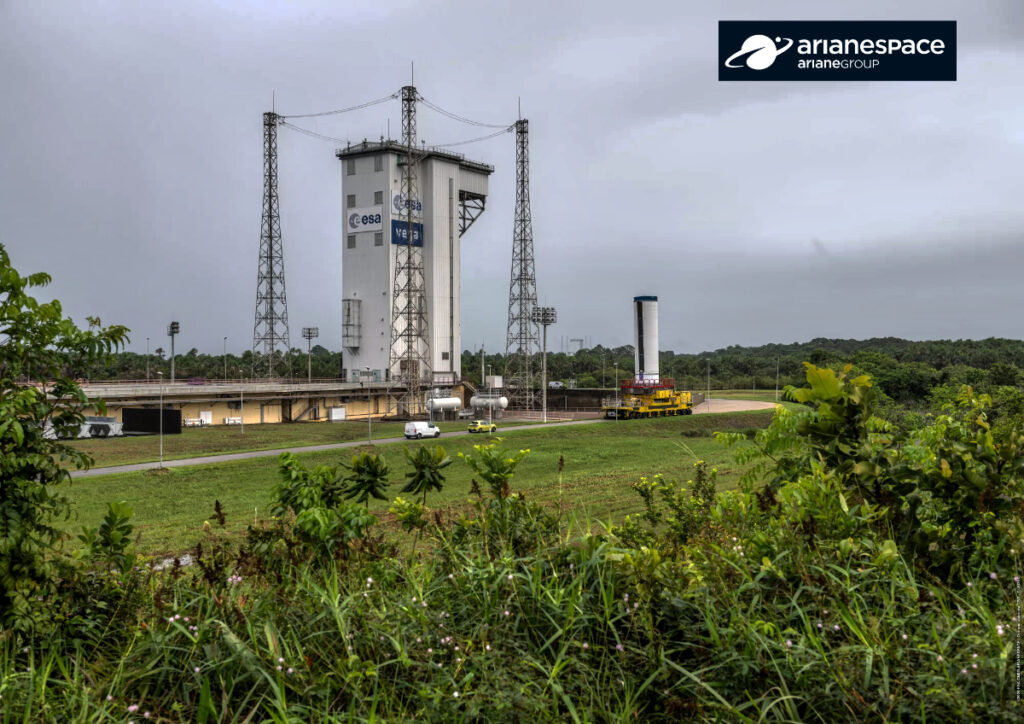
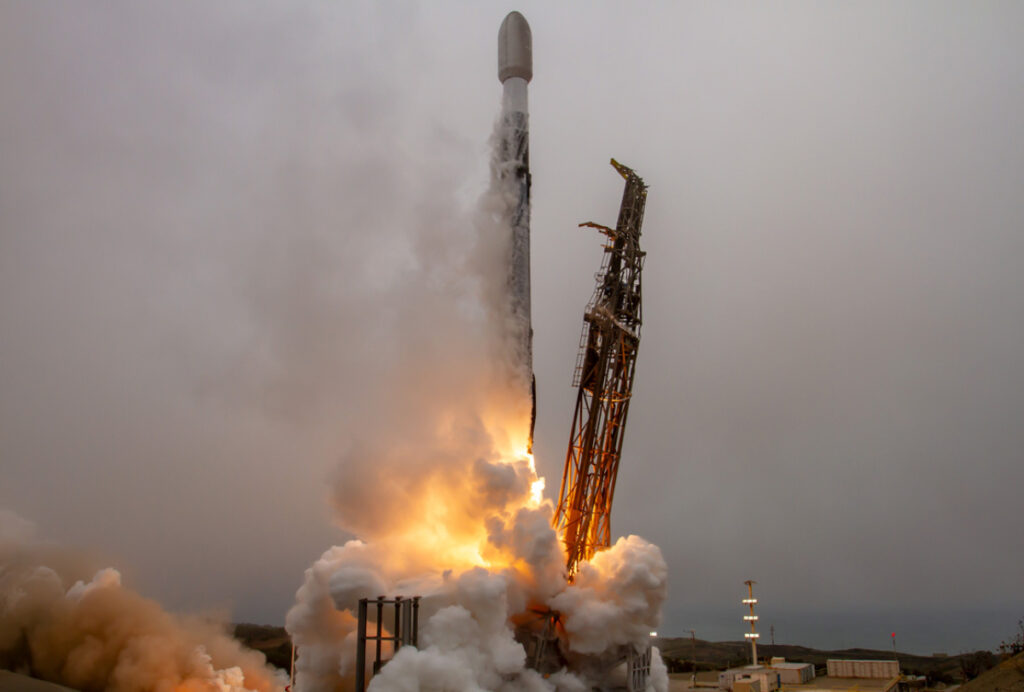
On July 25, 2025, Arianespace will place into orbit Airbus Defence and Space’s CO3D satellites, as well as the CNES’s MicroCarb satellite, with a Vega C rocket.

