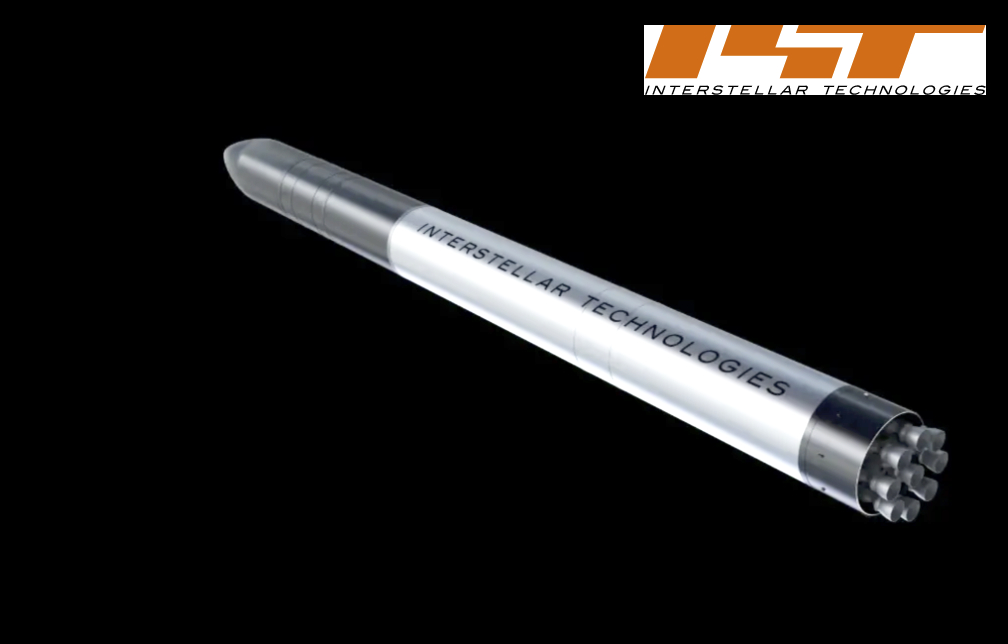
Interstellar Technologies Inc. has established a basic agreement, signed on March, 2024, with the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), regarding the procurement of launch transport services.

This agreement is designed to select private-sector entities capable of launching satellites developed under JAXA’s small satellite missions, thereby advancing the commercialization of space transportation services by startups and other entities through launch contract procurement. Notably, the Japanese government has proposed a policy initiative (*1) to secure approximately 30 domestic launch opportunities annually, using both government and private rockets, by the early 2030s. In light of this initiative, Interstellar will continue to further autonomous domestic space access through the ongoing development of the rocket ZERO, which integrates reliability and cost competitiveness.
This agreement is established in accordance with JAXA-SMASH (JAXA – Small Satellite Rush Program), a program aimed at expanding transportation and small satellite missions. Privately selected transport services under this program will launch small satellite missions publicly solicited by JAXA(*2). Interstellar has been designated as “Launch Operator A,” receiving priority for future procurement contracts.

