INNOSPACE (KS:462350) has begun functional checks and satellite–launch vehicle interface tests for customer satellites and experimental payloads as part of the operational procedures for its first commercial launch mission SPACEWARD of the ‘HANBIT-Nano’.

This procedure verifies the electrical and mechanical connections between the payload adapter (PLA) and other integration hardware with the satellites and payloads. It is an essential pre-launch step to ensure stable mounting and integrated operation.
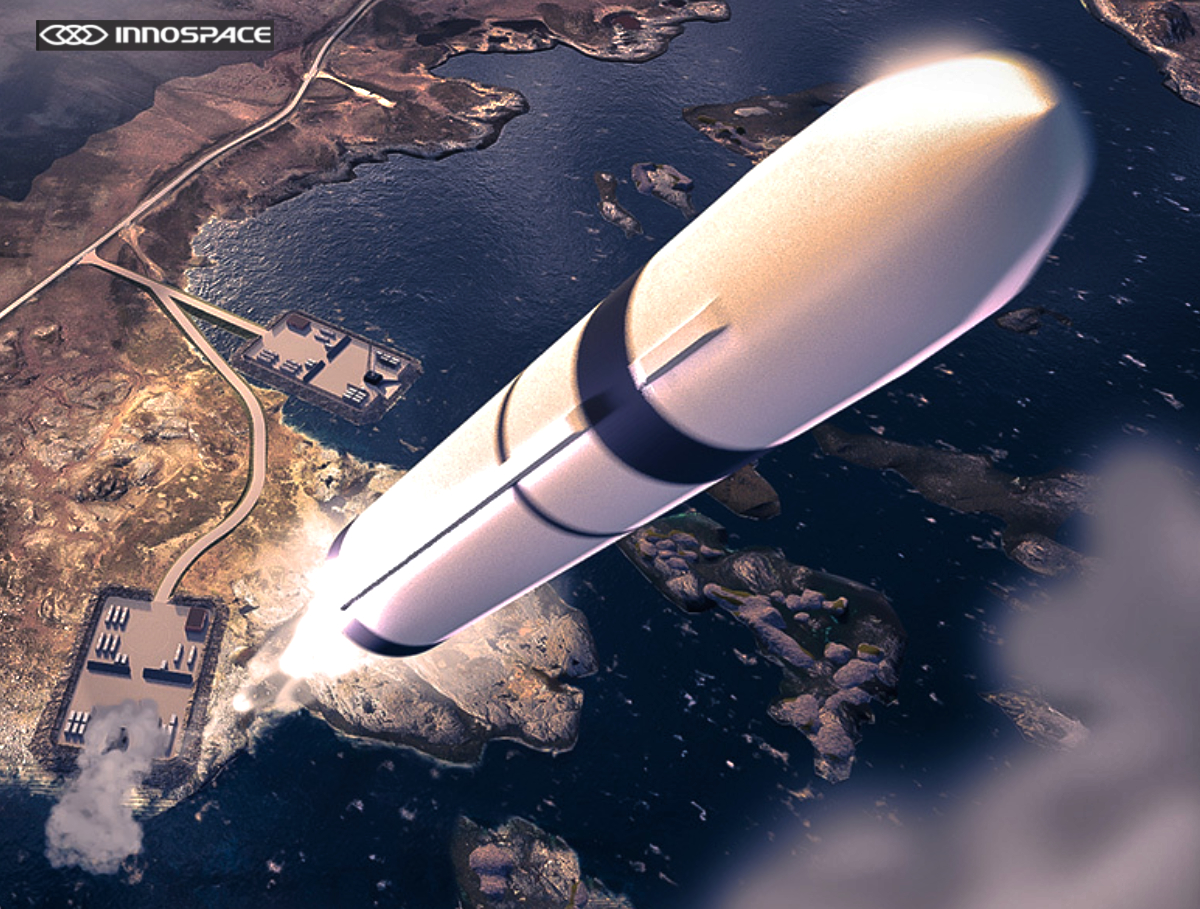
With its first commercial launcher HANBIT-Nano, INNOSPACE plans to deploy five customer satellites into LEO at 300 km altitude and 40° inclination, while simultaneously performing missions for three non-separating experimental payloads and one branding payload.
The target launch time is November 22 at 3:00 PM (BRT), from the Alcantara Launch Center in Brazil. The launch window runs from October 28 to November 28.

with startups and national institutions
On the same day, three Brazilian customers—Federal University of Maranhão (UFMA), the Brazilian Space Agency (AEB), and Castro Leite Consultoria LTDA (CLC)—visited the launch site to conduct functional checks and interface testing. UFMA completed pre-launch procedures for two small satellites for technology development and education; AEB completed checks for two small satellites for climate and environmental data collection and one inertial navigation system (INS); and CLC completed procedures for one GNSS unit and one INS payload.
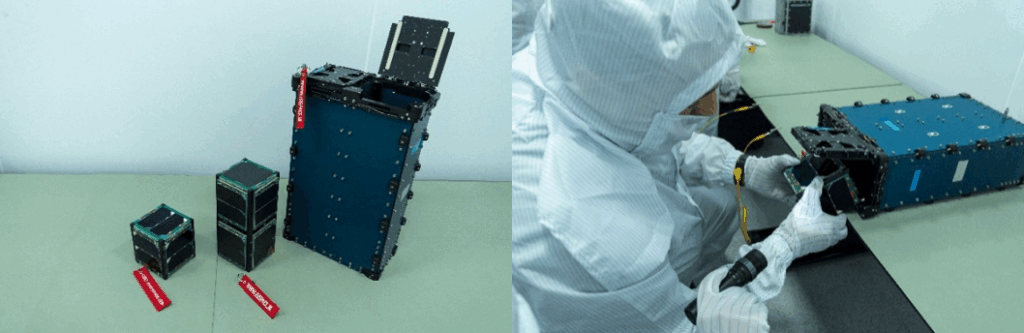
One small satellite from the Indian customer Grahaa SPACE is scheduled to follow the sequential integration process. In addition, one highball-can branding model from Korean company BREWGURU will be placed separately onboard as a symbolic participatory payload.
Following the completion of these functional checks and interface tests, INNOSPACE will proceed with final integration to mount the satellites onto the launch vehicle. Once completed, the process will move on to payload fairing installation, pre-launch rehearsal (dry run), comprehensive weather and environmental assessments, and finally the joint flight-safety and integrated-operations procedures with the Brazilian Air Force leading up to the final launch countdown.
INNOSPACE’s satellite–launch vehicle interface test marks a significant step, as it is the first time a Korean private company has independently carried out the integration procedures required for commercial launch services in line with customer requirements. This is symbolic of Korea’s private launch service industry entering true commercialization, supported by practical preparations to serve satellite customers,” said Soojong Kim, Founder and CEO of INNOSPACE.