Photo is courtesy of the company.
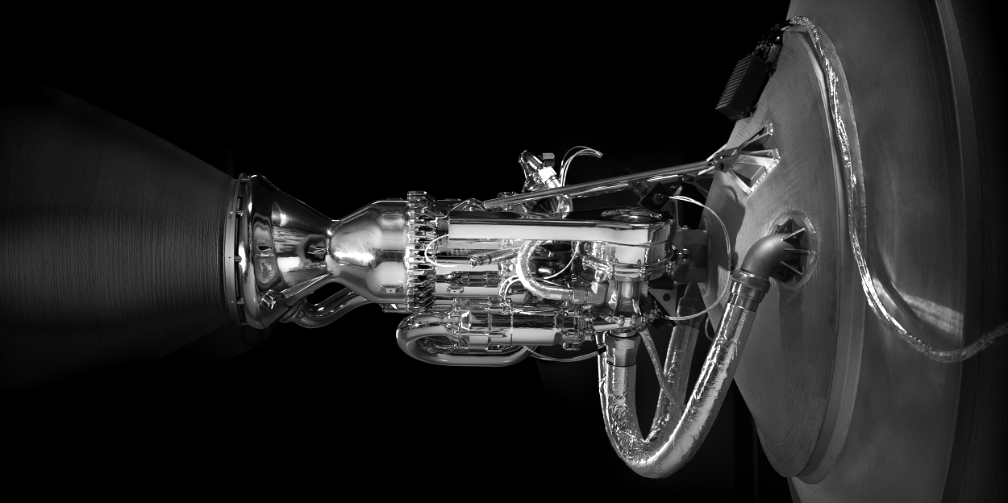
Rocket engineers at Gilmour Space Technologies in Queensland, Australia, have completed the first in a series of major technology demonstrations this year — a successful 45-second ‘hot fire’ of their upper-stage hybrid rocket engine.
Unlike most commercial launch vehicles fueled by solid- or liquid-propulsion engines, Gilmour Space is developing new cost-effective, safe and green hybrid-propulsion technologies.
2020, the year of testing
As with most companies in Australia, Gilmour Space has been impacted by the severe bushfires and global COVID-19 pandemic. Despite the challenges, the company is tracking to complete a number significant tests this year, including a series of low-altitude flight tests of their guidance, navigation and control systems, a thrust vector control system test, and a more powerful static fire of their first-stage rocket engine.
Now with 50 employees in the company’s Gold Coast rocket facility, Gilmour Space is pushing the frontiers of Australian manufacturing and growth across the commercial, civil and defence space.
In December last year, the company signed a Strategic Statement of Intent with the Australian Space Agency to demonstrate its commitment to delivering ‘Access to Space’ as a civil priority area. In May, it signed a collaboration agreement with Australia’s Defence Science Technology Group to work on technologies that will enable sovereign launch capabilities in Australia.
Executive Comment

“This was our longest and most efficient test fire to date,” said Gilmour Space CEO and Co-Founder, Adam Gilmour. “It’s a key demonstration of our ability to produce repeatable, stable, and high-performance combustion over a long duration burn; and a significant achievement in hybrid rocket development,” he added. “This engine will have the capability to power the upper stage of our Eris orbital launch vehicle, and deliver our customer payloads to required orbits. Our next test will be a full duration mission duty cycle firing of this engine.” He added, “Clearly, the momentum for launch is building here. With the right focus, investment, and hopefully a ready launch site by 2022, we believe that space could be a significant future industry for Australia – one that builds on our advanced manufacturing capabilities, and offers real opportunities for jobs, recovery and growth.”
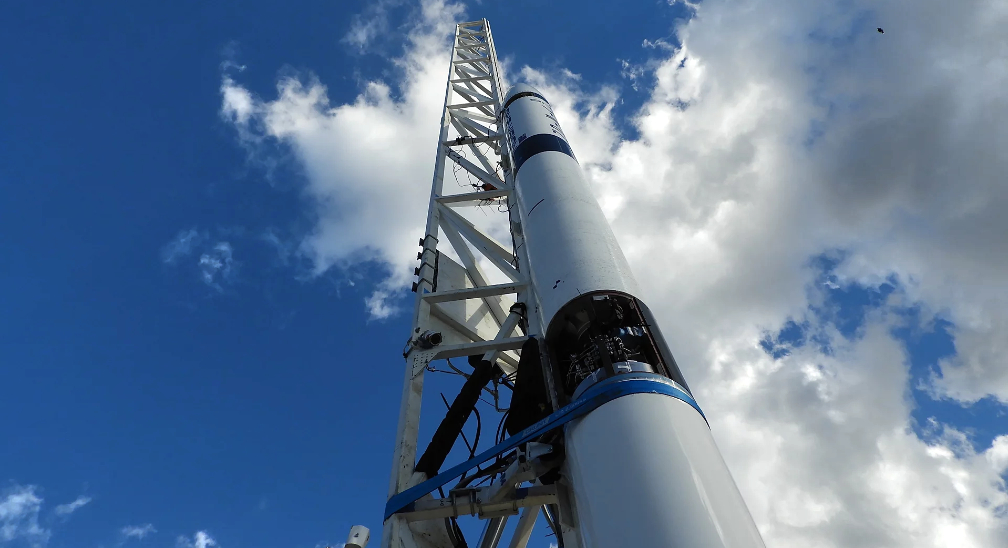

Recent Gilmour Space news…
Gilmour Space Receives Millions in Funding for Australian Government Flight-Ready Cryotanks