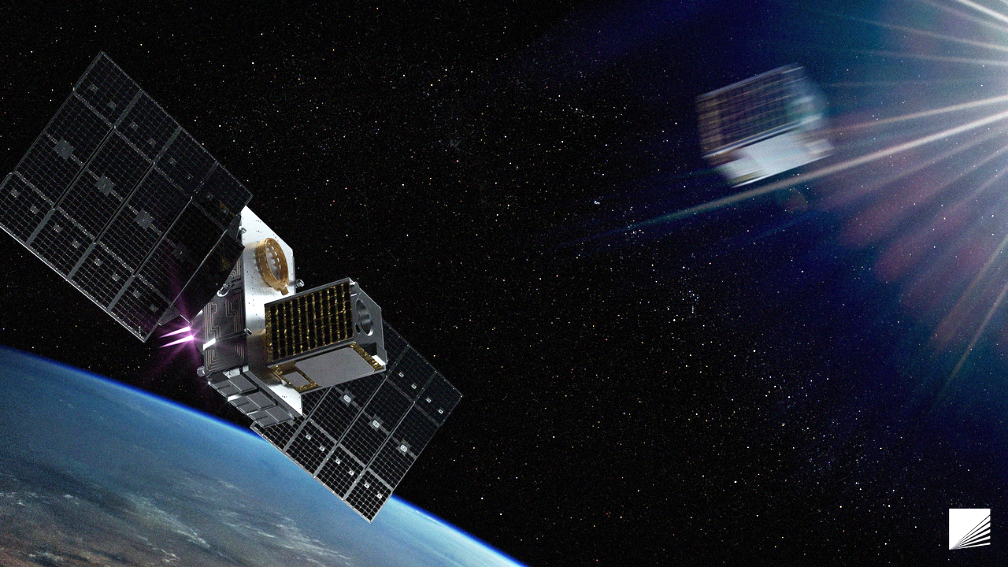
Momentus Inc. (NASDAQ: MNTS) has deployed all customer payloads from its Vigoride-6 Orbital Service Vehicle that launched in April of 2023 aboard the SpaceX Transporter-7 mission.

To date, Momentus has deployed a total of 15 customer satellites over three missions conducted over the past year and has also placed three Vigoride Orbital Service Vehicles (OSVs) into orbit. While these initial three missions were demonstration missions focused on testing the performance of the Vigoride OSV, Momentus orbited a number of customer satellites in the missions summarized below:
Vigoride-3 launched in May of 2022: Momentus’ inaugural mission deployed six satellites for FOSSA Space Systems and the SelfieSat satellite for Orbit NTNU from Vigoride. The Company also used a third-party deployer to deliver a satellite to orbit for CalPoly Pomona for a total of eight satellites deployed from Vigoride-3 and a third-party deployer.
Vigoride-5 launched in January of 2023: Momentus’ second mission included the deployment of the Qosmosys Zeus-1 payload. The Company is providing ongoing hosted payload services to Caltech’s Solar Power Project Demonstrator (SSPD) mission. Caltech reports that its payload recently demonstrated its ability to wirelessly transmit power in space and to beam detectable power to Earth. Momentus will continue to provide hosted payload support to SSPD over the coming months as it continues its operations.

During the Vigoride-5 mission, the Momentus team also tested its Microwave Electrothermal Thruster (MET) that uses water as a propellant. This included 35 firings of the thruster that demonstrated its ability to perform its intended use cases in LEO.
