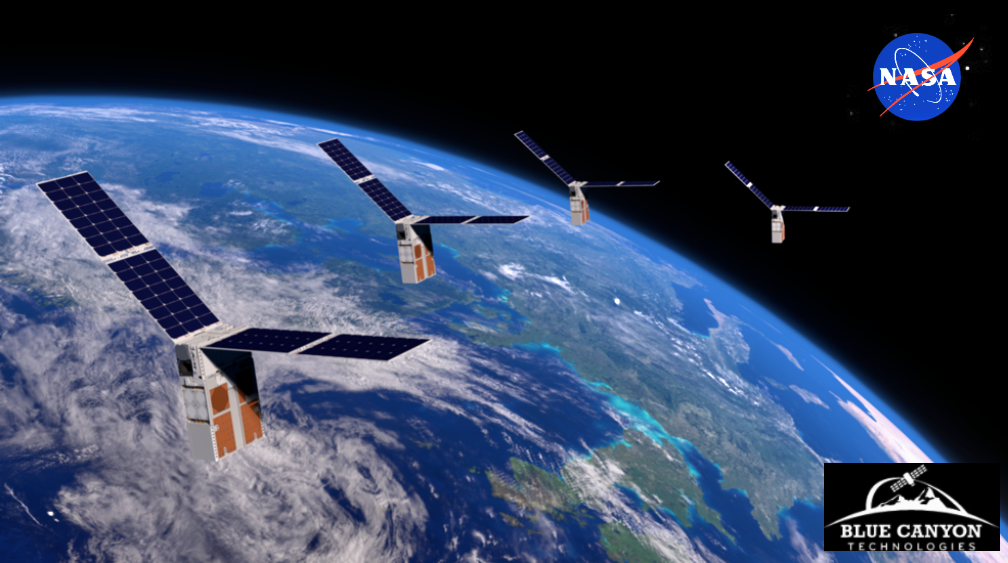
Rocket Lab USA, Inc. (Nasdaq: RKLB) has signed a double-launch deal with NASA to deliver the Agency’s climate change, research-focused mission, PREFIRE, to LEO in 2024.

The two dedicated missions on Electron will deploy one smallsat each to a 525 km. circular orbit from Rocket Lab Launch Complex 1 in New Zealand from May of 2024. The PREFIRE mission has specific LTAN (Local Time of the Ascending Node) requirements and a need for the second satellite to be deployed to space shortly after the first, which is made possible by Electron’s ability to deploy dedicated small satellite missions on highly responsive timelines. The launches will be the 7th and 8th missions Rocket Lab has launched for NASA since 2018.


NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) mission will help close a gap in understanding of how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space, especially from the Arctic and Antarctica. Analysis of PREFIRE’s measurements will inform climate and ice models, providing better projections of how a warming world will affect sea ice loss, ice sheet melt, and sea level rise. Improving climate models can ultimately help to provide more accurate projections on the impacts of storm severity and frequency, as well as coastal erosion and flooding. PREFIRE consists of two, 6U CubeSats with a baseline mission length of 10 months.
The PREFIRE mission was awarded to Rocket Lab through NASA’s Venture-class Acquisition of Dedicated and Rideshare (VADR) program, a $300 million dollar five-year contracting vehicle for placing NASA’s science and technology payloads on U.S. commercial launchers.
PREFIRE joins a long list of NASA missions awarded to Rocket Lab, including the CAPSTONE mission to the Moon on Rocket Lab’s Electron launch vehicle and Lunar Photon satellite bus, the back-to-back launches in May 2023 of the TROPICS satellites for NASA’s hurricane monitoring mission, and the NASA Starling mission launched last month on Rocket Lab’s most recent Electron recovery launch.
“Missions like these are core to the whole reason why Rocket Lab was founded in the first place – to open up access to space to improve life on Earth – and climate change is a hugely urgent cause for us all. It’s a privilege to be able to support this important mission and an honor to be a continued trusted launch provider for small satellite missions with big impact.” — Peter Beck, Founder and CEO, Rocket Lab