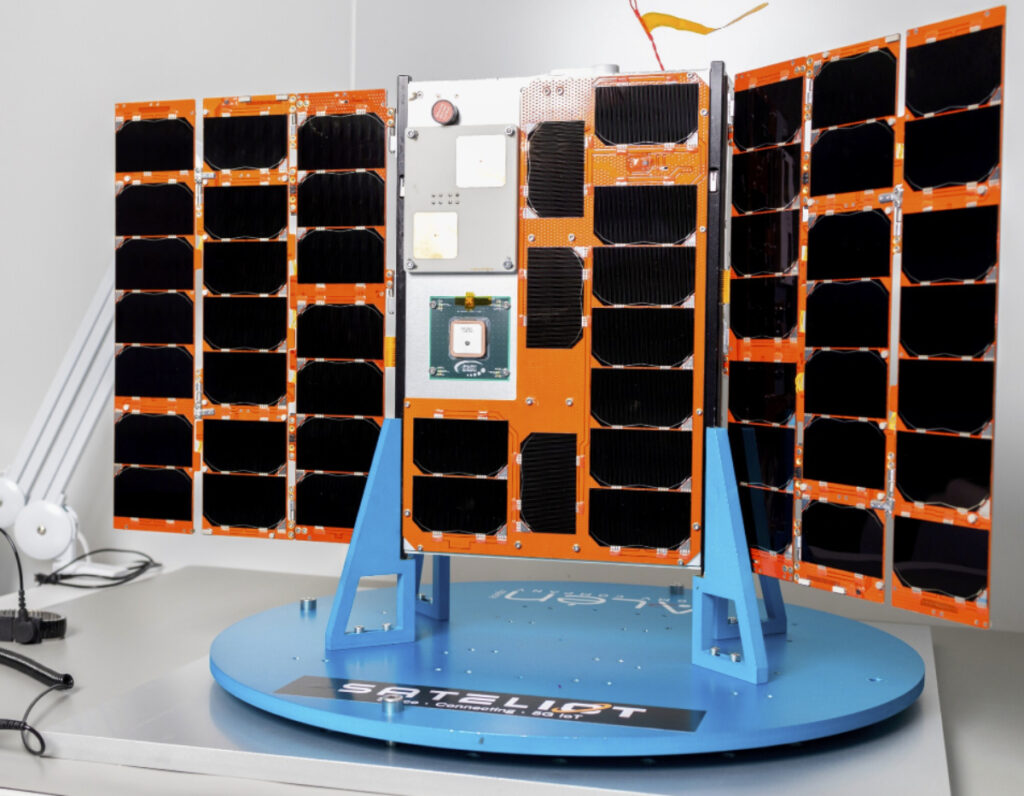
Sateliot has taken another step forward in the deployment of its satellite constellation by entrusting the manufacture of its next five satellites to the Spanish firm Alén Space. These satellites, which will become part of its LEO network, are scheduled for launch in 2026 and reinforce Sateliot’s position as a dual-use —civilian and defense— 5G satellite connectivity operator, in line with Europe’s strategic push for space autonomy.
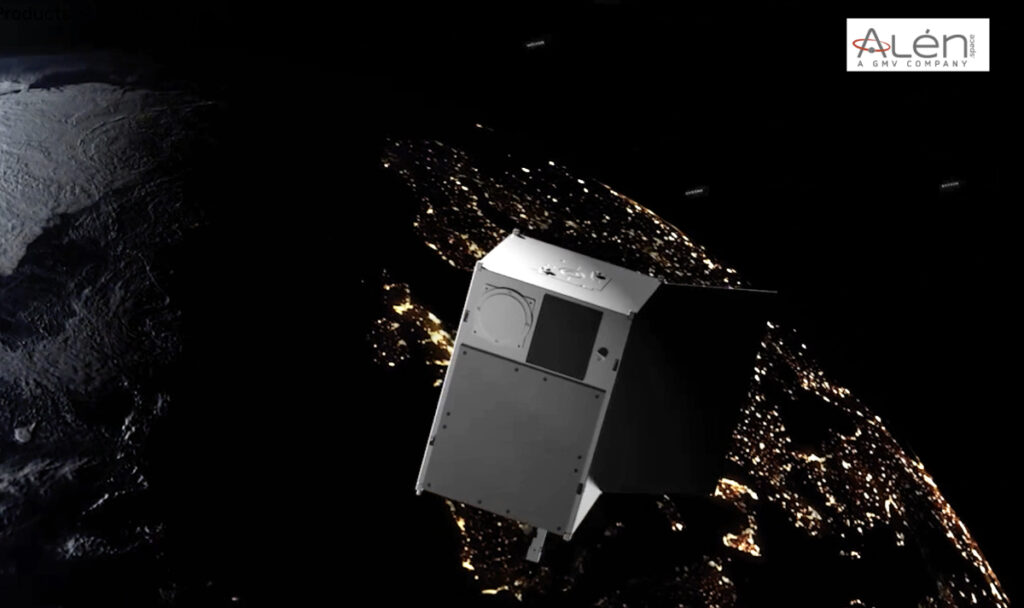