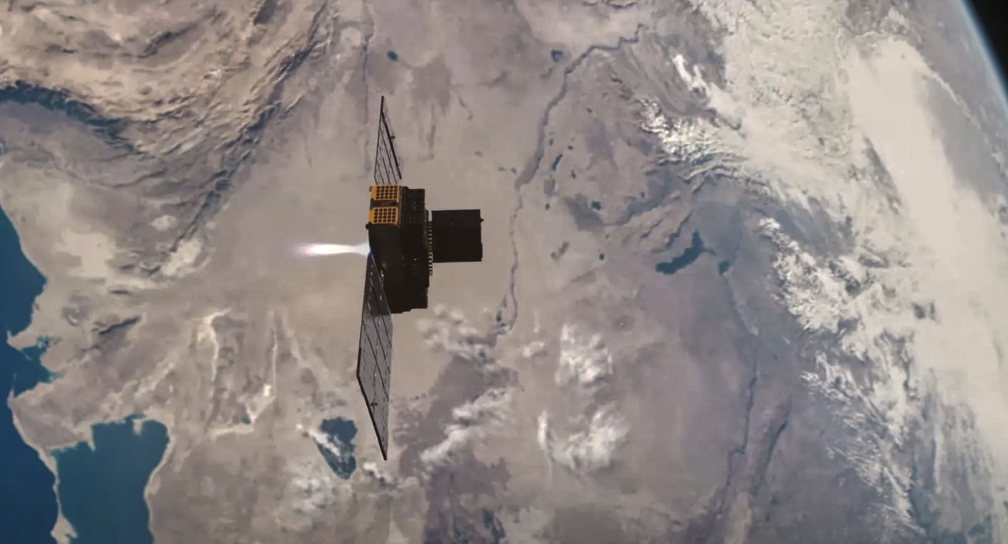

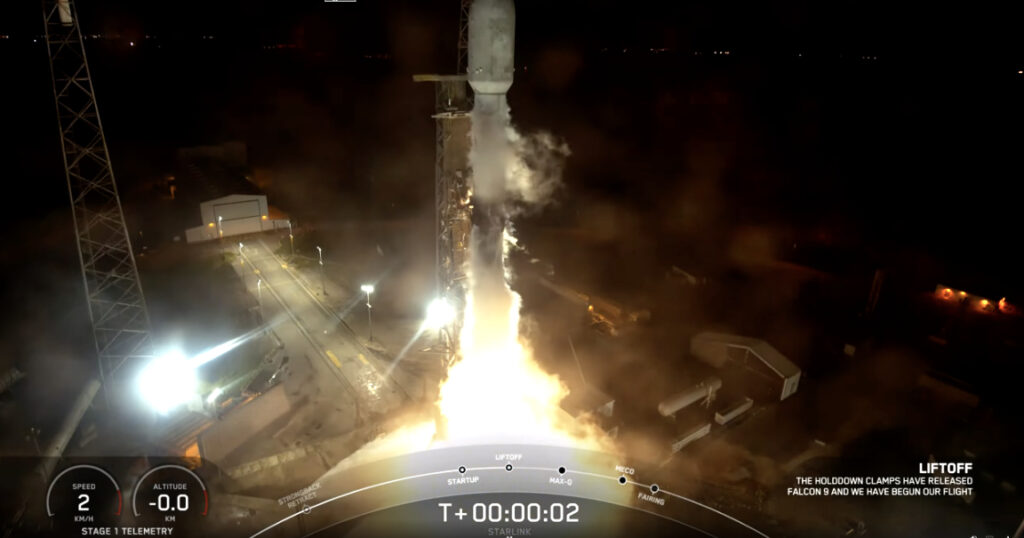
Vigoride-6 launched in April of 2023: The Vigoride-6 mission successfully deployed the REVELA payload for ARCA Dynamics, the VIREO CubeSat for C3S LLC., the DISCO-1 CubeSat for Aarhus University, and the IRIS-C payload for an Asian customer booked through ISILAUNCH.
During the Vigoride-6 mission, Momentus also deployed two CubeSats into LEO as part of the NASA LLITED (Low-Latitude Ionosphere/Thermosphere Enhancements in Density) mission. These two CubeSats, housed behind a single deployer door, were released from the Vigoride OSV earlier than scheduled.
While the CubeSats were deployed at the intended altitude of 495 km., they were deployed at a different inclination than the intended target orbit needed for the science experiment. NASA has confirmed the two CubeSats are functional and the team will be able to operate the science instruments onboard. Momentus conducted a thorough investigation and identified the root cause as human error in the mapping of a software command. The Company is implementing corrective actions to prevent a recurrence.
LLITED launched in April as ELaNa 40 (Educational Launch of a Nanosatellite) managed by NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative.
The TASSA features 11-meter-long metal sheets with flexible solar cells bonded to them. To stow, they are tightly coiled around a mandrel. After launch, motors unroll the mandrel, deploying the solar array. The goal of the TASSA program is to reduce the cost per watt of power generated by 50% over arrays currently on the market. Momentus aims to drive down vehicle production costs and streamline on-orbit operations, while reducing the cost of power for the satellite, with this technology once operational.
