Kongsberg Defence & Aerospace (KONGSBERG) has signed two contracts with ArianeGroup to deliver technology to Europe’s new Ariane 6 launcher, managed and funded by the European Space Agency (ESA).

KONGSBERG will deliver the forward booster attachment and release mechanism (UPPA), the Optical Safety Barrier (OSB) and the Level Conditioner for the next-generation launcher. The contract is a 30 year frame agreement with a total value of up to 200 million euros.

UPPA, the forward booster attachment and release mechanism, transmits power from the engines to the lower part of the launcher during the critical time of liftoff. The boosters use all their fuel within the first two minutes after the rocket launcher lifts off from the launch pad, and are then with extreme precision released and discarded from the launcher. KONGSBERG has delivered the booster attachment for Ariane 5 since 1996. The booster attachment for Ariane 6 is modified to fit the new launcher design.
The Level Conditioner (LC) is an important part of the fuel level measurement system and it is used for monitoring the fuel levels of liquid Oxygen and Hydrogen. The LC units are part of the functional chain and are used during all phases of the flight, check of full tanks before lift-off, level control during flight and stop control of the engines when the tanks are empty. There are typically 25 LC’s in each launcher. The Level Conditioner was originally designed for Ariane 5 and has been used in all flights since 1996 and will continue into Ariane 6. More than 3,400 flight models of the Level Conditioner are built and launched.
The Optical Safety Barrier (OSB) acts as a safety barrier for the fiber-optic based pyrotechnic control and command system onboard the Ariane 6. Pyrotechnic is used in both launchers and satellites in space and is traditionally based on electro pyro and pyro lines with primary explosives. The fiber-optical pyro system onboard Ariane 6 offers significant cost reductions in terms of installation and procurement. The devices are relatively simple, light and compact and provide near-instantaneous response with very little input energy. This will be the first time Opto-Pyrotechnics has been successfully integrated and used on a European space launcher. The control and command system onboard the Ariane 6 system is a technological breakthrough, and will enhance the safety, reliability and performance of the launch system.
According to ESA, the Ariane 6 launcher will have the flexibility to launch both heavy and light payloads. While the Ariane 5 mainly launches satellites into GEO two at a time, the Ariane 6 is designed to launch a wider range of satellites, including LEO, smallsat constellations and small, geostationary satellites.

Ariane 6 is modular, flexible and competitive and will be the optimum launch solution for commercial and institutional customers. This new launcher – developed by ArianeGroup and its European industrial partners – combines proven solutions with innovation in order to address the changing needs of the market, allied with the unparalleled reliability of the Ariane family.
Ariane 6 will be available with two or four solid rocket boosters, depending on the required performance. The launcher will be more than 60 meters, and the weigh will be almost 900 tons when launched with a full payload.
Kongsberg Defence & Aerospace’s division for Space and Surveillance is Scandinavia’s largest supplier of space equipment to ESA, and the division is a leading supplier of equipment to scientific satellites, Earth Observation (EO) satellites and launchers. With strong design & manufacturing capability, and with more than 30 years’ experience with development, qualification and delivery of products for launcher and satellites, KONGSBERG has contributed to over 100 successful launches.
Ariane 6 will be launched from Europe’s Spaceport, in Kourou, French Guiana (South America).
“We are very pleased that this contract allows us to continue our long-lasting and valuable collaboration with ArianeGroup, the Lead industrial contractor and design authority for Ariane 6. This represents an important milestone to KONGSBERG,” said Harald Aarø, Executive Vice President KONGSBERG’s division for Space and Surveillance.
“These contracts are a result of our strong and reliable product deliveries to Ariane 5. We have also contributed to a technology shift in the European launcher industry through the development of the OSB, in addition to developing a product for the future, “ said Sedsel Fretheim Thomassen, Program Manager, KONGSBERG Launcher Mechanisms & Electro-Optics.






 precision LEO PNT (Positioning, Navigation and Timing) service leverages the recent advances in smallsat technology to provide users with a secure and robust alternative to traditional GNSS. Xona’s patent pending system architecture uses the efficiency of smallsats to provide an affordable global service with more than 10x better accuracy and 100x better interference mitigation than the legacy systems.
precision LEO PNT (Positioning, Navigation and Timing) service leverages the recent advances in smallsat technology to provide users with a secure and robust alternative to traditional GNSS. Xona’s patent pending system architecture uses the efficiency of smallsats to provide an affordable global service with more than 10x better accuracy and 100x better interference mitigation than the legacy systems.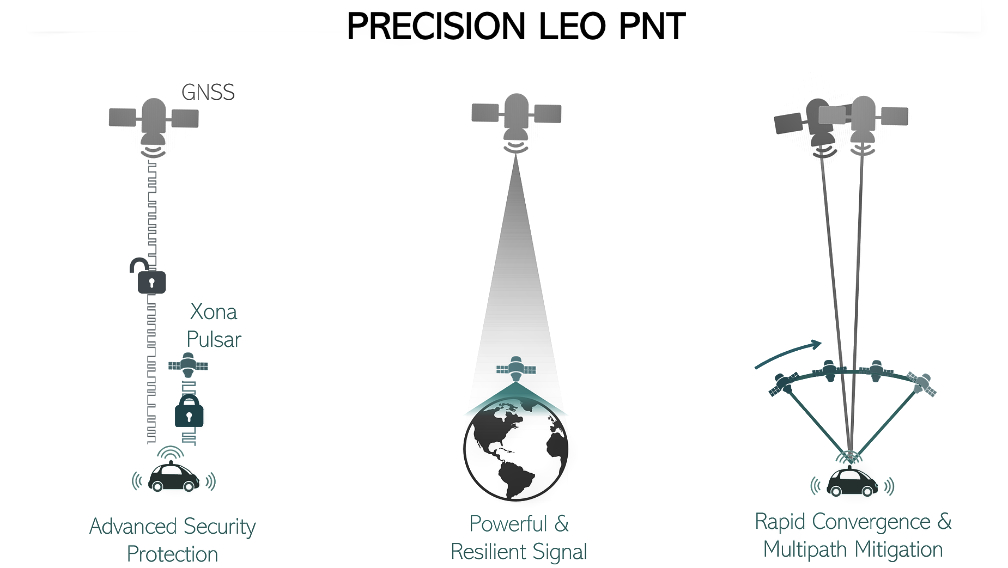













