Startical, the company created by ENAIRE (Europe’s fourth-largest air navigation services provider), and Indra will use a satellite produced by Kongsberg NanoAvionics to test the systems of the company’s future constellation of more than 270 smallsats that are set to provide air traffic services from space.

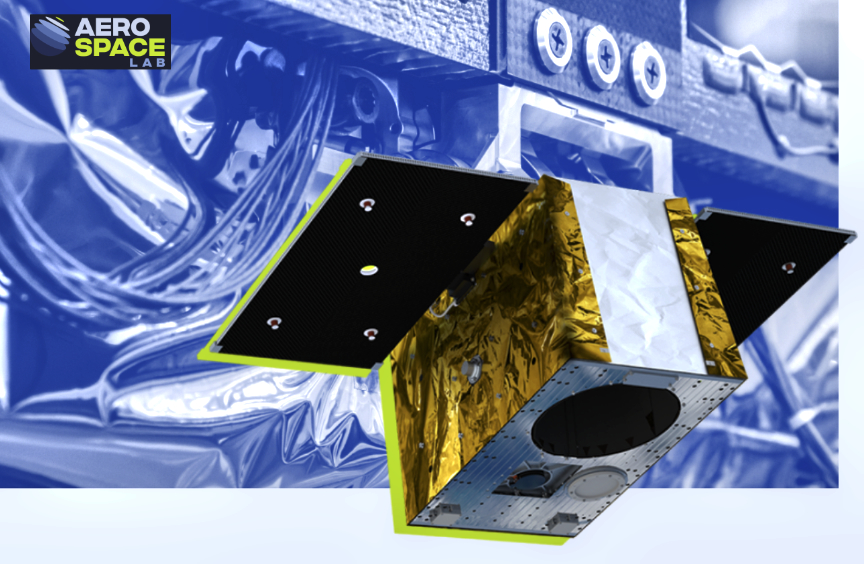
Startical has chosen NanoAvionics’s MP42 microsatellite bus, weighing approximately 110 kg, for a series of tests lasting six months. The mission will assess the performance of the smallsat’s VHF radio communication systems and the ADS-B surveillance systems directly from space. The test satellite will become operational in 2025.
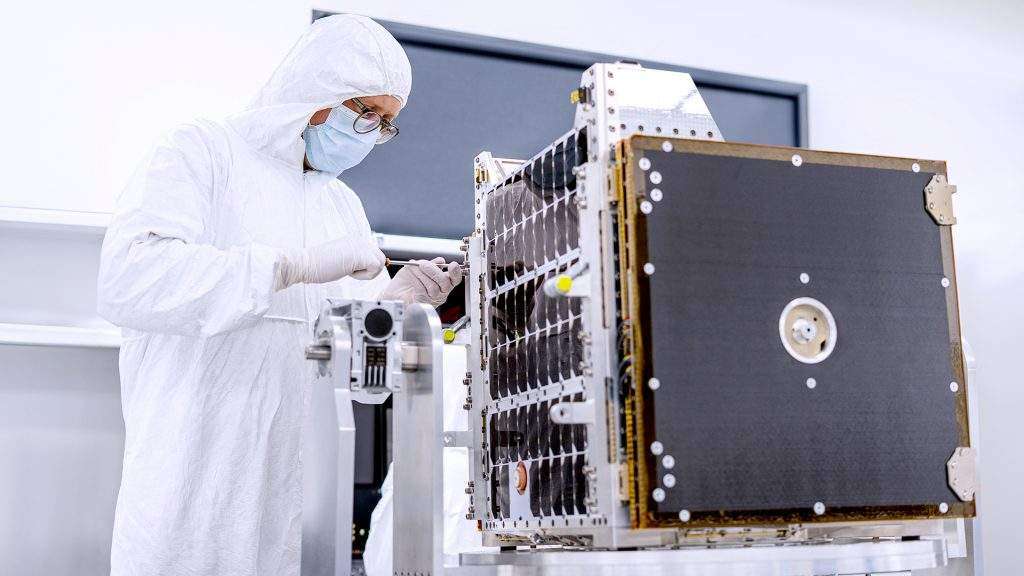

NanoAvionics will be tasked to provide the bus, integrate the payload, and to launch and execute the first mission operations to enable Startical’s experts to manage the ATM systems onboard.
Startical will carry out these tests in the wake of the International Telecommunication Union’s approval last December of the use of the aeronautical communications band from space – a historic milestone and a definitive boost for this pioneering project and a milestone for the aviation world, the company said.
J. Enrique González Laguna, CEO of Startical, said, “Our goal is to become the main global provider of air traffic management technology in the space segment and a market leader in satellite surveillance and voice and data communications services. Our constellation will call on highly innovative and distinctive technological solutions, including the incorporation of pioneering links between satellites and the use of artificial intelligence to make controlling them easier. Partnering with NanoAvionics will provide us with satellite technology and market-leading experience and allow us to test our new technology. This in turn will open new markets and services for us. They understand our requirements, have the skills to perfectly integrate our technology into their satellite bus and operate it from the ground.”
Žilvinas Kvedaravičius, CEO of NanoAvionics, said, “This is an excellent opportunity for us at NanoAvionics to become Startical’s partner. We will bring our leadership and expertise in small satellite technology, which will be ideally complemented by Startical’s advanced vision of air traffic management. We are committed to this mission and we will strive to demonstrate the capabilities and ongoing reliability of our small platform and mission services geared towards the customer. We are striving to speed up the deployment and lifespan of our systems in space in order to move New Space initiatives such as Startical on to their next phase of development. Bringing performance standards to the industry requires the robust quality and procedural assurance to which we are dedicated.”
About Startical
Startical is a public-private initiative for satellite technological innovation created by ENAIRE and Indra. The goal of Startical is to develop and deploy a constellation of small satellites at low altitude to enhance air traffic management with a global service vision across the entire planet. Startical aims to build and launch a satellite platform that will expand surveillance and communication coverage with aircraft, especially over vast oceanic or remote areas without coverage from ground-based air navigation infrastructure systems. Startical will be the first satellite platform for air navigation that includes, alongside aircraft position surveillance services (ADS-B), a VHF radio communication system between the controller and the pilot compliant with aeronautical standards. This represents a differentiating factor compared to similar initiatives. These new services will enhance safety, capacity, efficiency, and punctuality of flights, providing clear benefits for both airlines and passengers.
About Kongsberg NanoAvionics (NanoAvionics)
Kongsberg NanoAvionics is reshaping the space economy with our standardized small satellite platforms. We offer efficient, cost-effective satellite products and services that help organizations launch their space missions swiftly. Since 2014, over 120 projects in 50 countries have trusted us for our experience, technology and higher return on their satellite investment. We’re a globally local team of close to 300 international professionals with dedicated facilities in Lithuania, the United States, and the United Kingdom. As part of Kongsberg Defense and Aerospace since 2022, we’re further strengthening our commitment to robust, innovative, secure and reliable space solutions.













 weather risk mitigation platform, maritime route optimization, and renewable energy power forecasts. The Company will provide its customers in various sectors, including energy, commodity hedging and trading, maritime, aviation, supply-chain, insurance, transportation, defense and more, with lower latency, extended lead times and heightened forecast accuracy.
weather risk mitigation platform, maritime route optimization, and renewable energy power forecasts. The Company will provide its customers in various sectors, including energy, commodity hedging and trading, maritime, aviation, supply-chain, insurance, transportation, defense and more, with lower latency, extended lead times and heightened forecast accuracy.