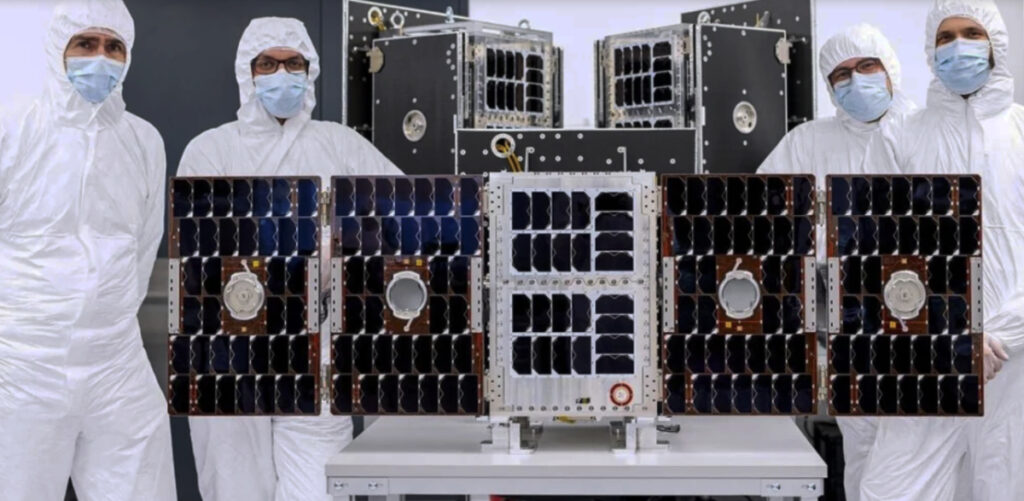
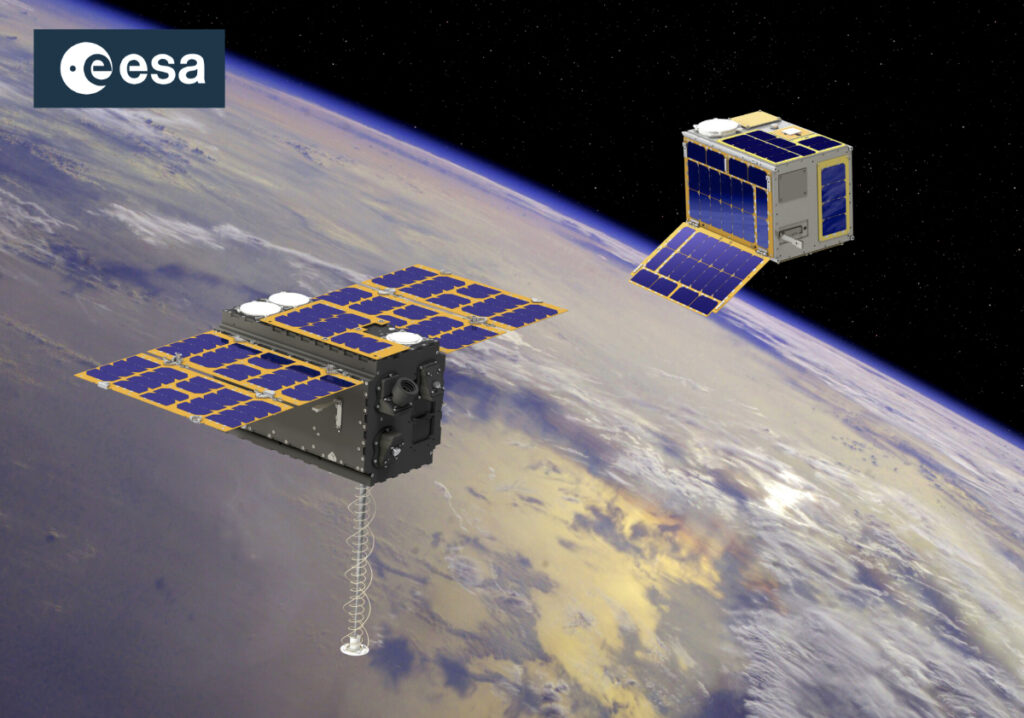
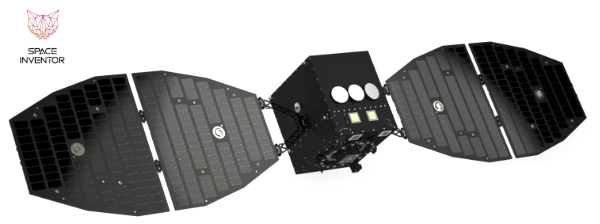
The CO3D mission is a constellation (Constellation Optique en 3D) composed of four small satellites which are set to map the globe in 3D from LEO, serving public and private sector needs.