In line with the new Space Basic Plan approved by the Japanese Cabinet in June 2023, the Japanese government targets the launching all domestic satellites, regardless if government or private, using Japan’s flagship rockets or private rockets, starting from fiscal year 2028. This initiative also aims to capture overseas demand.
In September of 2023, Interstellar was selected for the “Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR Phase 3)” by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, encouraging research and development by startups and others (*3), with governmental support to be provided for both research and development and launch contract procurement to achieve early realization of affordable, frequent private space transport services domestically.5
ZERO is a smallsat launch vehicle designed to target the growing market for small-sized satellites in recent years. Building on the knowledge gained from the successful launch of the private suborbital launch vehicle MOMO, the first of its kind in Japan’s private sector, Interstellar is progressing toward the first launch of ZERO.
ZERO’s space transportation service distinguishes itself with competitive pricing—at less than 800 million JPY per launch (in mass production)—made possible through an integrated development and manufacturing process. Another key strength is its flexibility to provide customized launches tailored to the rising needs of satellite companies. For satellite companies in Japan, Asia, and Oceania, proximity to the launch site ensures convenience, reducing launch-related time and costs and enhancing overall value.
With an eye on recent trends and the demand both locally and globally, ZERO is enhancing its capacity to launch satellites of up to 800 kilograms into LEO. This strategic contributes to the establishment of an independent domestic space transportation service. Simultaneously, it positions Interstellar to establish a firm presence in the Asia-Oceania and European markets.
Takahiro Inagawa, CEO of Interstellar Technologies, said, “Space technology’s complexity and the limited opportunities for challenges have hindered the expansion of space utilization and industrial growth. JAXA-SMASH presents an innovative opportunity for demonstrating cutting-edge technology with satellites to break through these limitations. We are honored to be part of it, bringing our space transport services to the table. Looking ahead, we anticipate a substantial increase in space transport opportunities domestically. However, we’re all hands on deck, pushing ahead with technology demonstration and business development, ready to seize the day in this new era.”
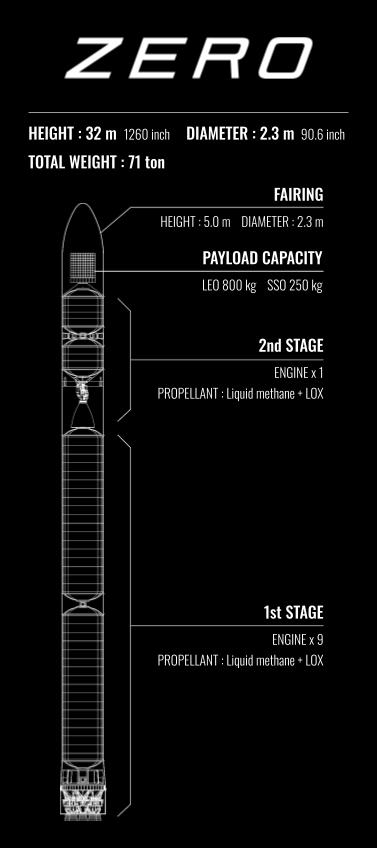
ZERO: Specifications
Height: 32m
Diameter: 2.3m
Wet mas: Weight: 71 ton
Propellant: Liquid Methane (Biomethane) Oxidizer: Liquid Oxygen
Number of Engines: 1st Stage: 9, 2nd Stage: 1
Payload Capacity: LEO 800kg / SSO 250kg (Future Maximum Capacity)
*1 Space Policy Committee 109th Meeting Agenda https://www8.cao.go.jp/space/comittee/dai109/gijisidai.html
*2 JAXA-SMASH Web Page https://aerospacebiz.jaxa.jp/jaxa-smash/launch-service/
*3 Press Release dated September 29, 2023 https://www.istellartech.com/en_news/830


























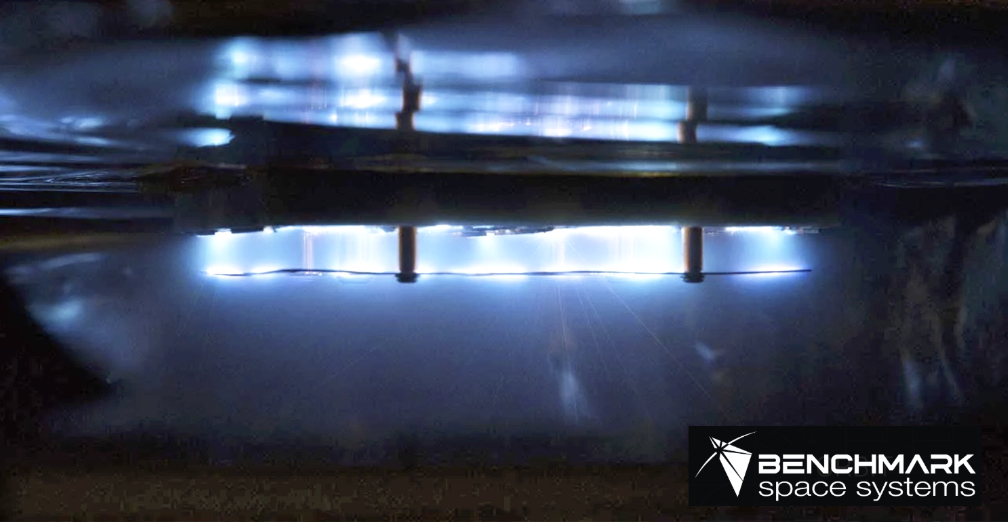
 electric propulsion system has successfully deployed and will undergo subsystem health check and operational verification, including a range of firing modes, aboard mission prime
electric propulsion system has successfully deployed and will undergo subsystem health check and operational verification, including a range of firing modes, aboard mission prime