Lynk Global Inc. has filed for a commercial operator’s license with the Federal Communications Commission (FCC). Commercial service is expected to begin around the world starting next year upon FCC approval.

The startup’s patented technology will eventually allow anyone with an existing cell phone to stay connected, anywhere in the world, at all times. Most importantly, Lynk’s system requires no changes to the phone. The existing phone in your pocket will work.
Lynk’s initial commercial license application intentionally uses the FCC’s new streamlined process for up to 10 smallsats to accelerate the license. Previous applications suggest this streamlined process will take 10-12 months, allowing Lynk to start their global service next year. This is the first step in Lynk’s plans for a larger constellation that will grow to several thousand satellites to begin continuous global service in 2025. Ultimately, Lynk’s full constellation will reach 5,000 satellites to provide broadband speeds to your phone.
Using a low-risk development approach, Lynk will integrate some of the most advanced space sustainability methods today to prevent and mitigate orbital debris and is actively advocating within industry and government to develop stronger orbital debris mitigation approaches for tomorrow.
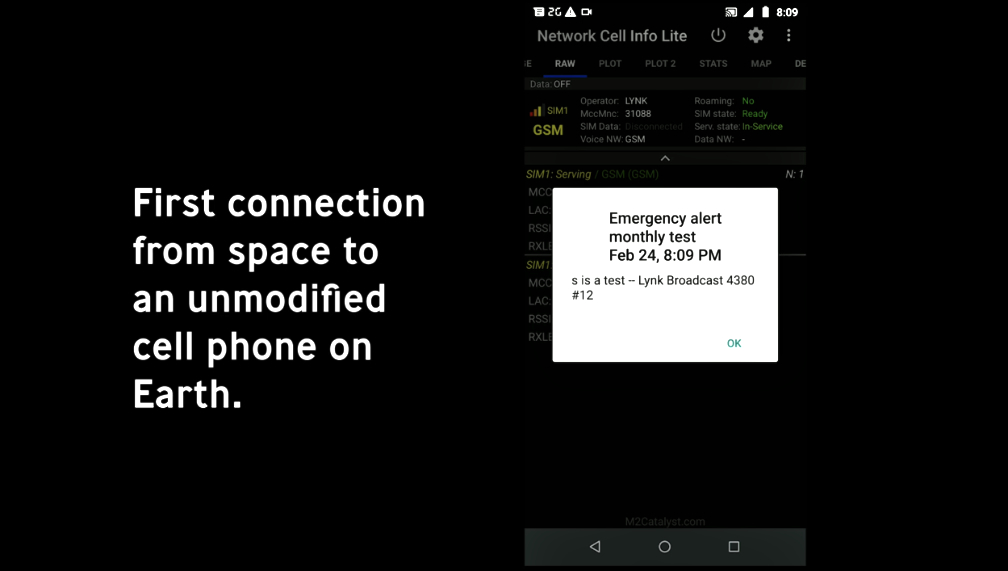
In February 2020, with the help of NASA and mobile network operators (MNO), Lynk sent the world’s first text message from a satellite in orbit to a standard mobile phone on the ground. Lynk has also signed contracts with the U.S. Air Force and the U.K. Space Agency to support development of the Lynk system.T o date, Lynk has signed dozens of testing agreements with MNOs.
Charles Miller, CEO of Lynk, said, “Lynk is introducing a brand-new, never-been-done-before service—satellite-direct-to-standard-phones. As an American company, we are fortunate to have the FCC, whose process is trusted by officials around the world, to license our satellites. We believe that being good corporate citizens means at every point in the process you must be rigorous—whether it is eliminating harmful interference or minimizing orbital debris. Because using cellular frequencies from space has never been done before, we believe that being licensed by the FCC will help regulators worldwide embrace this groundbreaking technology.”
Miller continued, “There is a huge amount of interest in Lynk’s service … we actually have too many testing partners at this time. To manage this demand and ensure the highest quality testing protocols and commercial service, we are implementing a “Flagship Carrier”program. Under this program, we will be limiting initial commercial services to, at most, a dozen mobile network operators globally.”In partnership with mobile network operators, Lynk will provide a global service for the 5.2 billion existing cell phone users globally. Further, many of the 2.5 billion people currently without phones will be connected to global society and economy, materially improving their lives. Lynk will provide an instantaneous backup emergency communications layer everywhere on Earth.