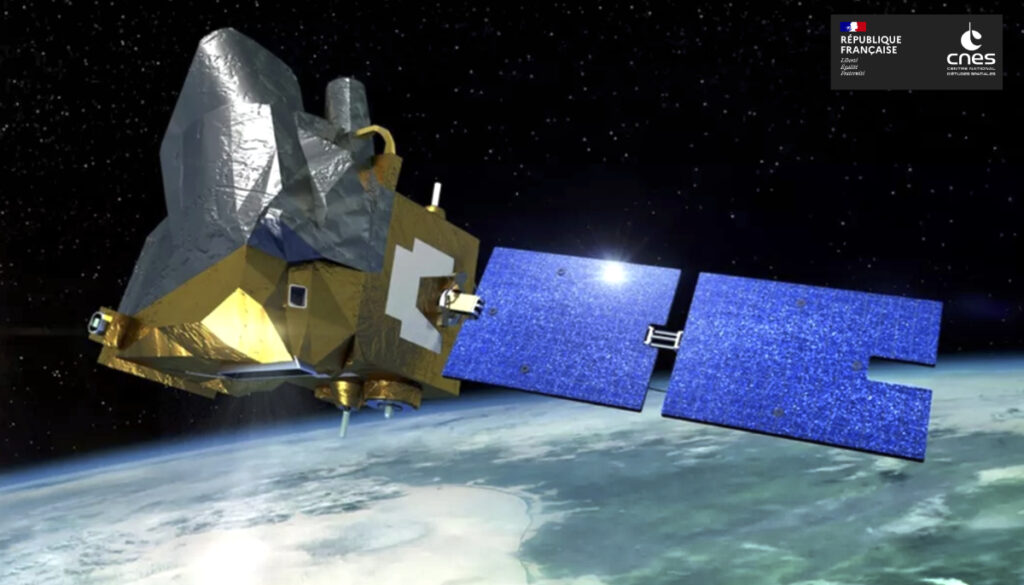

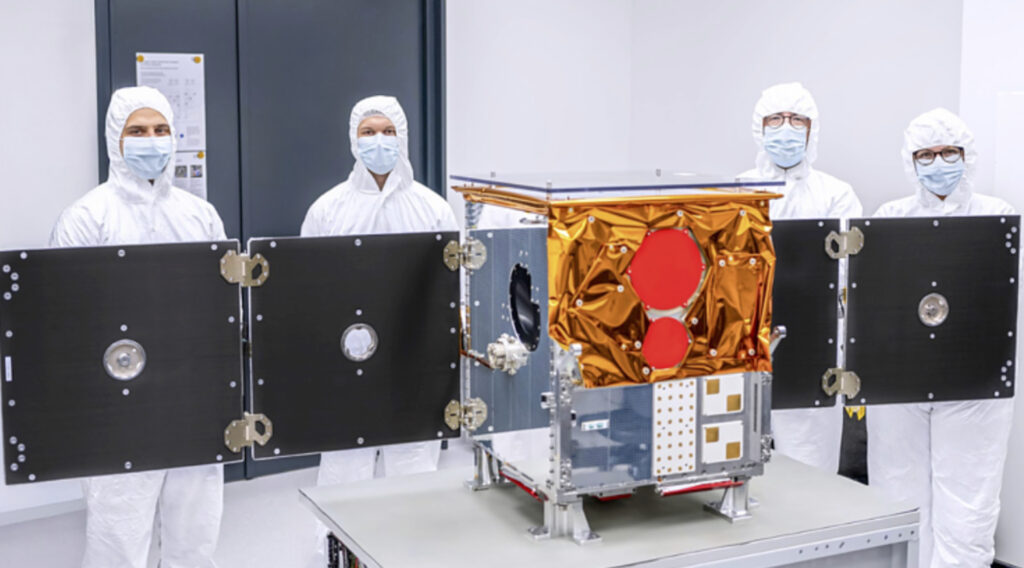
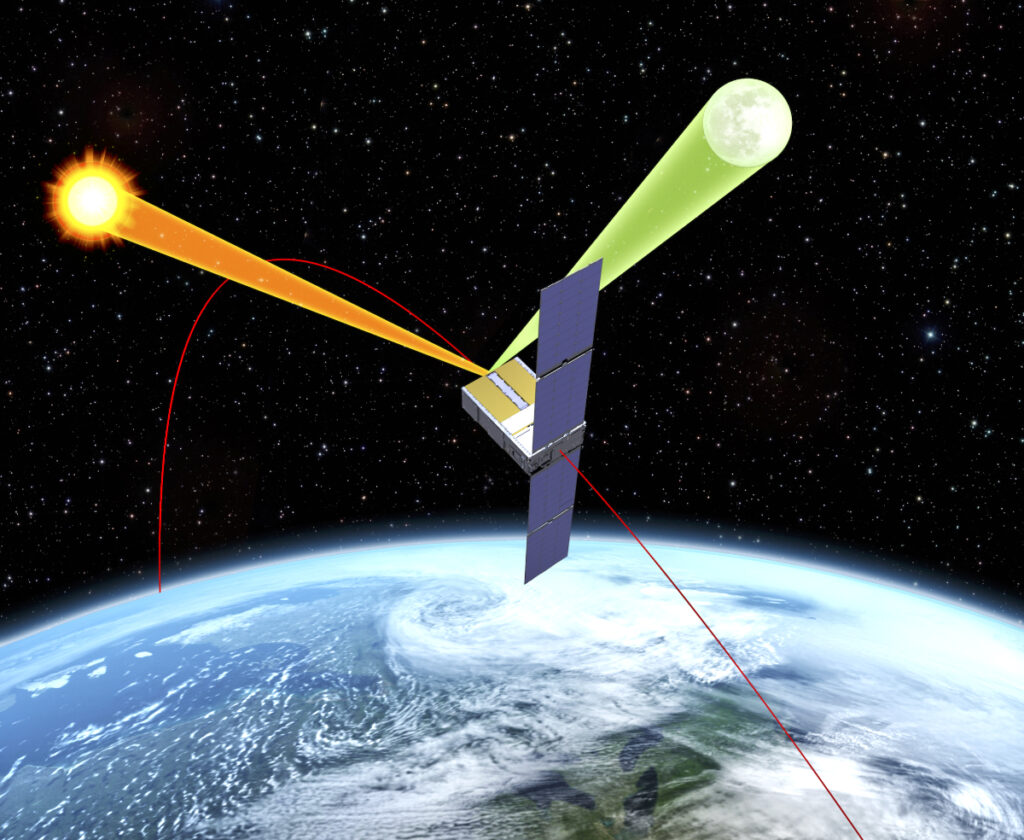
The MicroCarb mission is designed to map sources and sinks of carbon dioxide (CO2) – the most important greenhouse gas – on a global scale.
This data will answer both the military need for precise and up-to-date cartography as well as civil applications such as hydrology, geology, civil security, urban planning and land and resource management.
The CNES’ MicroCarb mission is designed to map sources and sinks of carbon dioxide (CO₂), the most important greenhouse gas, on a global scale. The satellite’s dispersive spectrometer instrument will measure atmospheric concentration of CO₂ globally with a high degree of precision.
