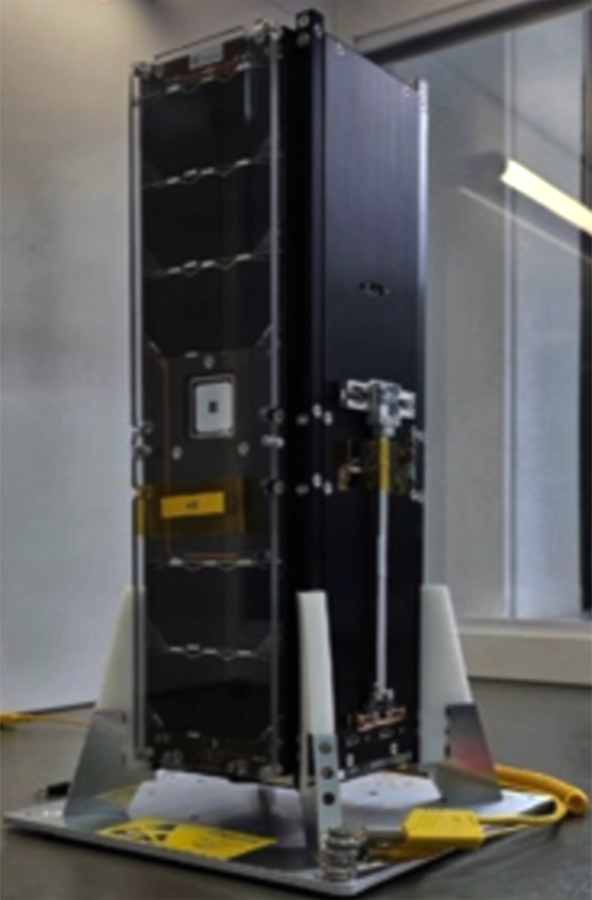
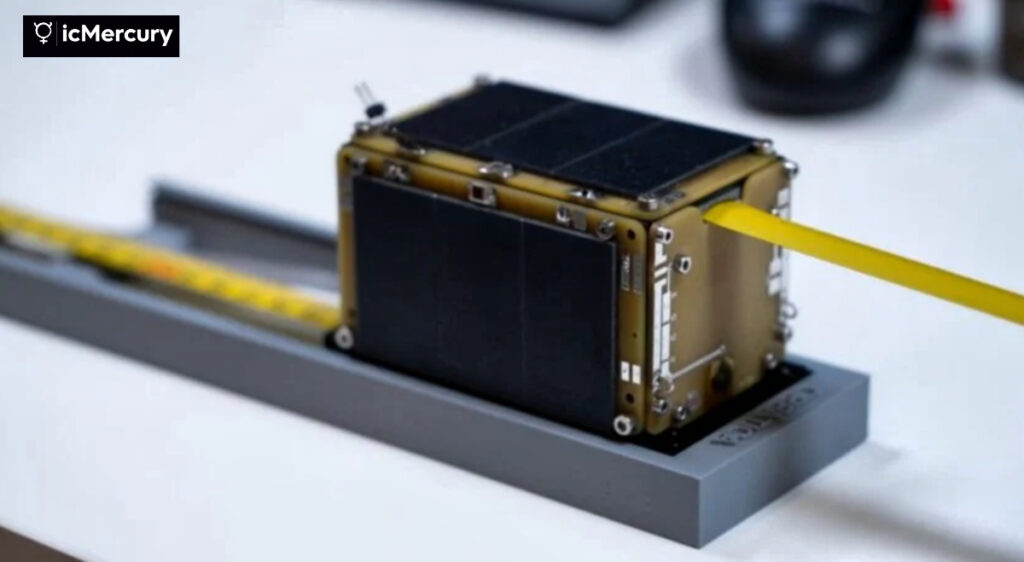
Startical, a company created by ENAIRE and Indra to optimize air traffic management from space, has launched its first satellite, the IOD-1 (In-Orbit Demonstrator-1), via launch integrator Exolaunch as part of the Transporter-13 rideshare mission with SpaceX.


Startical entrusted GomSpace with the satellite’s manufacturing, while its specification and validation have been carried out by Indra with support from ENAIRE. Additionally, Exolaunch handled the satellite’s integration into the rocket and subsequent deployment into orbit. The launch occurred at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
Equipped with a powerful VHF antenna and an ADS-B surveillance system, IOD-1 aims to demonstrate the feasibility of real-time communications between air traffic controllers and aircraft using signals transmitted from space. The satellite is part of ECHOES project, which aims to gather evidence on how this satellite-based solution can enhance ATM services and generate positive environmental effects.
The project is co-funded by the European Union through the Connecting Europe Facility (CEF) and managed by the European Climate, Infrastructure, and Environment Executive Agency (CINEA), with support from the SESAR Joint Undertaking.
