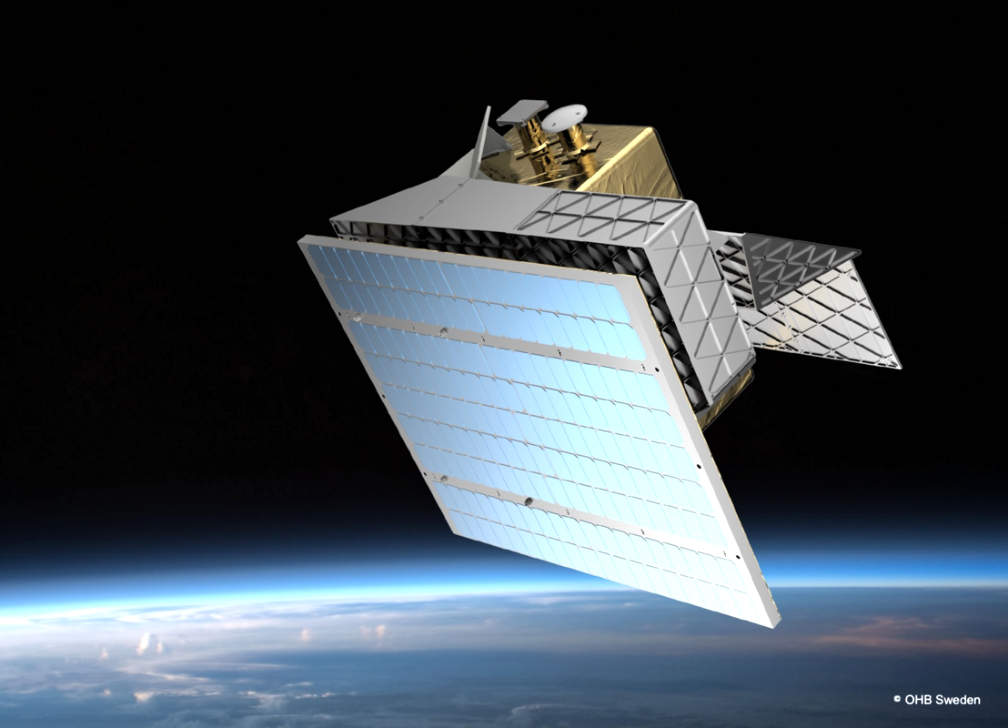
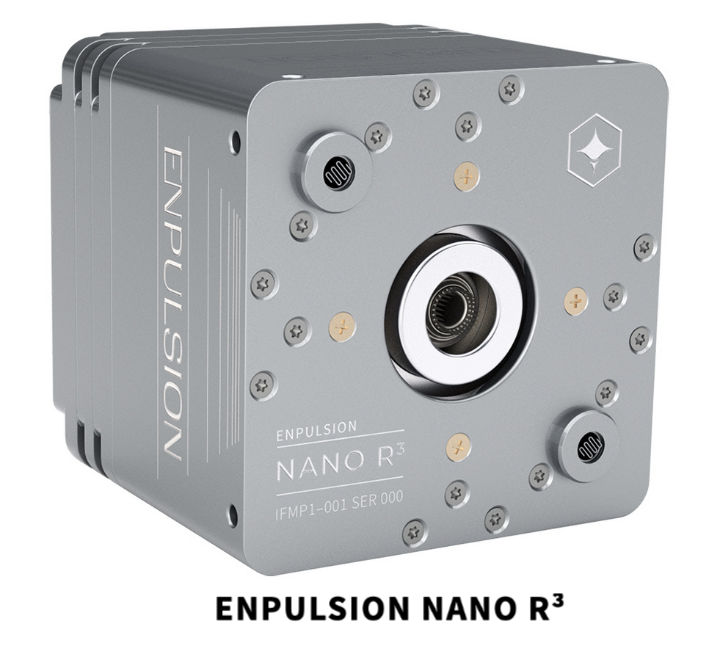
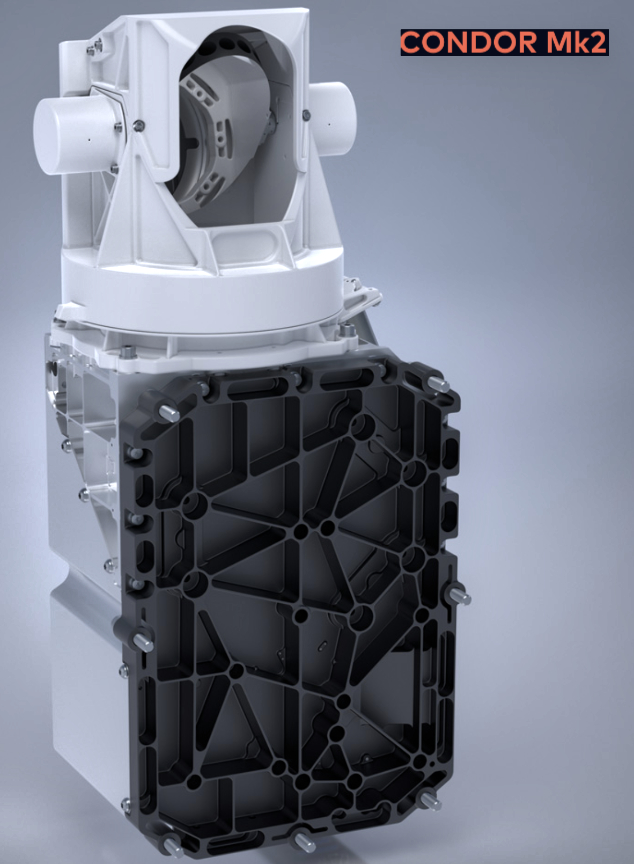
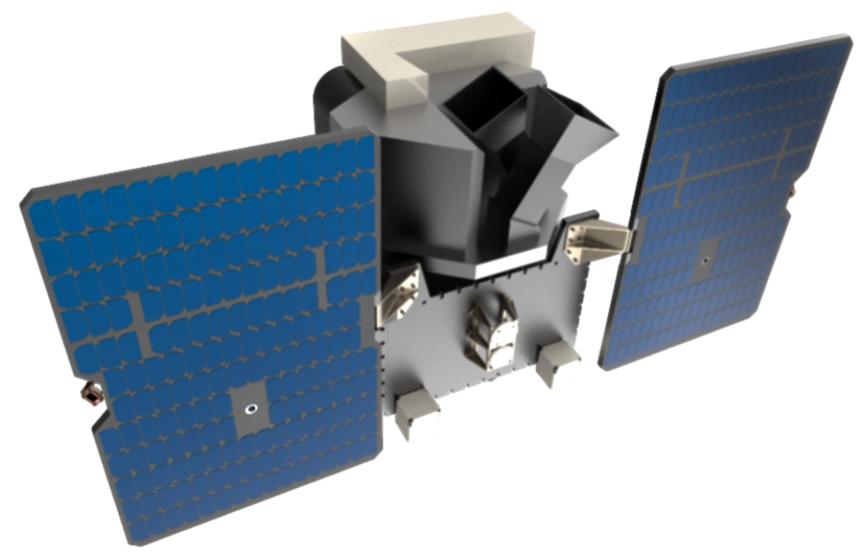
Designed as “multi-purpose” cost-effective products, the scalable and powerful Triton-X platforms are easily adaptable to various typologies of LEO missions and payloads, also in small and/or hybrid constellations.
DCUBED’s new line of release actuators Micro Pin Puller and Micro Release Nut will fly aboard LuxSpace’s multipurpose small-satellite platform Triton-X on the upcoming Genesis mission.
The Triton-X Genesis project is the first step in the roll-out of the Triton-X platform, a multi-mission product providing high on-board processing power and scalable in the 50-250 kg range.
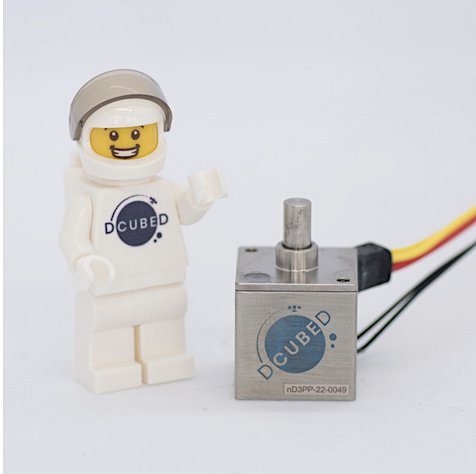

Later last year, LuxSpace sold a Triton-X Heavy satellite for the Seranis project of the University of the German Bundeswehr, leveraging 15+ years of Space systems design, manufacturing, and in-orbit delivery.
DCUBED and LuxSpace share the goal of enabling missions to take their capabilities to the next level and look forward to demonstrating their new technologies with their upcoming mission.
DCUBED’s CEO Thomas Sinn in Germering (Bavaria, Germany) can assist with COTS release actuators and COTS deployables that are specifically designed for SmallSat applications. DCUBED’s pin puller and release nut actuators are space-proven, readily available, easy to use, and small in size. The DCUBED SmallSat deployables (Space Selfie Stick, 100W 1U solar array and deployable radiator) tackle the needs of new space customers by maximizing performance in space while remaining efficiently packed in a standardised volume for launch.
LuxSpace (CEO Edgar Milic) was established in Luxembourg in 2004 as a subsidiary of OHB SE and is an integrated provider of small satellites and space-based applications and services. The company can look back on seven successfully launched space systems, including the Triton-2/ESAIL satellite launched , and has over 16 years of experience in data applications with a particular focus on the maritime sector and Earth observation.