General Atomics Electromagnetic Systems (GA-EMS) was recently awarded a contract from the Space Development Agency (SDA) to demonstrate the capabilities of the company’s Optical Communication Terminals (OCTs) hosted on GA-EMS’ GA-75 (75 kilogram class) spacecraft while in LEO.
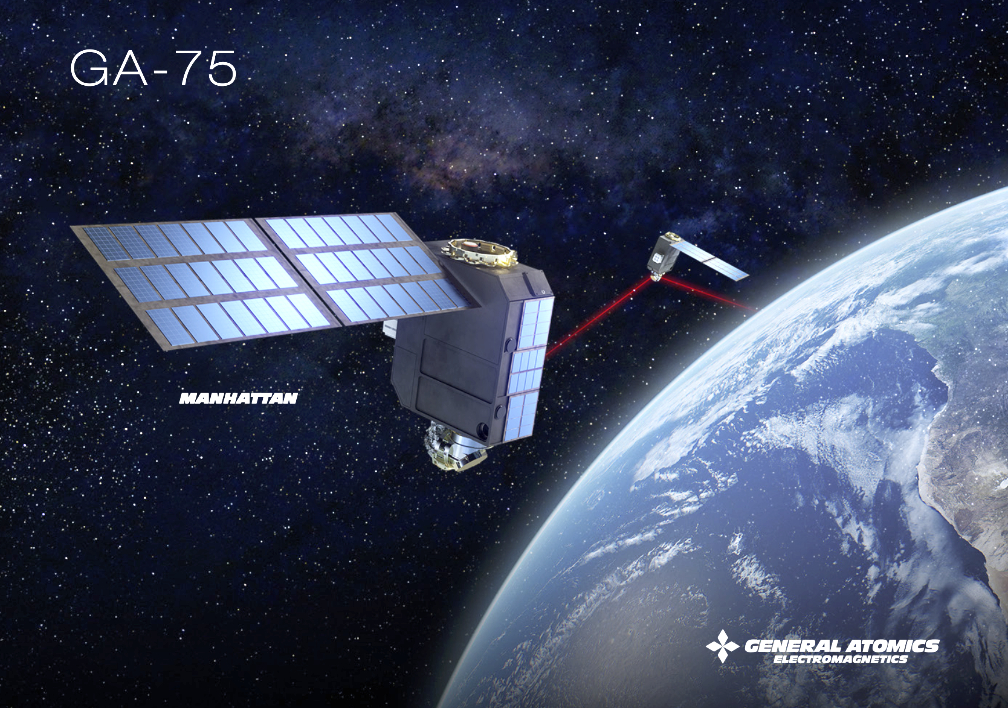

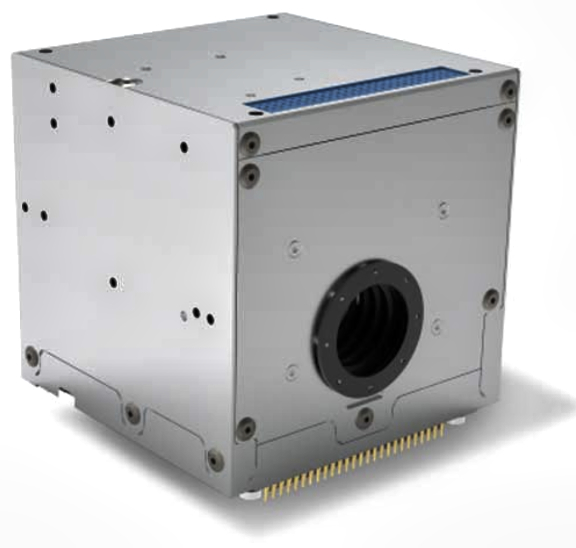
GA-EMS is designing and building two OCTs to provide robust space-to-space communication in a degraded environment and establish and maintain links to meet SDA standards and requirements. The OCTs can support a vast network of satellites, data and information sharing, and collective on-orbit computing resources to support customer and mission requirements.
