With thousands of satellites and countless debris bound for busy orbits, Kayhan Space has now unveiled their next-gen Pathfinder spaceflight safety platform to enable satellite and mission operators to better manage operational risks and make preemptive maneuvers based on precision analytics to avoid pileups in space.
spaceflight safety platform to enable satellite and mission operators to better manage operational risks and make preemptive maneuvers based on precision analytics to avoid pileups in space.
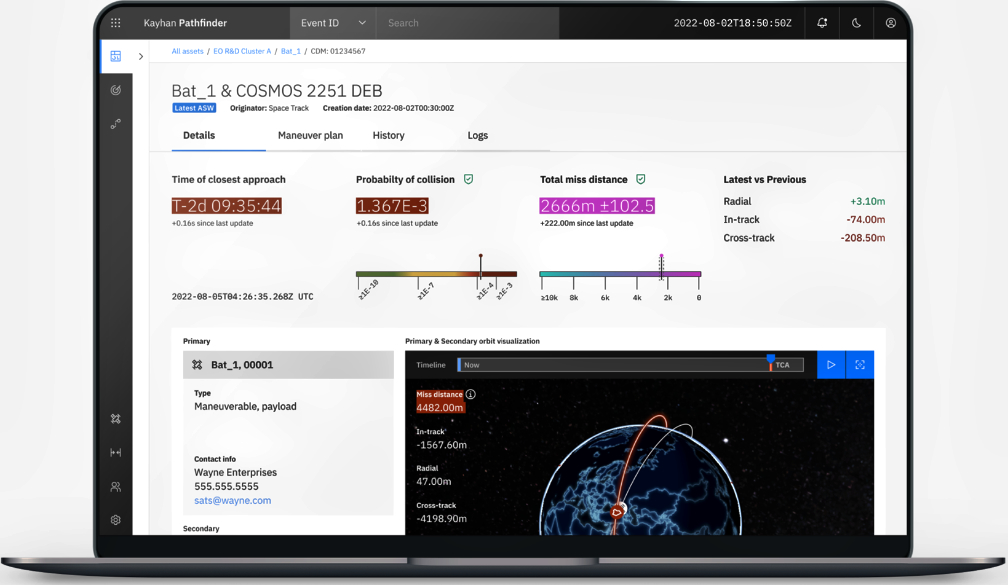
Capella Space, Globalstar and Lynk Global are among an initial group of leading operators using Kayhan’s subscription-based, autonomous, Pathfinder platform following successful beta deployments of the solution, which was officially rolled out for general availability last week.
Among the product’s advanced capabilities, the cloud-delivered offering uses proprietary advanced algorithms along with precise space catalog data, the operators’ GPS positioning signals, propulsion capabilities, and flight plans to simulate, coordinate and quickly generate optimal maneuver options in the event of a potential oncoming collision threat or conjunction. This breakthrough platform enhances communication and coordination capabilities across operators and agencies to improve overall situational awareness in global space.
Kayhan Pathfinder can also optimize revenue-generating missions whenever possible by scheduling preemptive and preplanned maneuvers during operational downtimes. An advanced edition of the product enables precise orbit determination capabilities to significantly improve the accuracy of the satellite trajectory predictions, keeping rendezvous proximity operations (RPO) and other sophisticated in-space servicing moves safe.
The Kayhan Space roadmap leads to a spaceflight safety software solution that encompasses the full mission lifecycle – from launch and on-orbit collision avoidance maneuvers to deorbiting and decommissioning the spacecraft.
“Our next-gen Kayhan Pathfinder comes at a critical time as satellite and mission operators need precise, real-time data to inform automatic alerts and decisions to safely navigate busy orbits and evade accidents in space,” said Siamak Hesar, Kayhan Space co-founder and CEO. “Manual collision avoidance processes are prone to human error and simply can’t stay ahead of the increasingly congested orbits and the growing number of complex collision scenarios they represent. Kayhan Pathfinder is an autonomous spaceflight safety platform that enables operators to run their missions in the busiest orbits with confidence.”
“We are thrilled to be among the first to use Kayhan Space’s next-gen Pathfinder spaceflight safety platform across a portion of our satellite fleet,” said Rico Walker, Director of Mission Operations for Capella Space. “Capella is committed to making space operationally sustainable and safe. Our collaboration with Kayhan Space plays a big part in our ability to fly in increasingly congested orbits that have become a priority for the communities and businesses depending on connectivity and content around the world.”
“Kayhan Space is already providing a broad range of spaceflight safety services to many of the world’s leading satellite operators, running hundreds of satellites on our Pathfinder platform in multiple orbital regimes around the Earth,” said Araz Feyzi, Kayhan Space co-founder and CTO. “Pathfinder allows operators to optimize missions by avoiding unnecessary and costly maneuvers and provides an exciting path for safe and secure operations across the new space economy.”