The demonstrator will explore the limits of implementing these technologies on CubeSats, which are characterized by their standardized miniaturized format, low cost, and high efficiency. Placing it into orbit will validate a space-based solution designed specifically for air traffic management, fully compliant with existing aeronautical communication standards.
Currently, in transoceanic flights or over remote areas, aircraft traverse regions without real-time voice communication coverage. This requires them to maintain large separation distances to ensure safety, reducing airspace efficiency and limiting traffic volume management.
With Startical’s solution, aircraft positions will be continuously monitored via satellite, while real-time, high-quality voice and data communications between controllers and pilots will be possible even in areas currently lacking coverage. This technology will enable more efficient and safer air traffic management, particularly useful in critical situations such as route changes due to storms or onboard medical emergencies. Additionally, it will contribute to more sustainable aviation by allowing aircraft to select optimal routes, thereby reducing fuel consumption.
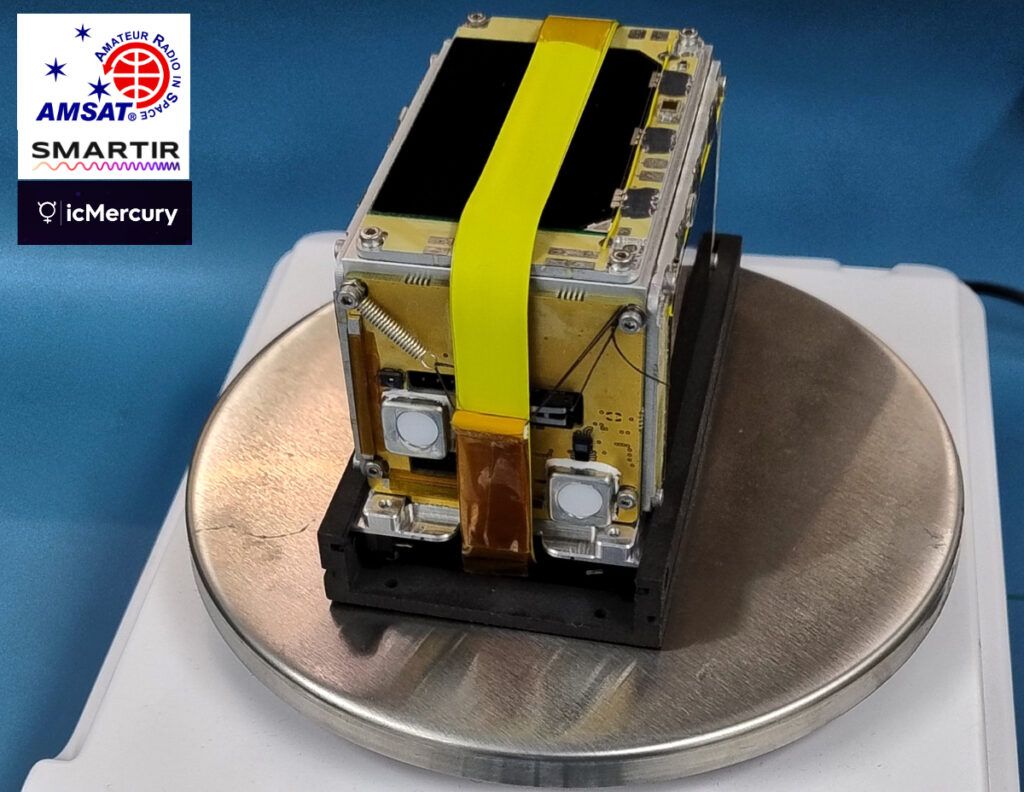
In February 2025, Startical introduced its second satellite, IOD-2, which has undergone testing at Spain’s National Institute for Aerospace Technology (INTA) in Madrid. Like its predecessor, IOD-2 is part of the ECHOES project.
Following the deployment of the IOD-1 and IOD-2 demonstrators, Startical will conduct various proof-of-concept tests to confirm the technological viability. These studies will take place in the South Atlantic corridor, covering airspaces (FIR) over the Canary Islands, Azores-Santa Maria, Dakar Oceanic, Cape Verde, and the Atlantic region of Brazil. The initiative will involve air navigation service providers such as ENAIRE, NAV Portugal, ASA, ASECNA, and DECEA, highlighting international collaboration and interest in Startical’s vision.
“We are proud to become a space-based company with the launch of IOD-1, a demonstrator that paves the way for the Startical constellation. With over 200 satellites in low Earth orbit, this constellation will provide global coverage, transforming air traffic management,” said Juan Enrique González Laguna, General Manager of Startical.
Carsten Drachmann, CEO of GomSpace, said, “We appreciate Startical’s trust in our 16U CubeSat for this mission, which will have a positive impact on the efficiency and sustainability of air traffic management. We look forward to seeing the performance of IOD-1 in orbit.”