Planet has announced a multi-year, multi-launch agreement solidifying SpaceX as the firm’s go-to-launch provider through the end of 2025. The first planned launch under this agreement is Flock 4x, 44 SuperDoves on the Falcon 9 Transporter-3 SSO rideshare mission scheduled for launch December 2021.

The demand for flexible, high-resolution imagery of the Earth has skyrocketed in recent years as companies across the world seek daily global insights for their industries. While Planet already operates the world’s largest constellation of Earth Observation (EO) satellites, with 200 currently in orbit, the company is continuing to innovate by rapidly building satellites with the newest advances in imagery technology. Planet’s accessible data has transformed the industry by pushing the satellite imagery market past only serving the traditional satellite imagery consumer, multi-billion dollar governments, to also serving a new future of global companies and non-traditional users.
SpaceX’s rideshare program has allowed companies such as Planet to meet their ambitious targets for product launch. This multi-year launch agreement enables Planet to efficiently launch much of the firm’s emerging satellite projects including future SuperDoves and Carbon Mapper. The company is accelerating its work to deliver insights in EO in high resolution and with hyperspectral imaging. Building this collaborative agreement with SpaceX marks an important step for agile aerospace in the New Space industry.

To date, Planet has launched 83 satellites with SpaceX over the course of seven launches, the most recent of which included the launches of SkySats 16-18 and 19-21 aboard Starlink missions, and the launch of Flock 4s, 48 SuperDoves, on the record-breaking Transporter-1 SSO rideshare launch.
Beyond SpaceX, Planet maintains a diversified launch manifest to mitigate risks inherent to the launch industry. Moving forward, Planet will continue to operate with a variety of launch providers to ensure that launch needs can still be met in the event of the unavailbility of specific providers. By engaging with a diversified manifest, Planet can find launches to the right orbit in the right time frame for each evolving satellite project.
Last month, Planet entered into a definitive merger agreement with dMY Technology Group, Inc. IV (NYSE:DMYQ), a special purpose acquisition company (SPAC) to become a publicly-traded company.

“I‘m excited to continue our partnership with SpaceX. We’ve had seven launches to date. But more than that, we’ve pioneered together rapid planning, manufacturing, and launch of satellites that only Planet and SpaceX could together have achieved,” said Planet CEO Will Marshall.
“We’re honored that Planet has chosen SpaceX as its go-to launch provider,” said SpaceX Vice President of Commercial Sales, Tom Ochinero. “As the demand for Planet’s services continues to soar, SpaceX’s regular launch cadence will allow Planet’s customers to use its services with as little downtime after manufacturing as possible.”
















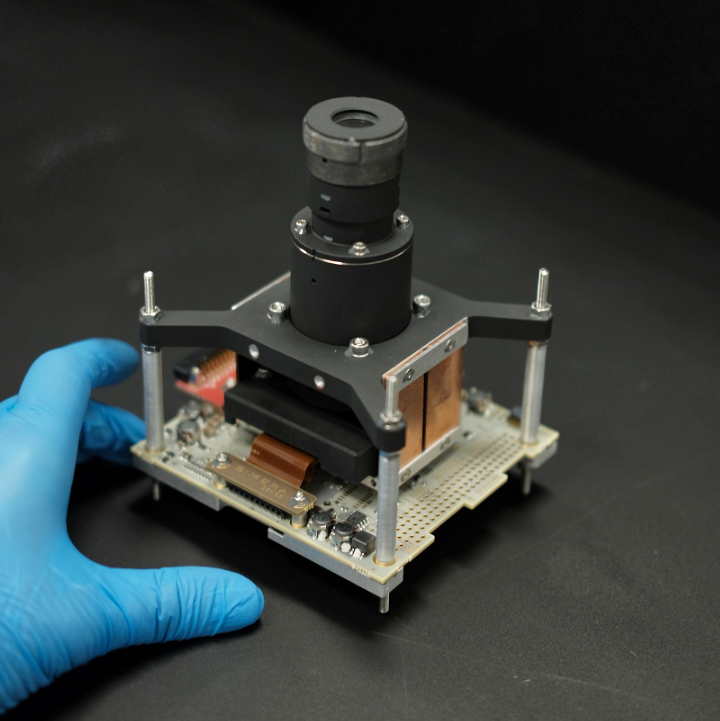













 , a powerful and the smallest radiation-characterized space AI GPGPU. The new, small form factor (SFF) system is rated for space flight and smallsat constellations used in Near Earth Orbit (NEO) and Low Earth Orbit (LEO) applications.
, a powerful and the smallest radiation-characterized space AI GPGPU. The new, small form factor (SFF) system is rated for space flight and smallsat constellations used in Near Earth Orbit (NEO) and Low Earth Orbit (LEO) applications.