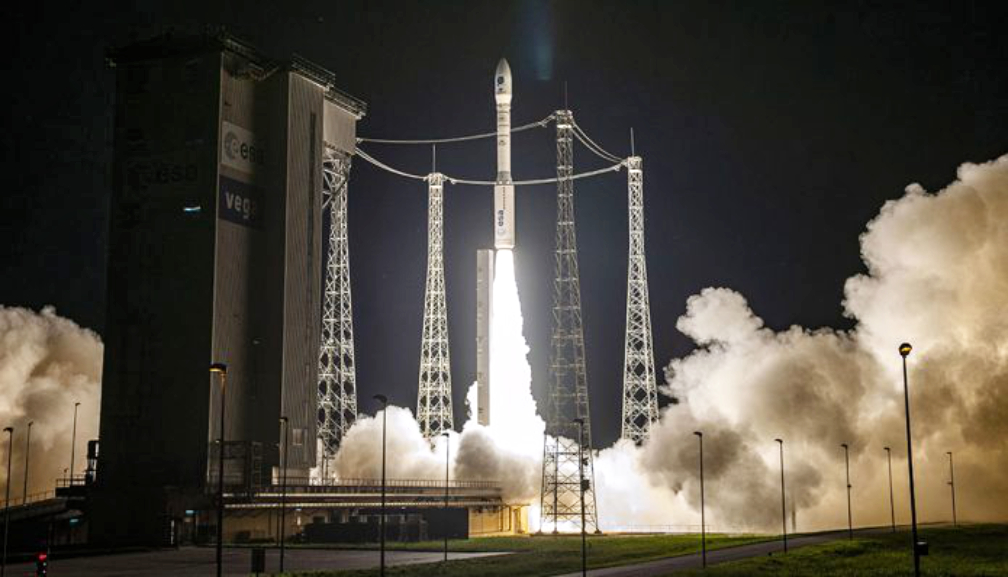
Arianespace has given the “green light” go-ahead for its Vega launch on November 16, which will orbit a pair of European-built satellites: Spain’s SEOSAT-Ingenio and TARANIS of France.
The approval followed today’s launch readiness review in French Guiana, which confirmed the preparedness of Vega, along with the payloads, the Spaceport’s launch site infrastructure, and the network of tracking stations.
All is now set for the nighttime liftoff on November 16 at precisely 10:52 p.m. local time in French Guiana (1:52 UTC on November 17), initiating a flight that will last 1 hr. and 42 min. until final payload separation. Total payload performance is estimated at 1,192 kg.
This mission to Sun-Synchronous Orbit (SSO) is designated VV17, and it will be performed from the Spaceport’s ZLV launch complex – where Vega was assembled and now stands in a flight-ready configuration, protected by a mobile gantry that will be withdrawn prior to liftoff.
Flight VV17 will mark Arianespace’s seventh mission in 2020, and is the company’s second this year using a lightweight Vega – which is one of three launch vehicles operated by Arianespace at the Spaceport, along with the medium-lift Soyuz and heavyweight Ariane 5. Vega’s production prime contractor is Avio.
Vega began operations from Europe’s Spaceport in 2012, with the upcoming Flight VV17 to become its 17th. SEOSAT-Ingenio and TARANIS are to be the 84th and 85th satellites orbited by this vehicle – and the 745th and 746th lofted on an Arianespace mission overall.
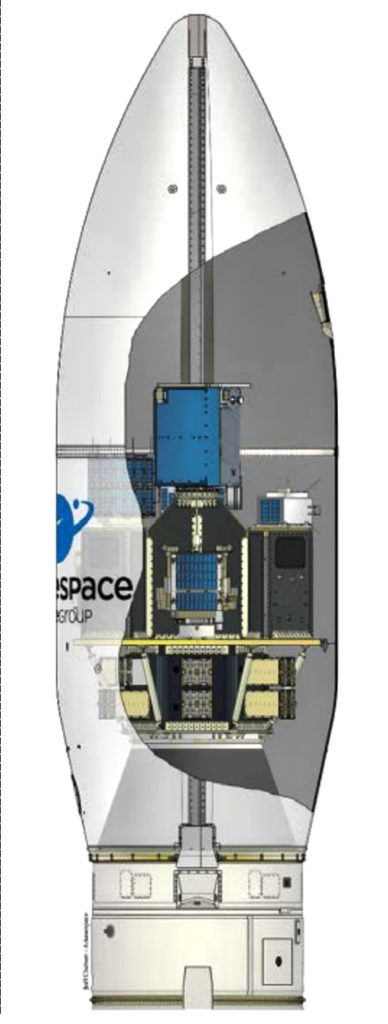
For this latest Vega flight, the launcher is equipped with a Vega Secondary Payload Adaptor (VESPA), which enables the multi-satellite payload to be carried and deployed. VESPA is produced by Airbus Defence and Space in Spain for Avio.
