NASA has selected 15 companies to provide flight and payload integration services to advance technologies and procedures for operating in space, including testing in high-altitude, reduced gravity, or other relevant environments — examples of payloads include NASA science instruments or technology demonstrations.
The indefinite-delivery/indefinite-quantity (IDIQ) base contract awards are firm-fixed-price with a total combined value of $45 million and a performance period of five years. The flights and other services covered by these contracts are for use by NASA and other government agencies. The types of platforms that will be used for testing include suborbital rockets, high-altitude balloons, orbital spacecraft and satellites, and, in some instances, suborbital rockets that can accommodate carry people.
The following companies have been awarded contracts to provide services through demonstrated commercial capabilities:
- Aerostar International, Inc., of Sioux Falls, South Dakota
- Angstrom Designs Inc., of Santa Barbara, California
- Astrobotic Technology Inc., of Pittsburgh
- Astro Digital US Inc., of Santa Clara, California
- Blue Origin Texas, LLC of Van Horn, Texas
- Galactic Enterprises, LLC of Las Cruces, New Mexico
- Loft Orbital Federal, LLC of Golden, Colorado
- Momentus Space LLC of San Jose, California
- Near Space Corp., of Tillamook, Oregon
- Rocket Lab USA Inc., of Long Beach, California
- Space Exploration Technologies Corp., of Hawthorne, California
- Spire Global Subsidiary, Inc., of Vienna, Virginia
- Tyvak Nano-Satellite Systems, Inc., of Irvine, California
- Varda Space Industries, Inc., of El Segundo, California
- World View Enterprises Inc., of Tucson, Arizona
The contracts are in support of NASA’s Flight Opportunities and Small Spacecraft Technology programs, both part of the NASA’s Space Technology Mission Directorate at the agency’s headquarters in Washington. These programs support technology development and missions to change the pace of space exploration, discovery, and space commerce.






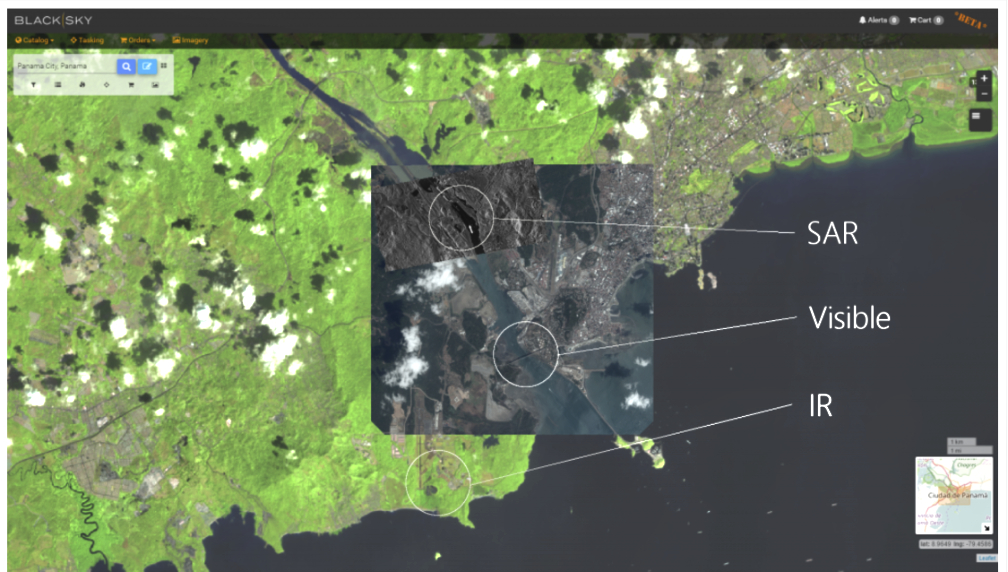









 signifies a monumental achievement for Sidus Space, marking the company’s entrance into the next era of space technology and data services.
signifies a monumental achievement for Sidus Space, marking the company’s entrance into the next era of space technology and data services.