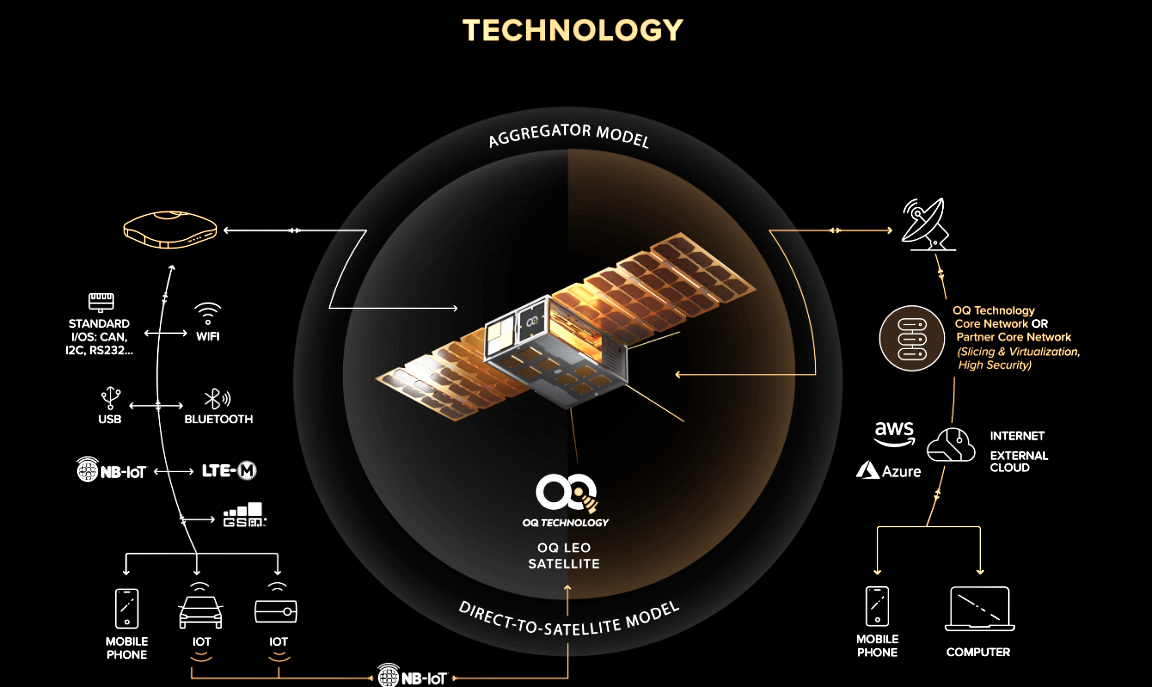
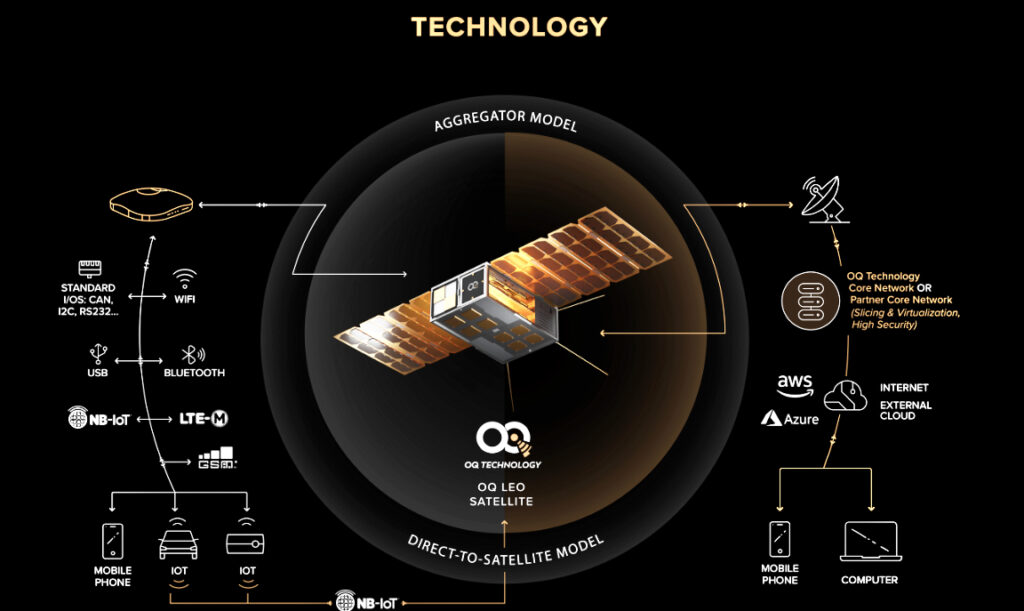
The United States Space Force (USSF) Space Systems Command (SSC) Commercial Satellite Communications (COMSATCOM) Office (CSCO) is seeking sources that are capable of supporting a Department of Defense (DoD) effort to launch and maintain communications satellites that allow for greater maneuverability and smaller size than traditional Geostationary Earth Orbit (GEO) satellites.
As the national security of the United States and its mission partners becomes ever more reliant on space-based capabilities, it is necessary to move in the direction of resilient constellations that can offer advanced capabilities.
