Leaf Space is progressing with the launch phase of a new, innovative use of telemedicine via satellite for home monitoring of patients with COVID-19 as part of the CARES project led by the company and co-funded by the European Space Agency (ESA).

CARES is a set of medical devices connected to a smartphone, which collects patient vitals using medical software and adds that information to a database, remotely. This database is accessible by a doctor directly from a web browser and is designed by project partner H&S to provide comprehensive, almost real-time data with ease.
H&S’s Health Platform is also enabled to trigger an alert system if the monitored patient’s vitals are recorded outside of the safe range and provides options for management including contacting the patient or even sending an ambulance.
The pilot trial of the CARES project is currently ongoing in collaboration with Fatebenefratelli Hospital in Erba, Molinette in Torino and Villa Gioia in Sora, where discharged and recovering COVID-19 patients can recover from the comfort of their homes while having the confidence that their progress and vitals are being consistently and reliably monitored by medical professionals.
By integrating the remote monitoring health platform with satellite telecommunication infrastructure to guarantee the service everywhere, Leaf Space’s support of the CARES system allows patients without reliable internet based on ground-based infrastructure to receive the remote monitoring and care that is incredibly important, especially for those patients recovering from COVID-19.
This same model can be applied to patients with chronic diseases, rehab processes and any type of condition that require strict monitoring and multiple medical examinations anywhere in the world. Leaf Space’s satellite backed telecommunication structure ensures capturing and distributing the signals transmitted by the telemedicine systems to the satellite and back to Earth at the hospital are reliable, fast and compliant with current GDPR and patient privacy laws.
“The unprecedented situation caused by the COVID-19 pandemic has saturated the emergency departments of European hospitals and is creating a huge stress on the screening processes,” said Arnaud Runge, medical engineer at ESA. “To respond to this unprecedented effort to contain and mitigate the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, we have offered to support European companies in developing their best ideas and proposing effective solutions to respond to this crisis, evidencing the contribution that space can bring in these circumstances. A fast-track approach has been put in place to respond as quickly as possible to the impellent needs of citizens and institutions.”
“We are so grateful to have the opportunity to work with ESA on this incredible project, and we hope that this technology can bring much needed support and peace of mind to people who have suffered so much,” said Jonata Puglia, co-founder and CEO of Leaf Space. “We see a massive opportunity to connect satellite communications with telemedicine technology and hope that our continued work with the CARES project can serve as an example of what can be achieved and applied to so many patients and healthcare systems around the world. We are eager to continue to explore the possibilities of what this technology can do to increase access to healthcare worldwide.”
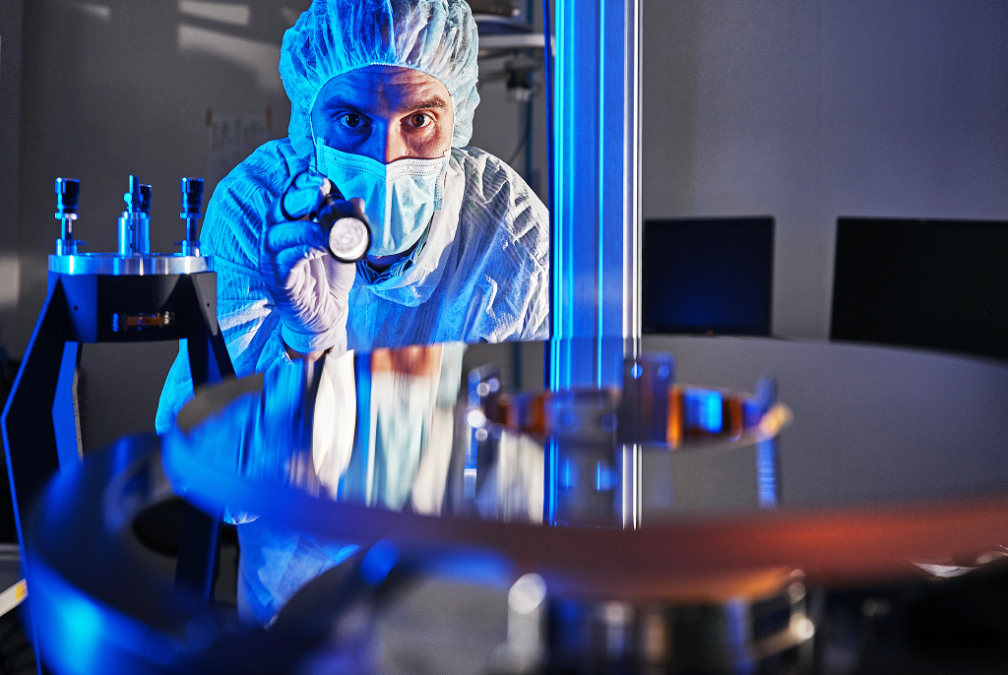







 (Next Generation) EO satellite constellation. ISI is part of an exclusive group of companies that operate ultra-high resolution, EO satellite constellations that are serving Governments, Institutions, Defense & Security organizations and Commercial customers with unique, mission-critical intelligence capabilities.
(Next Generation) EO satellite constellation. ISI is part of an exclusive group of companies that operate ultra-high resolution, EO satellite constellations that are serving Governments, Institutions, Defense & Security organizations and Commercial customers with unique, mission-critical intelligence capabilities.