With this move, Sateliot continues to implement its roadmap to deploy a constellation of over 100 satellites, fully developed in Barcelona and validated by 3GPP—the international telecommunications standards body—with the goal of delivering secure and interoperable global coverage.
The new satellites, which will be manufactured at Alén Space’s facilities in Nigrán (Spain), include significant enhancements compared to the models already in orbit, enabling improved performance and greater payload capacity. This architecture is capable of supporting advanced communication services in both civilian contexts and critical security operations, territorial protection, or emergency response scenarios. As such, it positions Sateliot as a key player in the European space ecosystem.
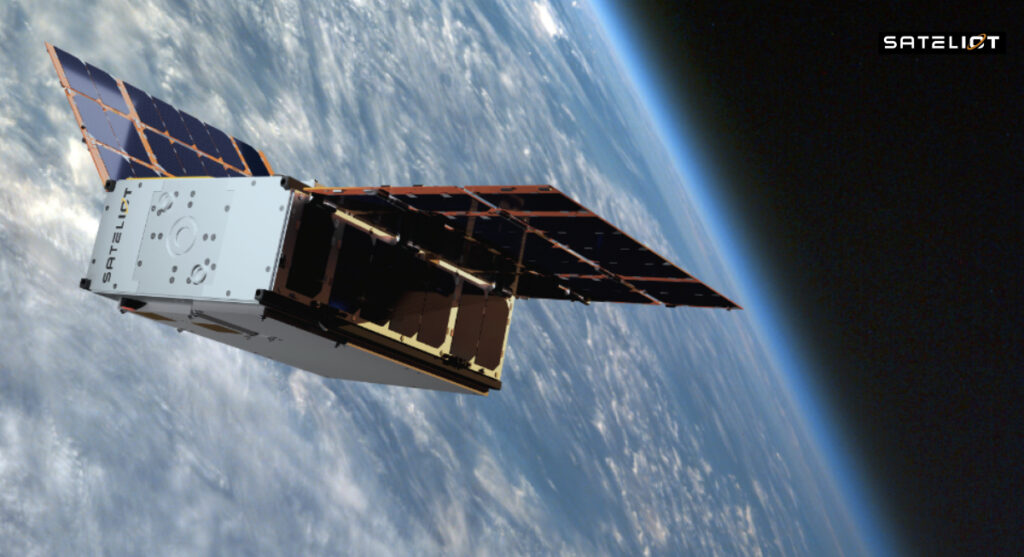

The collaboration with Alén Space is not new, as both companies previously worked closely on the manufacture of the first four commercial satellites in the constellation, which were successfully launched in August 2024 aboard a SpaceX rocket.
Sateliot already holds contracted commitments worth approximately €270 million with over 400 clients across 50 countries. On this foundation, the company projects revenue of €1 billion by 2030, consolidating its position as a pioneering European operator of global 5G satellite connectivity.

This project demonstrates that we are capable of building critical infrastructure from scratch in Spain,” said Jaume Sanpera, CEO of Sateliot. “We have developed open and interoperable, made-in-Spain technology that not only meets global connectivity needs, but also contributes to European technological sovereignty.”
Guillermo Lamelas, CEO of Alén Space, said, “We are proud to collaborate with Sateliot on such an innovative and pioneering project, which will redefine the future of communications from Spain. This agreement acknowledges the quality of the work carried out on the first four satellites and strengthens our position as the most reliable small satellite manufacturer.”