AAC Clyde Space has won an order for satellite subsystems valued at USD 2.3 M (approx. SEK 23.8 M) from a U.S. development company supplying spacecraft and other multi-mission systems.
The U.S. company will integrate the subsystems on satellites for several new development programs. The order has been preceded by a smaller order on subsystems for tests on ground. The subsystems will be delivered in several batches, starting in the second quarter of 2023 with the last delivery in the fourth quarter of 2023.

The U.S. company develops technology solutions for space for a variety of customers, with their headquarters in California. The company has 15 000 employees worldwide with annual revenue of 2.8 BUSD for 2021.
“These are state-of-the art subsystems developed to offer satellite operators both the capabilities and reliability required to operate efficiently in a complex space environment. Winning this order is the result of the strong competitiveness of AAC Group’s products in small satellite technology and a milestone for us,” says AAC Clyde Space CEO Luis Gomes.







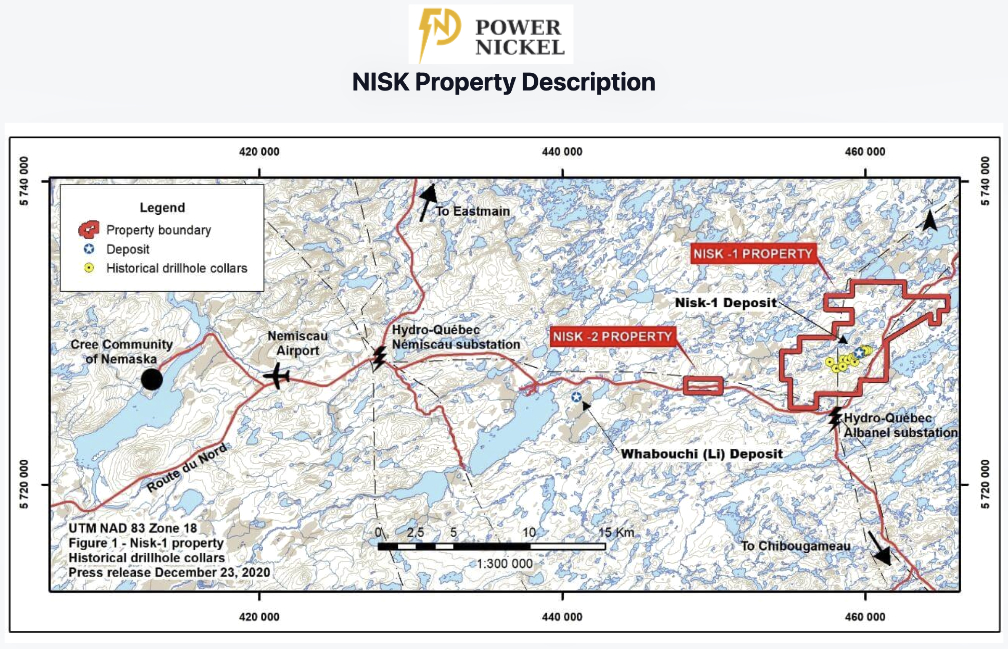

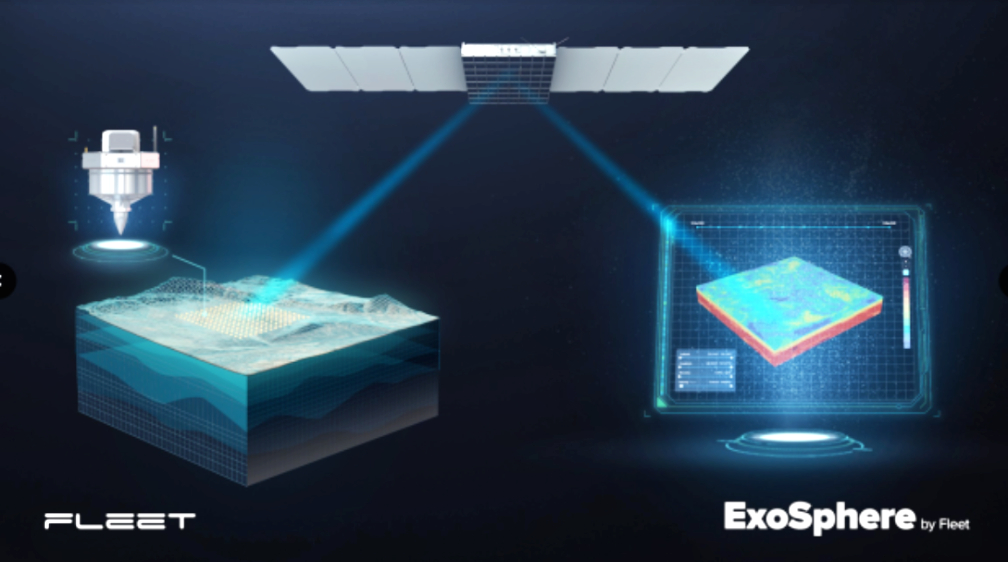




 , has been granted a remote sensing license from the
, has been granted a remote sensing license from the 


 12U CubeSats designed to demonstrate how small satellites can serve an essential role in sustaining critical space architectures in any orbit. LINUSS was designed to demonstrate how small CubeSats can regularly upgrade satellite constellations to add timely new capabilities and extend spacecraft design lives.
12U CubeSats designed to demonstrate how small satellites can serve an essential role in sustaining critical space architectures in any orbit. LINUSS was designed to demonstrate how small CubeSats can regularly upgrade satellite constellations to add timely new capabilities and extend spacecraft design lives.
