Blue Canyon Technologies, a subsidiary of RTX (NYSE: RTX), announced the firm’s contributions to the recent SpaceX Transporter-8 launch on June 12th, kickstarting several defense-critical missions.
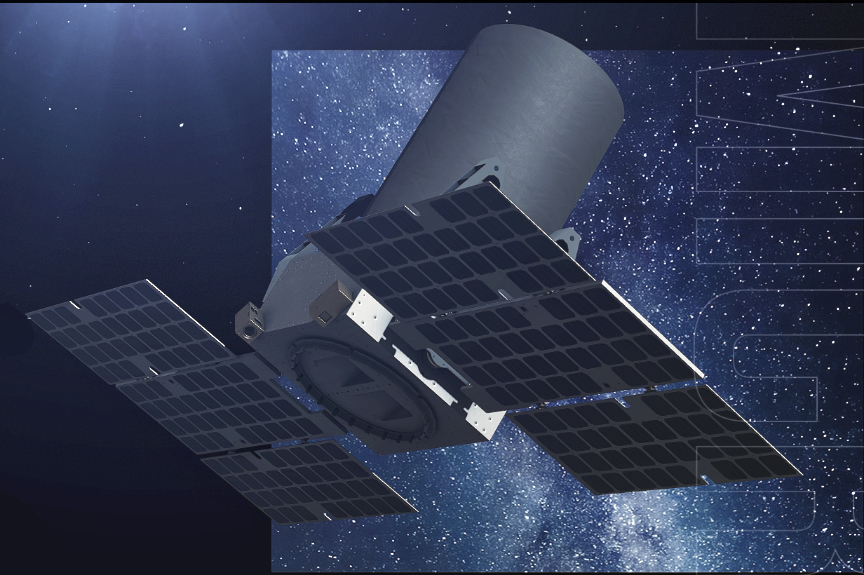

Blue Canyon’s products on the Transporter-8 launch included four, Saturn-class smallsats for DARPA’s Blackjack mission, two 6U CubeSats for the Department of Defense (DoD) Modular ISR program (MISR) and one 12U CubeSat for a government customer.
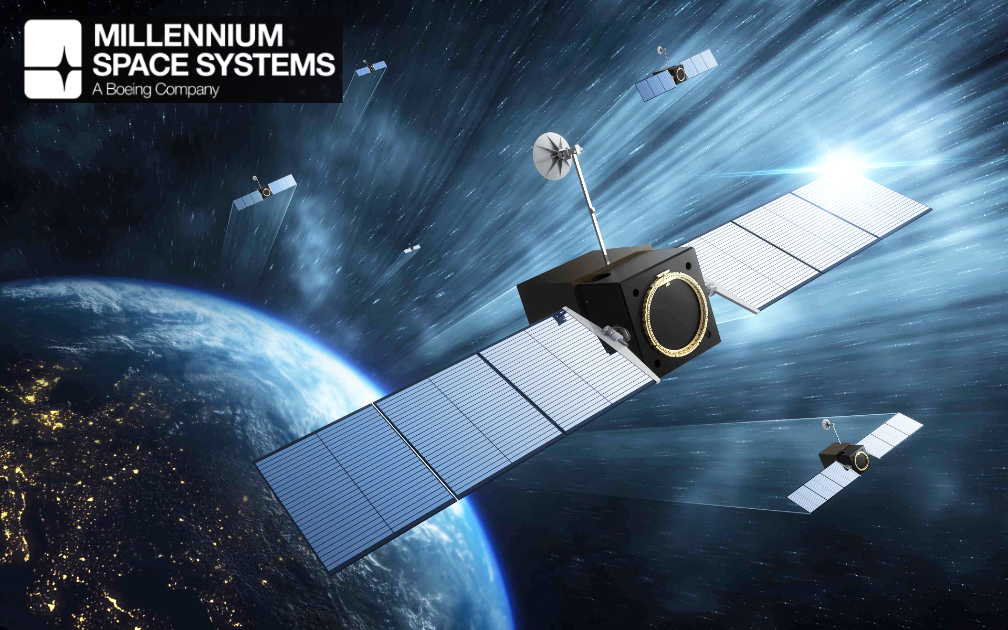
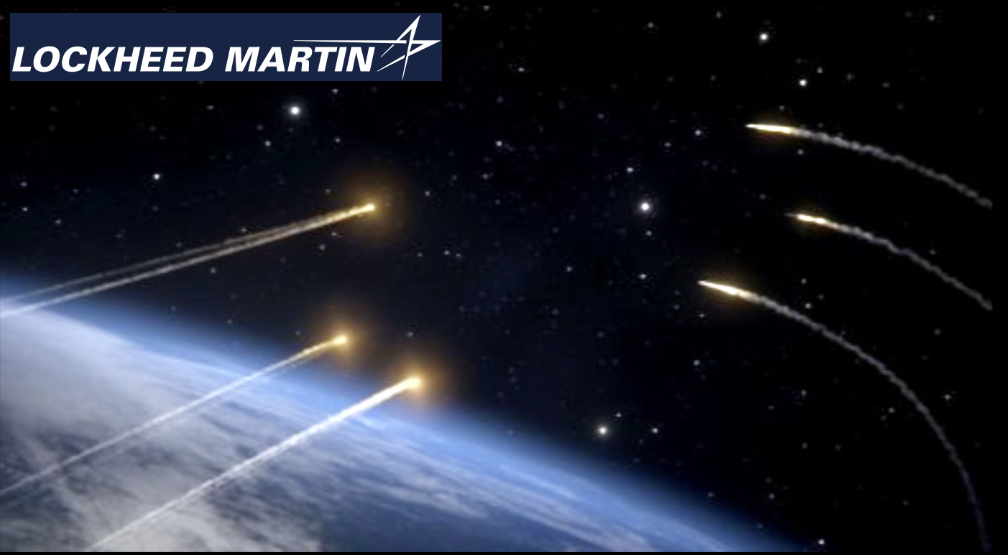
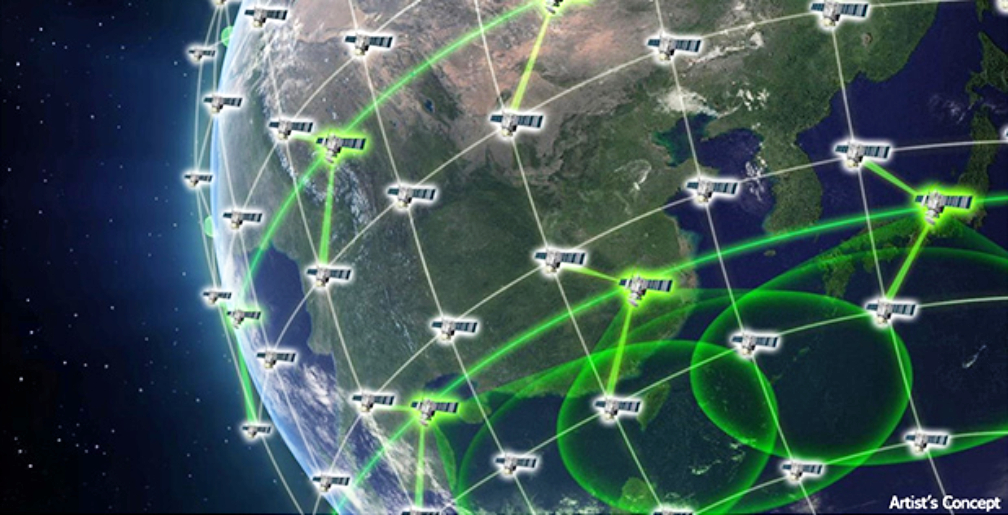
DARPA’s Blackjack mission aims to lay the groundwork for a high-speed, global network in LEO (artistic rendition below). This network will provide the DoD with connected, resilient, and persistent coverage. Each Blackjack satellite has a Pit Boss data processing node and a Storm King radio-frequency (RF) payload made by SEAKR Engineering, also an RTX subsidiary.
The MISR program is intended to demo a robust, responsive, multi-mission, CubeSat capability to satisfy various requirements. The pair of MISR CubeSats are the start in a series of missions to demonstrate various capabilities and mission effectiveness.
All seven spacecraft are in good working order and performing as expected following the launch. Commissioning activities are ongoing.
Blue Canyon’s work was performed in Lafayette, Colorado.
“Blue Canyon’s product line of smallsat buses provide the proven performance and heritage needed to support these critical defense missions. Our ability to also manufacture most of the components and subsystems for the spacecraft are what sets us apart within the industry.” — Jeff Watts, General Manager, Blue Canyon Technologies