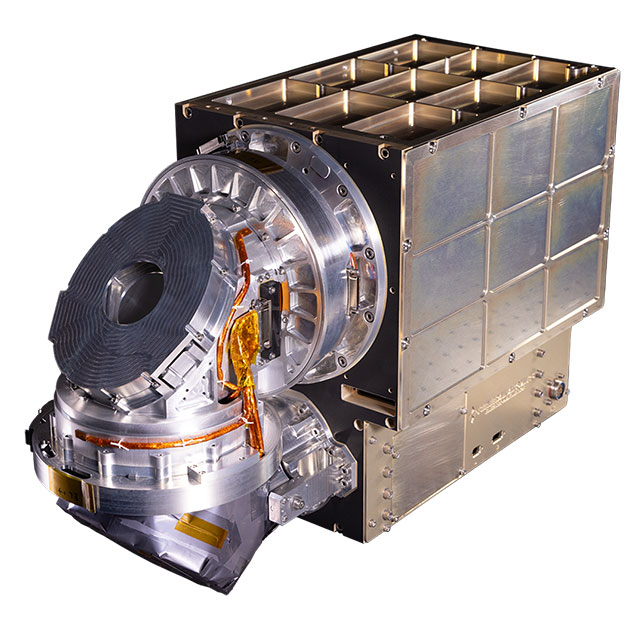
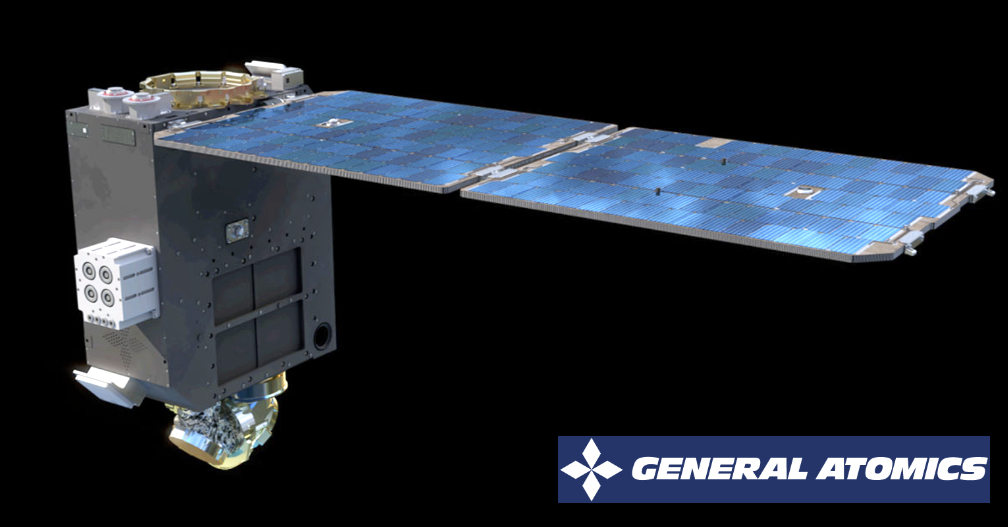
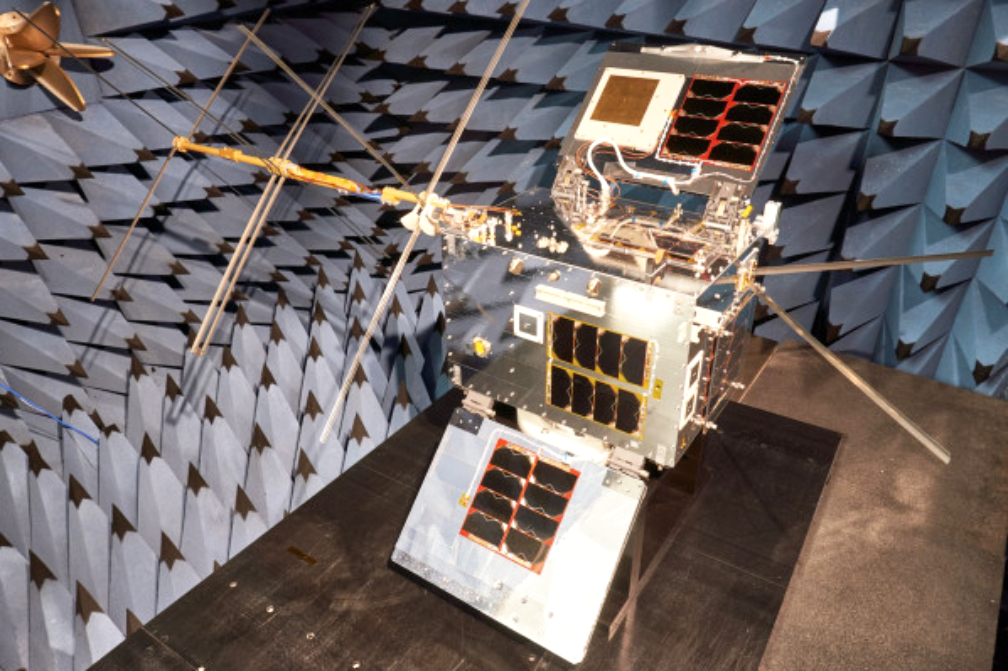
The OCTs will be integrated on two GA-EMS GA-75 spacecraft. The GA-75 is a resilient, modular, and configurable half-ESPA bus design with capabilities to support a variety of communications and Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR) payloads and missions. The GA-75 is a commercially available platform that utilizes standard payload interfaces to enable seamless integration and mission-ready delivery times. It is also compatible with multiple launch vehicles and can package two spacecraft per ESPA port or fill a single ESPA port depending on mission payload size.
“We’re excited to continue working with SDA and look forward to demonstrating our OCT capability developed, built, and tested by GA-EMS, and integrated on GA-EMS-designed and built spacecraft,” said Scott Forney, president of GA-EMS. “This contract supports the deployment of next generation optical communication technologies that will provide faster, more secure, higher fidelity transmissions, and greater resiliency to ensure 24/7 connectivity from the Earth to space.”
General Atomics Electromagnetic Systems (GA-EMS) Group is a global leader in the research, design, and manufacture of first-of-a-kind electromagnetic and power generation systems. GA-EMS’ history of research, development, and technology innovation has led to an expanding portfolio of specialized products and integrated system solutions supporting aviation, space systems and satellites, missile defense, power and energy, and processing and monitoring applications for defense, industrial, and commercial customers worldwide.








 (Rapidly Attachable Fluid Transfer Interface) refueling ports and its GRIP
(Rapidly Attachable Fluid Transfer Interface) refueling ports and its GRIP