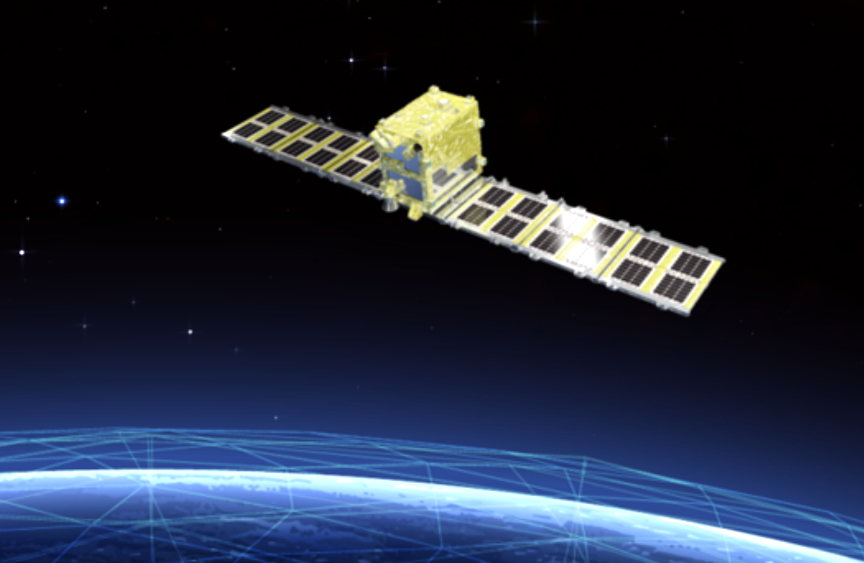
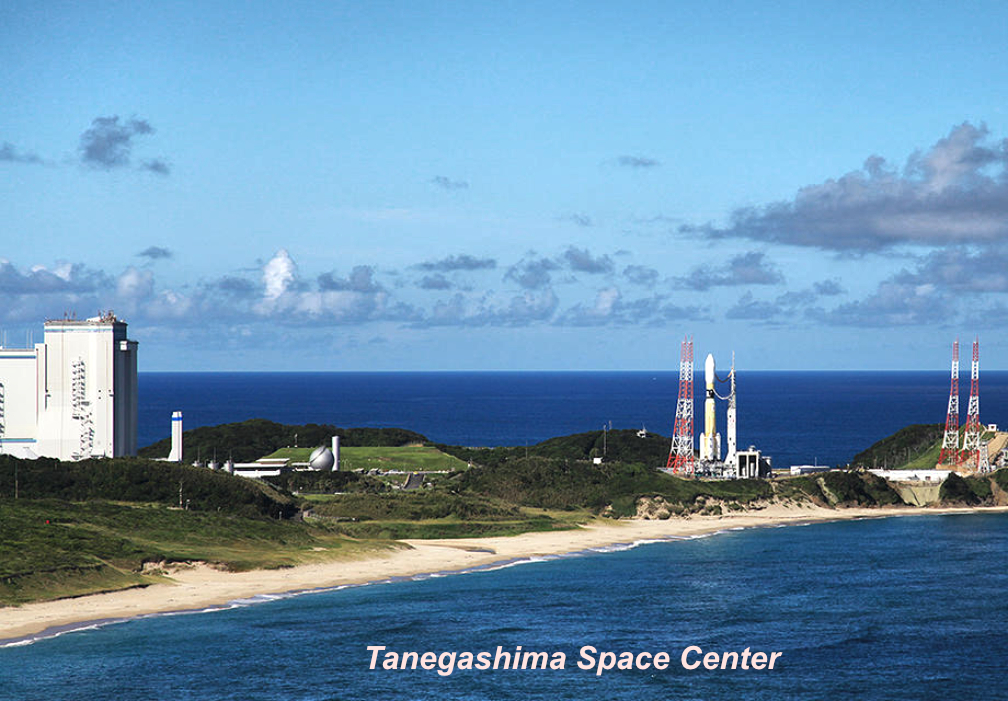
The launch schedule of MICHIBIKI No.5, Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZS-5) that will be aboard the 8th H3 Launch Vehicle (H3 F8: Flight No.8) is as follows…

- Launch date: December 7, 2025
- Launch Window: 1:30 (JST) through 12:30 (JST)*
- The time is the 24-hour clock
- Reserved Launch Period: December 8, 2025 through January 31, 2026
- Launch site:Yoshinobu Launch Complex at the JAXA Tanegashima Space Center
- Note: Launch time during the reserved launch period will vary.

QZSS (Michibiki) has been in operation since November of 2018 to develop a stable, satellite positioning service that can be used in all locations at all times. This system is compatible with GPS satellites and can be used with them in an integrated fashion. In this way, the satellite positioning service environment was dramatically advanced. QZSS can be used even in the Asia-Oceania regions with longitudes close to Japan, so its usage will be expanded to other countries in these regions, as well.