HawkEye 360 Inc. has announced that the company’s flagship RFGeo product can now map an expanded catalog of marine navigation radar signals to further improve global maritime situational awareness.
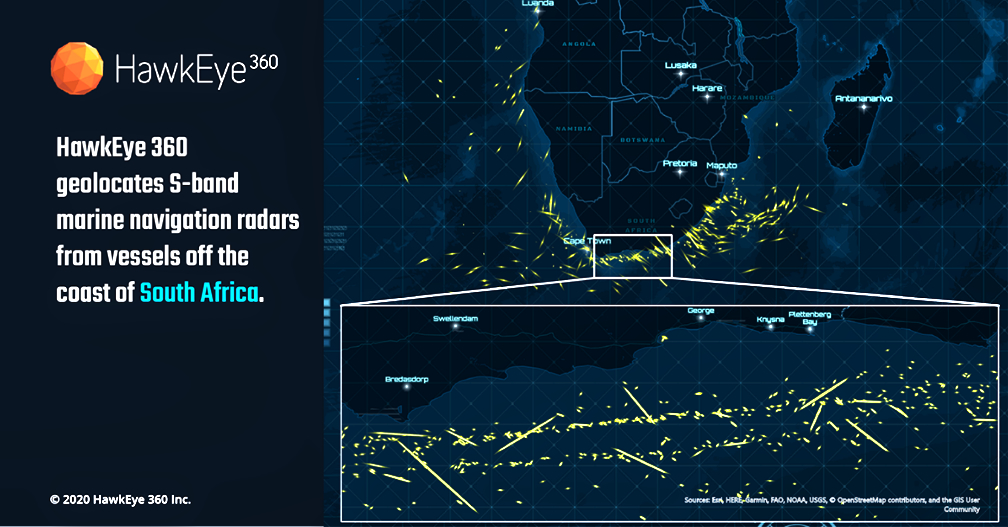
With this update, HawkEye 360 introduces the first S-band radar signal and quadruples the number of X-band radar signals in the company’s library. HawkEye 360 can now cover the most used frequencies for X-band magnetron-based radar systems, providing a more comprehensive view of maritime activity.
Vessels continuously operate marine radars to safely navigate from point to point and avoid nearby obstacles, making them an excellent means to track vessels that have otherwise ceased AIS transmissions and gone dark. Commercial vessels 300 gross tonnage or larger are required to be equipped with X-band radars (9 GHz).
The largest vessels also carry S-band radars (3 GHz) to penetrate deeper through rain or fog. Each new signal improves Hawkeye 360’s ability to develop vessel profiles. This data helps clients identify dark vessels that might be involved in illicit activities, such as smuggling or illegal fishing.
HawkEye 360’s RFGeo identifies and geolocates RF signals collected by HawkEye 360’s proprietary satellite constellation. RFGeo is the first commercially available product offering global spectrum awareness across a broad range of radio signals.
In addition to the newly announced signals, RFGeo can independently geolocate marine VHF marine radios, UHF push-to-talk radios, L-band mobile satellite devices, EPIRB marine emergency distress beacons, and vessel Automatic Identification Systems (AIS). HawkEye 360 is continually adding signals to the catalog to broaden the reach of RF identification across land, sea, and air domains.
Executive Comments

“We’re addressing critical gaps in Maritime Domain Awareness by revealing an entirely new data layer for vessel monitoring,” said John Serafini, Chief Executive Officer, HawkEye 360. “We’re excited to introduce our first signal in the S-band frequencies. By expanding our signal catalog, we’re not just collecting new and diverse RF data sets, we’re providing actionable intelligence to support the increasing number and scale of our customers’ missions.”
“Our customers need to maintain accurate and consistent visibility of vessels,” said Alex Fox, EVP for Business Development, Sales and Marketing, HawkEye 360. “Vessels are continuing to evade AIS detection to conduct illicit activities, making it difficult for organizations to identify and monitor their behaviors. We’re able to provide unique data sets that enable our customers to keep their finger on the pulse of vessel activity.”
Recent HawkEye 360 news…
HawkEye 360’s Keen Eye Adds More Defense Industry Expertise to their
Board of Directors
HawkEye 360 Reveals Iranian Tankers Evading Sanctions

