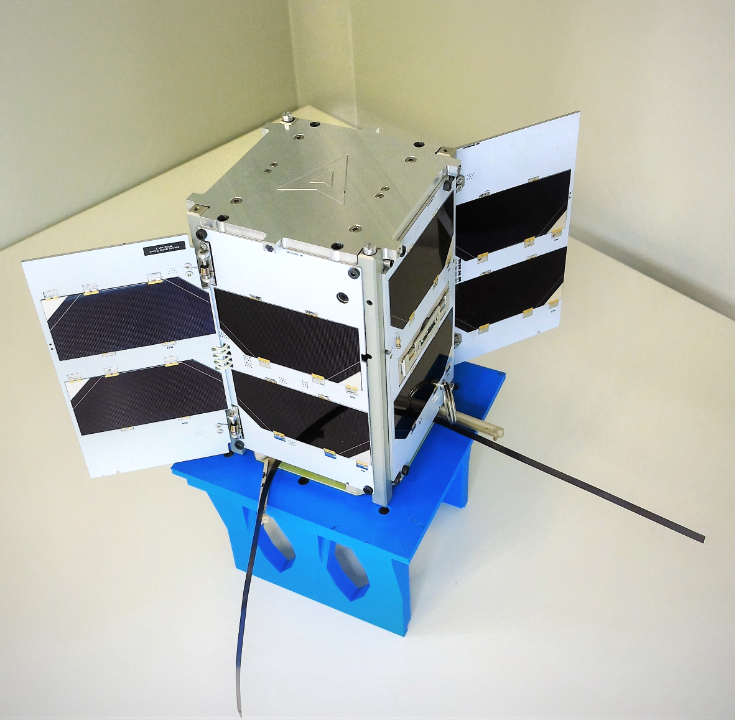
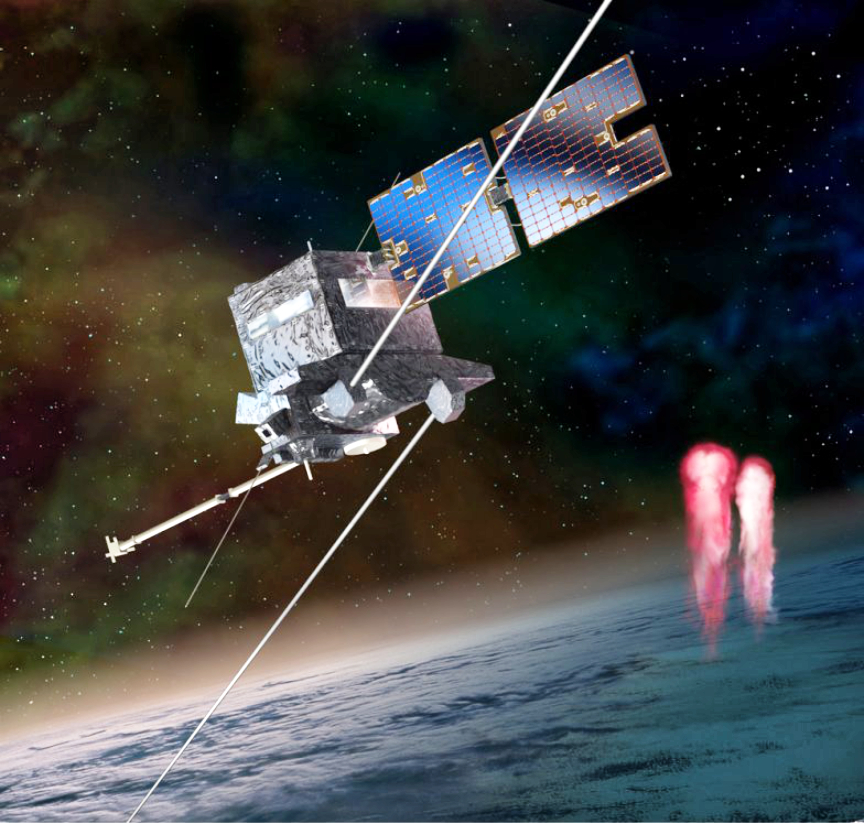
SEOSAT-Ingenio will be released first during the Vega flight sequence, deployed from atop the VESPA structure. As the initial Spanish Earth Observation (EO) satellite, this spacecraft was built by an industrial consortium of Spanish space-sector companies led by Airbus Defence and Space. It will be orbited for the European Space Agency (ESA) at the benefit of Spain’s CDTI (Center for Development of Industrial Technology). The Spanish Instituto Nacional de Técnica Aeroespacial (INTA) will own and operate SEOSAT-Ingenio.