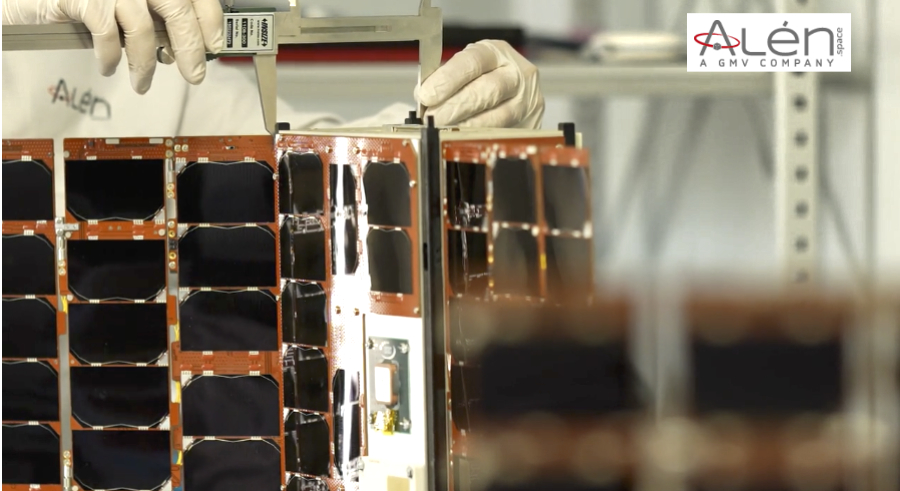
MicroCarb’s platform is based out of the lastest CNES Myriade model. Its instrument was built by Airbus Defence and Space, and the integration was realized by Thales Alenia Space UK through a dedicated partnership implemented with the UK Space Agency.
The VV27 launch at a glance:
- 354th launch by Arianespace, 5th Vega C launch
- 10% of the satellites launched by Arianespace are Earth observation satellites
- 147th-150th spacecraft built by Airbus Defence and Space launched by Arianespace (CO3D, 4 satellites)
- 108th spacecraft built by Thales Alenia Space launched by Arianespace (MicroCarb platform)