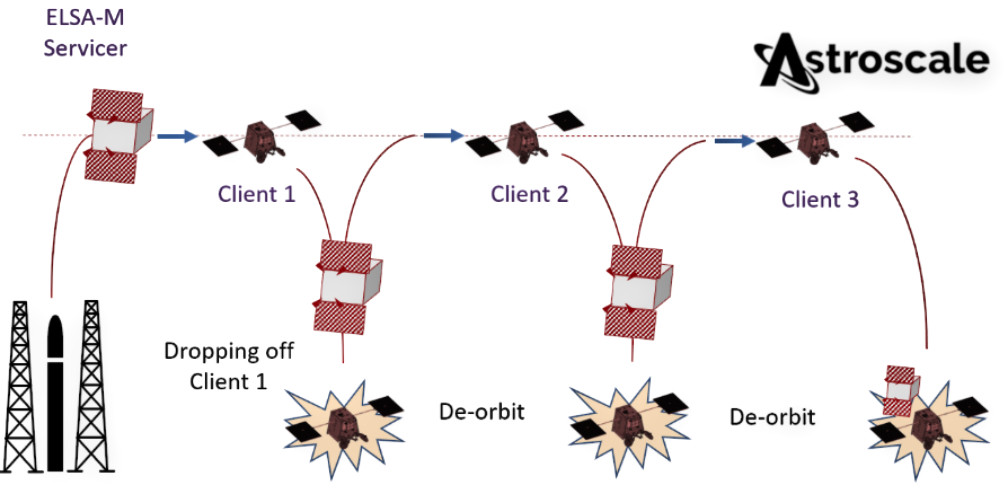

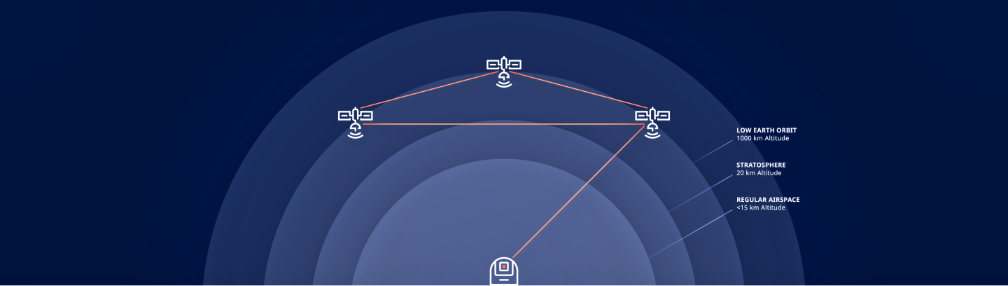
 is a patented, high-speed global cloud storage network of space-based data centers, each seamlessly interconnected together to provide exclusive and secure cloud infrastructure to service providers, enterprises and governments around the world.
is a patented, high-speed global cloud storage network of space-based data centers, each seamlessly interconnected together to provide exclusive and secure cloud infrastructure to service providers, enterprises and governments around the world.


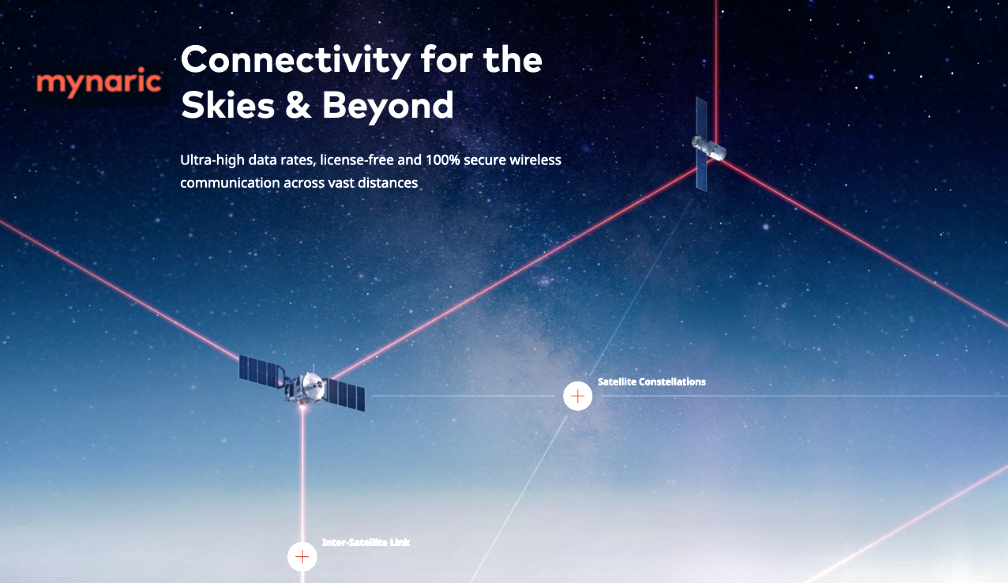

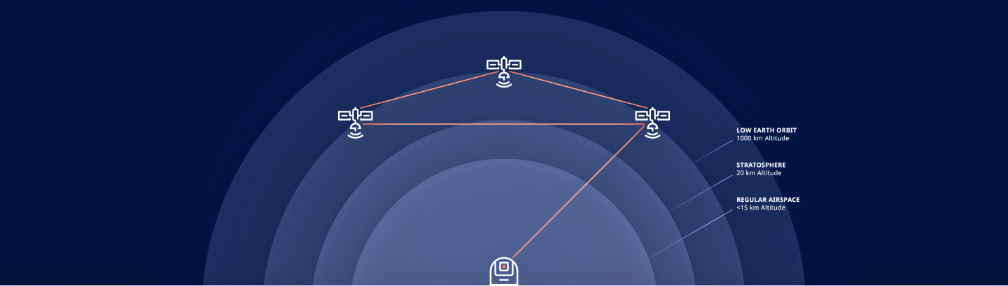
 is a patented, high-speed global cloud storage network of space-based data centers, each seamlessly interconnected together to provide exclusive and secure cloud infrastructure to service providers, enterprises and governments around the world.
is a patented, high-speed global cloud storage network of space-based data centers, each seamlessly interconnected together to provide exclusive and secure cloud infrastructure to service providers, enterprises and governments around the world.