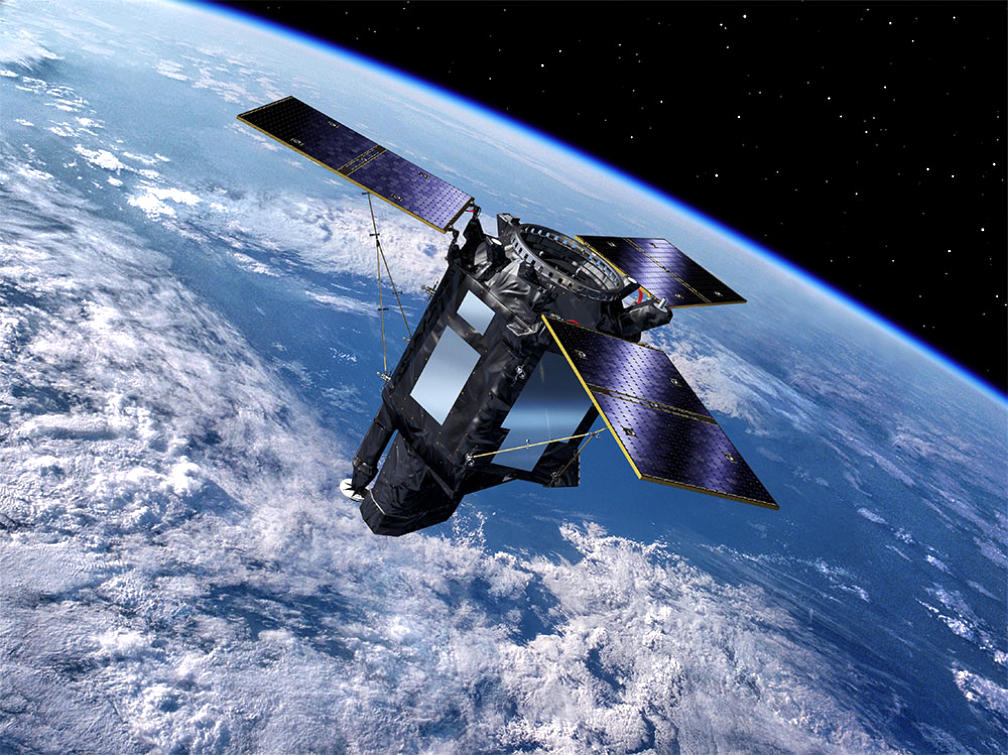

TARANIS is installed inside VESPA, and will be deployed to complete Arianespace’s Flight VV17 – sending this spacecraft on its scientific mission to observe the mysterious red sprites, blue jets, elves and sprite halos that occur at altitudes of 20 to 100 km. above thunderstorms. It is being launched for the French CNES space agency as both customer and spacecraft prime contractor.


















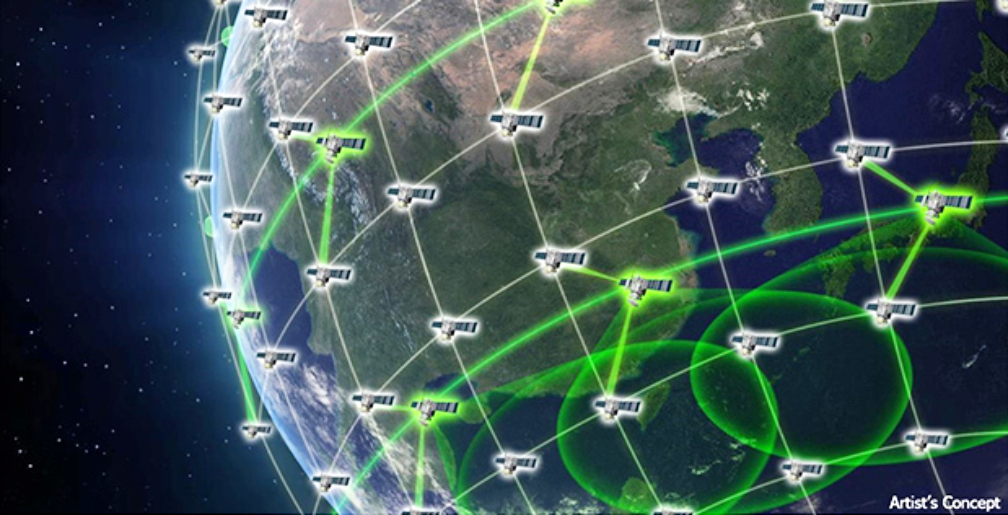 As part of the deal, Mynaric will also establish the industry’s first laser communication interoperability lab at its Los Angeles premises. The lab will be equipped with a link testbed capable of emulating conditions in space and testing inter-vendor operability – a key requirement of DARPA for its proliferated LEO constellation plans.
As part of the deal, Mynaric will also establish the industry’s first laser communication interoperability lab at its Los Angeles premises. The lab will be equipped with a link testbed capable of emulating conditions in space and testing inter-vendor operability – a key requirement of DARPA for its proliferated LEO constellation plans.