Along with Vigoride-6, Momentus is concurrently operating its Vigoride-5 spacecraft that launched in January of 2023. As mentioned above, the Vigoride-5 spacecraft is providing ongoing hosted payload services to Caltech’s SSPD mission.
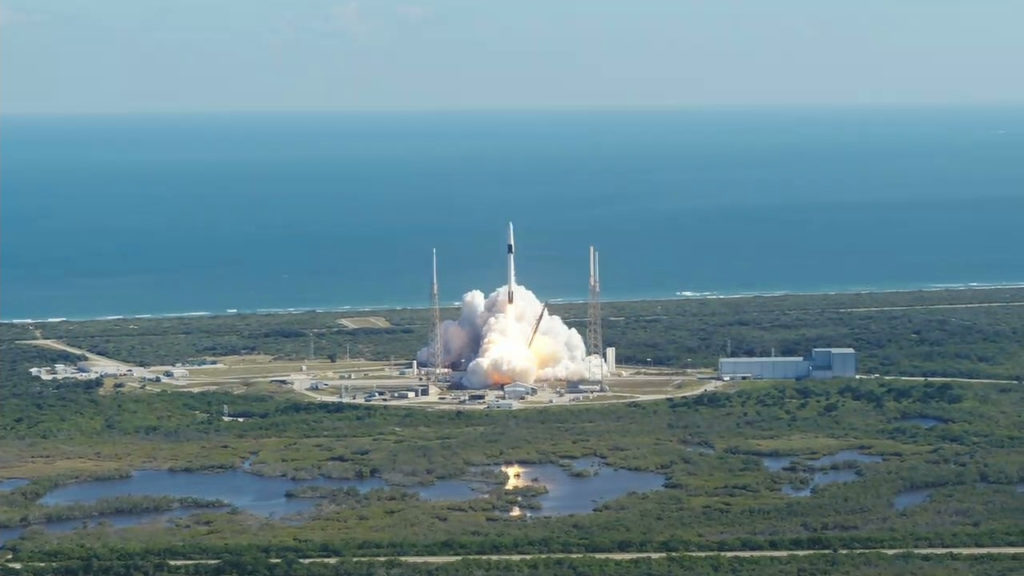
The Company’s next flight is targeted for no earlier than November of 2023 aboard the SpaceX Transporter-9 mission. During this mission, Momentus will use a deployer to place three satellites into Low-Earth Orbit for three different customers:
- The AMAN-1 Earth Observation satellite will be deployed for SatRev. The satellite can also be used for other services such as land survey, precision agriculture, weather, environmental and smart cities.
- The JINJUSat-1 satellite will be deployed for CONTEC Co. of the Republic of Korea. JINJUSat-1 is spearheaded by three entities: Jinju City, Korea Testing Laboratory, and Gyeongsang National University. Once on-orbit, cameras mounted on the satellite will carry out a mission to take pictures of the Earth.
- The Picacho satellite will be deployed for Lunasonde – a U.S. sub-surface imaging company with the goal of making underground resources – such as water and minerals – easier to find. The Picacho CubeSat is a technology demonstration of Lunasonde’s sensors. It will measure the power spectral density of low-frequency radio signals in the ionosphere, which will help inform designs for the company’s future satellites.
Additionally, Momentus now plans to launch its Vigoride-7 OSV, originally scheduled for launch in October of 2023, on SpaceX’s Transporter-10 mission that is targeted for no earlier than February of 2024. On the Vigoride-7 mission, Momentus will aim to deploy several customer satellites in LEO and provide services to a hosted payload.
The Company will also release a target satellite and maneuver the OSV into proximity with the target satellite for a Remote Proximity Operations demonstration. The revised mission plans will enable Momentus to launch Vigoride-7 with a fuller load of payloads for deployment in LEO with better mission economics, while still meeting the needs of customers requiring orbital delivery in 2023.
“One of the upcoming events that we are looking forward to conducting on the Vigoride-6 mission is a test of the Tape Spring Solar Array (TASSA), a Momentus technology demonstration of a new kind of solar array.” — Krishnan Anand, Vice President of Program Management, Momentus








 SD-WAN router to connect the LEO and GEO networks together.
SD-WAN router to connect the LEO and GEO networks together.