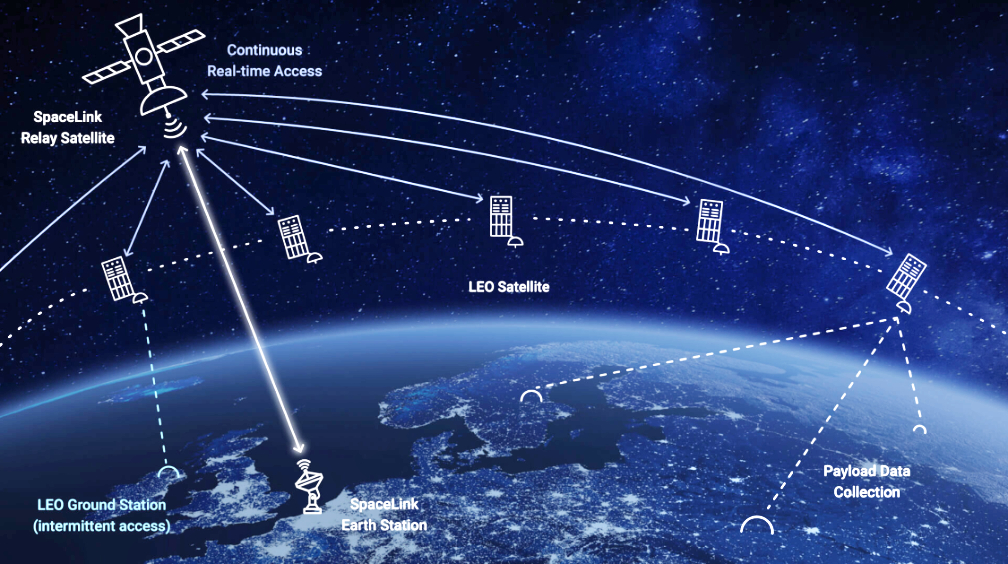

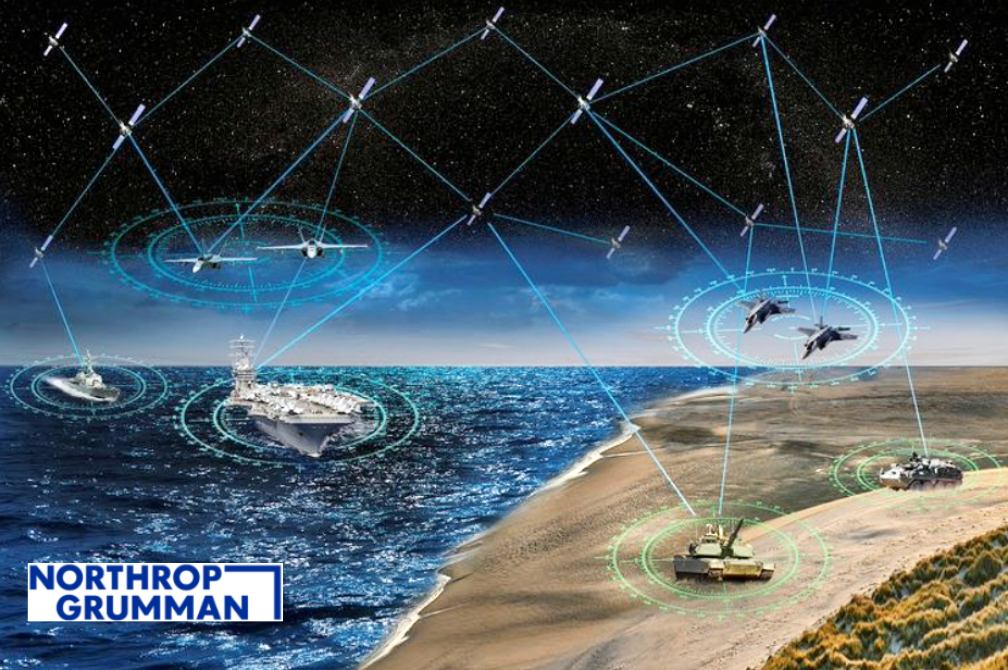
 data relay system provides global coverage to empower space system operators to maximize use of their assets.
data relay system provides global coverage to empower space system operators to maximize use of their assets.