose, the impact of space conditions (vacuum, temperature fluctuations, high radiation and microgravity) on the telescope’s components, on-board electronics and on the quality of the data collected will be tested.
The STAR telescope is a telescope operating in the visible light spectrum. Its sensor allows images to be taken at a resolution of 25 meters per pixel and provides a large field of view (102.4 x 76.8 km). This allows rapid data collection for many purposes, e.g., on climate change, natural disasters or data supporting efficient agriculture.
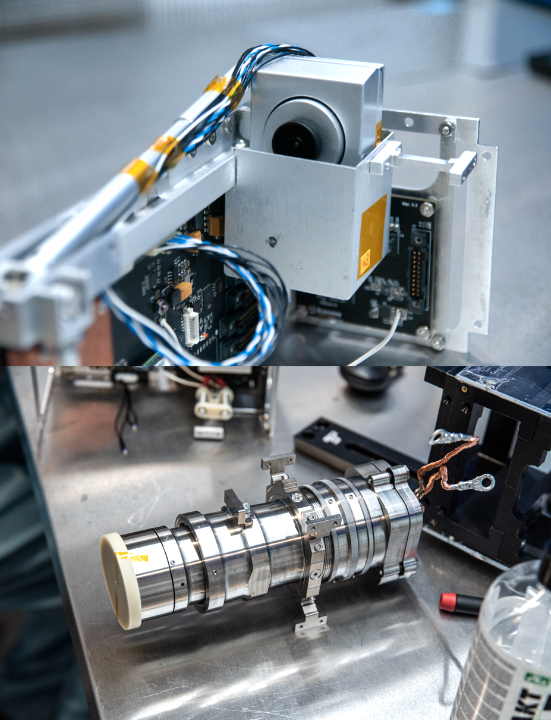
VIBE is an optical system that is one configuration of Scanway’s SHS system — Spacecraft Health Scanner — a system used for autonomous smallsat diagnostics. VIBE is a vision system located on a deployable beam. The camera is connected to the spacecraft’s onboard computer, which, by collecting images in its database, allows the data to be analyzed by artificial intelligence (AI), which is able to detect various defects, such as damage to the solar panels.
Prior to the integration of the satellite into the Falcon 9, the STAR and VIBE systems were tested several times to verify correct functionality. The tests were carried out in the company’s laboratory and at an independent scientific institution in Germany; among other things, vibration tests and tests in a thermal vacuum chamber were performed.
In addition, Scanway carried out stratospheric balloon tests, in which the test payload (on-board computer, STAR telescope and VIBE system) was hooked up to the balloon’s nacelle and sent to an altitude of about 35 km. Stratospheric testing allows payload be tested in conditions of low pressure, low temperature and elevated cosmic radiation, which can very much affect the performance of electronic systems.
The STAR VIBE mission is exceptional for the Polish space sector, primarily due to the dispatch of the VIBE instrument which is the first Polish optical instrument for auto-inspection of orbital infrastructure, which is equipped with an algorithm based on AI. Operational duration of the mission — a minimum of three months, but can be extended, depending on the demand for images from the STAR telescope.
