Phase Four, the creator of the radio-frequency thruster (RF Thruster) for satellite propulsion, announced that the company has finalized a lease for an expanded manufacturing facility to support high volume production of the firm’s Maxwell engine product line for commercial and government missions.

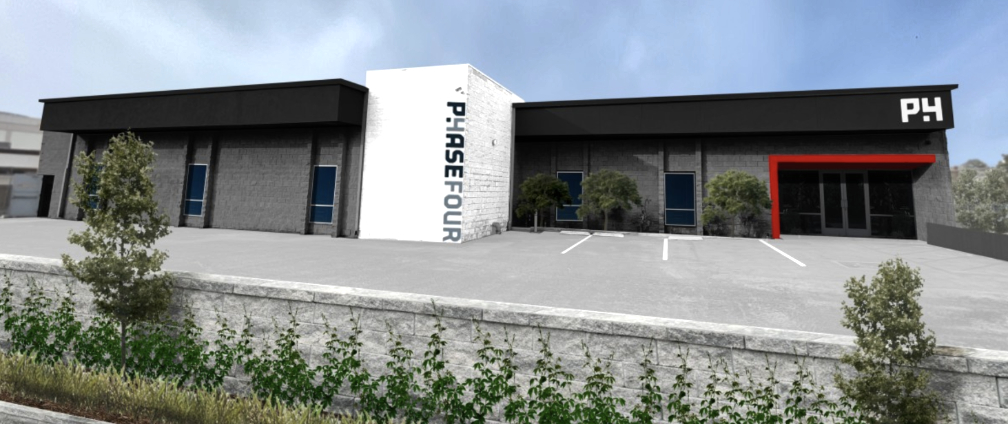
The new site, located in Hawthorne, California, will host a manufacturing facility more than 3x the size of Phase Four’s current facility in El Segundo. The facility will also house a dedicated environmental testing facility, which will continue to reduce the company’s industry leading, sub-4 month, lead times. As part of its expansion, Phase Four will also stand up a dedicated R&D cell to support the development of higher performance thrusters and higher power propulsion systems for larger spacecraft.

Phase Four’s Maxwell Block 1 engine gained flight heritage in 2021 and is currently operating on several commercial small satellites. The company is set to begin production of its Block 2 Maxwell engine in the second quarter of 2022. Block 2 uses the company’s second generation RF Thruster and offers significant performance improvement over the Block 1 engine.
Phase Four is also working to adapt the RF Thruster to operate on nontraditional propellants that are less expensive and more readily obtained than purified noble gases like xenon and krypton. The company is currently performing thrust measurements with its Maxwell engine adapted to operate on iodine on an Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) sponsored program, and recently won a Space Force Pitch Day award to test on green propellant.
“With the increased demand for our high performance Maxwell engine to support the steadily growing number of small satellite constellations, we made the decision to first focus on our manufacturing process ” said Phase Four CEO, Beau Jarvis. “We demonstrated through several production runs in 2021 that Maxwell engines can be built, tested and delivered to customers in under four months. Now with a larger, dedicated manufacturing facility we will scale up production runs to support delivery of over 100 Maxwell engines annually.”
“Our aim is to catalyze industry in space by delivering a short lead time plasma thruster, and developing a thruster that can operate on next generation propellants. Phase Four’s Hawthorne site is essential to achieving these goals. Our new facility will allow us to vertically integrate flight unit manufacturing and testing, removing key throughput limiters in our engine production line. Furthermore, the facility will allow us to disaggregate shared vacuum chambers between R&D and production, removing internal competition for resources and thereby accelerating the development of our RF thruster,” said Phase Four CTO, Umair Siddiqui. “This comes at the right time; given the supply chain insecurity of legacy plasma electric propulsion systems. Both government and commercial customers need domestic propulsion systems with short lead times to support rapid constellation deployments.”
In addition to the new facility opening, which is set for early Q4 2022, Phase Four is also gearing up for a hiring push. The Company hopes to double its employee count by the end of next year, said CEO Beau Jarvis. “We are excited to grow the Phase Four family as we begin to realize our mission of catalyzing the space industry through mass manufacturing of our Maxwell engines and the introduction of engines that enable new missions by leveraging advanced propellants.”
Phase Four is a disruptive provider of next generation electric propulsion (EP) solutions for small satellites. The company was founded in 2015 to address the demands of the rapid proliferation of satellite constellations and to accelerate the advancement of its radio-frequency thruster (RFT). The Phase Four RFT represents a revolutionary new architecture that realizes lower cost, mass-manufacturability, miniaturized power electronics, and propellant agnosticism over incumbent technologies, without compromising performance. In 2021 Phase Four’s Maxwell turn-key propulsion system achieved flight heritage and is now being regularly utilized by small satellite operators.