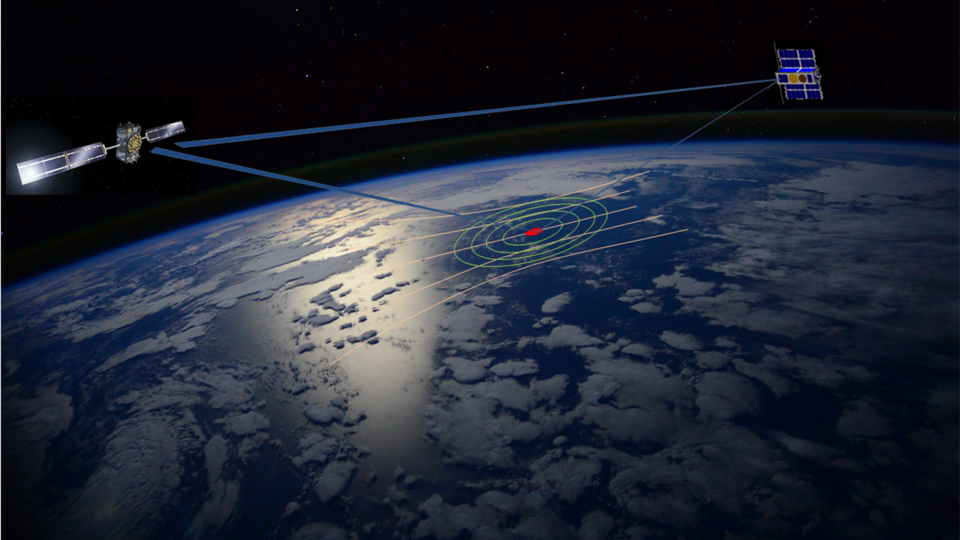
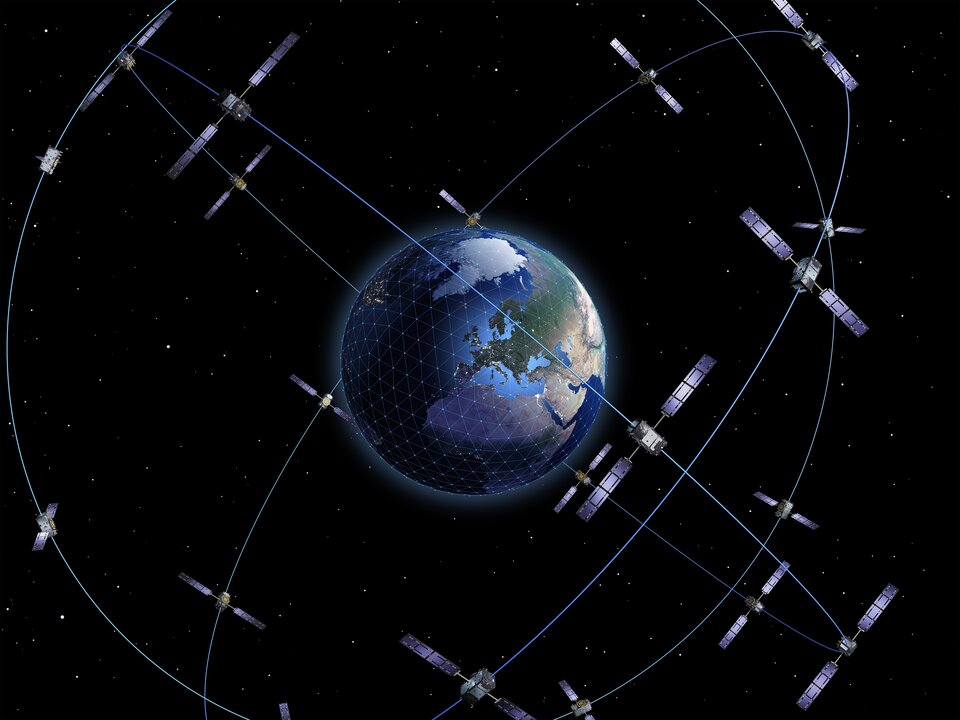
The SSC CSCO is seeking information for potential sources to provide support for a new class of commercially offered satellite communication services supported by GEO satellites using a constellation of small satellites capable of maneuvering between International Telecommunication Union (ITU) assigned orbital slots in the GEO arc.
Increased maneuverability using decentralized and spatially dispersed smallsats is imperative for the future resilience of both the constellation and the communications support for any user, without impact to existing user equipment and gateways.
In addition to providing a tailored capability statement indication the ability to provide the requested qualifications and services above, interested vendors, under NAICS Code 517410, are asked to submit the following information:
Vendor Information Requested
Name of Business and address
Cage Code
Business Type SB/Large
POC: Name/Phone number/email
Submit your response to the following individuals (include all):
Mr. LaMario Cato, Contracting Officer. Email: LaMario.Cato@spaceforce.mil
Mr. Jesse Guzman, Contract Specialist. Email: jesse.guzman.1@spaceforce.mil
This Sources sought is also posted on GSA under Reference number #RFQ1663982